Communication Skills Class 10 Notes are very important in day-to-day life; good communication skills will help the students to connect with each other. Good communication skills help to resolve the problems easily. All the important Information are taken from the CBSE Textbook Employability Skills Class X Based on CBSE Board Pattern.
Communication Skills Class 10 Notes
Session 1 : Method of Communication
1. What is Communication?
Exchanging the information between two or more people using any medium is known as communication. Communication helps to exchange information, thoughts or knowledge through speaking, writing or using any other mediums.
Definition: The word ‘communication’ comes from the Latin word commūnicāre, meaning ‘to share’.
2. What are the different parts of communication?
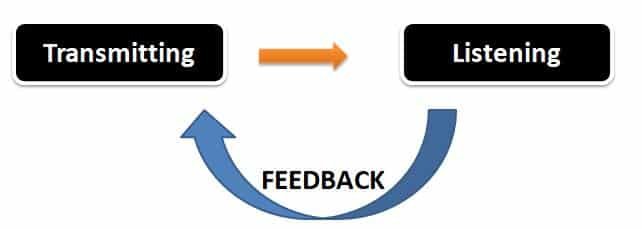
Communication has three important parts –
- Transmitting — The sender transmits the message through one medium or another.
- Listening — The receiver listens or understands the message.
- Feedback — The receiver conveys their understanding of the message to the sender in the form of feedback to complete the communication cycle.
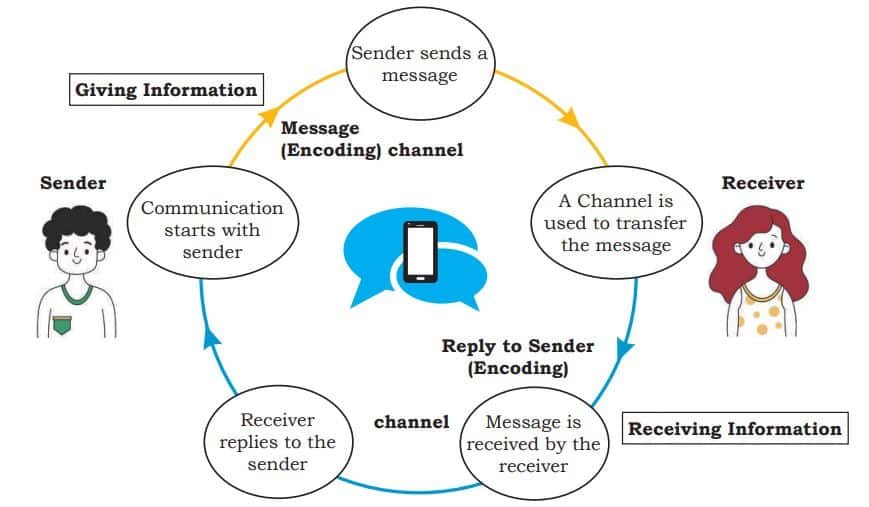
3. What are the different elements of communication?
The various elements of a communication cycle are:-
- Sender — The person beginning the communication.
- Message — The information that the sender wants to convey.
- Channel — The means by which the information is sent.
- Receiver — The person to whom the message is sent.
- Feedback — The receiver’s acknowledgement and response to the message.
| Method of Communication | Description |
|---|---|
| Face-to-face | There is nothing better than face-to-face communication. It helps the message to be understood clearly and quickly. |
| e-mail can be used to communicate quickly with one or many individuals in various locations. | |
| Notices/Posters | It is effective when the same message has to go out to a large group of people. |
| Business Meetings | Communication during business meetings at an organisation are generally addressed to a group of people. |
| Other Methods | There can be various other methods like social networks, message, phone call for communication, newsletter, blog, etc. |
Session 2: Verbal Communication
1. What is Verbal Communication?
Verbal communication includes sounds, words, language, and speech. Speaking is one of the most effective and commonly used way of communicating.
2. Different types of Verbal Communication?
There are several types of verbal communication –
| Type of Verbal Communication | Description |
|---|---|
| Interpersonal Communication | This form of communication takes place between two individuals and is thus, a one-on-one conversation. It can be formal or informal. |
| Written Communication | This form of communication involves writing words. It can be letters, circulars, reports, manuals, SMS, social media chats, etc. |
| Small Group Communication | This type of communication takes place when there are more than two people involved. Example – 1. Press conferences 2. Board meetings 3. Team meetings |
| Public Communication | This type of communication takes place when one individual addresses a large gathering. Example – 1. Election campaigns 2. Public speeches by dignitaries |
3. Advantages of Verbal Communication –
- Ease: Simple and straightforward way of communication.
- Adaptability: Allows for adjustments based on the listener’s response.
- Immediacy: Enables quick exchange of information.
- Clarity: Facilitates clear understanding through spoken words.
4. Disadvantages of Verbal Communication:
- Dependency on Words: Relies on the accuracy of spoken words, leading to potential misunderstandings.
- Lack of Permanent Record: Information is not always documented, making it challenging to reference.
- Limited Non-Verbal Cues: Absence of visual and body language cues can lead to misinterpretations.
- Potential for Confusion: Without precise wording, meanings may be unclear or confusing.
5. Mastering Verbal Communication:
- Clarity: Express thoughts clearly.
- Active Listening: Pay attention to others.
- Effective Tone: Use a suitable and respectful tone.
- Conciseness: Be brief and to the point.
Session 3: Non-verbal Communication
1. What is non-Verbal Communication?
Non-verbal communication is the expression or exchange of information or messages without using any spoken or written word.
In everyday communication:
- 55% communication is done using body movements, face, arms, etc.
- 38% communication is done using voice, tone, pauses, etc.
- Only 7% communication is done using words.
2. Example of the Non-Verbal Communication?
| Non-Verbal Communication | Examples |
|---|---|
| Gestures | 1. Raising a hand to greet or say goodbye. 2. Pointing a finger at someone. |
| Expressions | 1. Smiling when happy. 2. Making a sad face when sad. |
| Body Language | 1. Postures by which attitudes and feelings are communicated. Standing straight, showing interest. |
3. What are the Different types of non-verbal communication
| Type | How to use effectively? |
|---|---|
| Facial Expressions | a. Smile when you meet someone. b. Keep your face relaxed. c. Match your expressions with your words. d. Nod while listening. |
| Posture | a. Keep your shoulders straight and body relaxed. b. Sit straight while resting your hands and feet in relaxed position. c. While standing, keep your hands by your sides. |
| Gestures or Body Language | a. Keep your hands open. b. Avoid pointing your finger at people. c. Tilt your head a bit to show that you are attentive |
| Touch | a. Shake hands firmly while meeting someone. b. Avoid other touch gestures during formal communication. |
| Space | a. Maintain proper space depending on the relationship, which could be formal. |
| Eye Contact | a. Look directly at the person who is speaking. b. Avoid staring; keep a relaxed look. c. Maintain eye contact with intermittent breaks. |
| Paralanguage | a. Use a suitable tone and volume b. Maintain a moderate speed while talking |
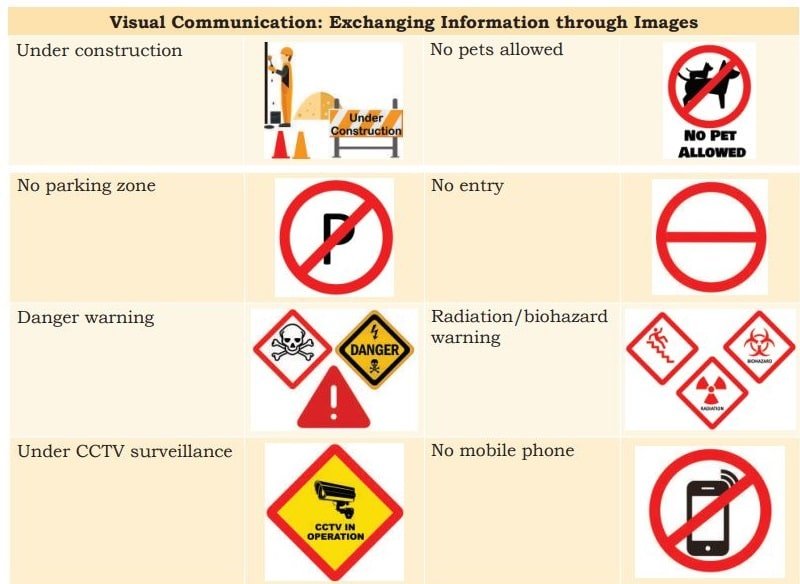
4. What is Visual Communication?
Visual communication is effective way of communication because it relies on conveying messages through images or pictures.
Session 4: Communication Cycle and Importance of Feedback
1. What is Feedback?
Feedback is an important part of the communication cycle. After a sender shares information, the receiver responds with feedback, which can be positive or negative.
Effective feedback is always-
- Specific
- Helpful
- Kind
2. Different types of Feedback in Communication Cycle?
Type of Feedback Examples
| Types of Feedback | Examples |
|---|---|
| Positive Feedback | a. I noticed you finished the work perfectly. Great job! b. I really appreciate you taking that call. Can you please also share the details? |
| Negative Feedback | a. You keep forgetting to smile at the hotel guests when you talk to them. b. You take really long to reply to e-mails! Are you always so busy? |
| No Feedback | a. It is also feedback in itself which indicates disagreement of ideas. |
3. What do you mean by good feedback?
Good feedback is one that –
- Specific
- Timely
- Polite
- Offering continuing support
4. What is the importance of Feedback?
- It validates effective listening
- Motivation
- Learning Boost
- Performance Improvement
Session 5: Barriers to Effective Communication
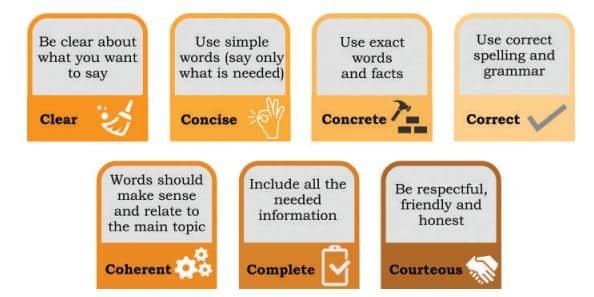
1. What is 7Cs of Effective Communication?
Essential Principles for Effective Communication:
- Clear – Express your thoughts in a clear and straightforward manner.
- Concise – Use simple and necessary words for effective communication.
- Concrete – Use accurate words and present facts clearly.
- Correct – Ensure proper spelling and grammar for correctness.
- Coherent – Ensure your words logically connect and relate to the main topic.
- Complete – Include all necessary information for a complete message.
- Courteous – Be polite, friendly, and truthful in your communication.
2. What are the different barriers to Effective Communication?
- Physical Barriers – When the surroundings or nature creates challenges for communication, it’s a physical barrier. For example, text messages are often less effective than face-to-face communication.
- Linguistic Barriers – Language barrier occurs when people can’t communicate because they don’t share a common language. It is the most common communication barriers.
- Interpersonal Barriers – Sometimes, when someone says something, the listener might understand it in a different way. This can be a problem in interpersonal communication.
- Organisational Barriers – Organisations are designed on the basis of formal hierarchical structures that follow performance standards, rules and regulations, procedures, policies, behavioural norms, etc. for example, Superior-subordinate relationships in a formal organisational structure can be a barrier to free flow of communication.
- Cultural Barriers – Cultural barriers is when people of different cultures are unable to understand each other’s customs, resulting in inconveniences and difficulties.
3. What are the ways to overcome Barriers of Effective Communication
- Use simple language
- Do not form assumptions on culture, religion or geography
- Try to communicate in person as much as possible
- Use visuals
- Take help of a translator to overcome differences in language
Be respectful of other’s opinions
Session 6: Writing Skills — Parts of Speech
Writing skills are part of verbal communication and include e-mails, letters, notes, articles, SMS/chat, blogs, etc. all these forms of written communication, we use sentences to express ourselves.
1. What is Sentence?
Sentence is a group of words that communicates a complete thought. A sentence always begins with a capital letter, and it always ends with a question mark, full stop or exclamation mark. For example, Pooja goes to school.
2. What is Phrase?
The group of words, which does not make complete sense, is known as a phrase. For example, Pooja goes.
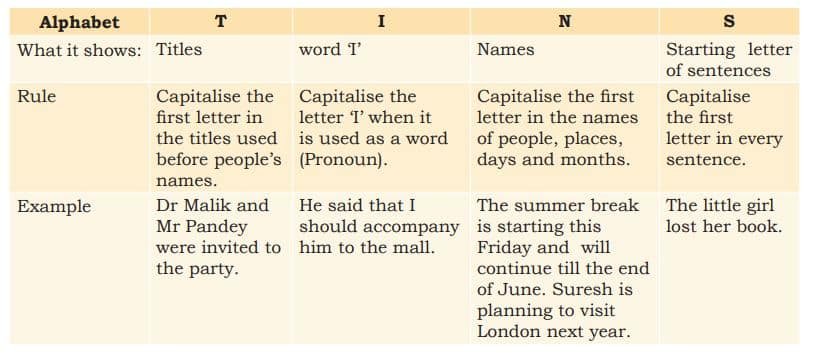
3. What are the different capitalization rules in communication cycle?
We know that all sentences begin with capital letters. However, there are certain other points in a Sentence where we should use capital letters. ‘TINS’ is a set of simple rules that help you capitalise words correctly.
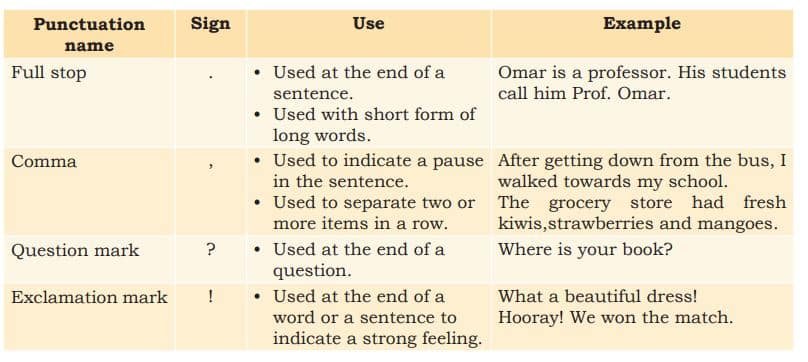
4. What do you mean by punctuation rules?
Certain set of marks, such as full stop, comma, question mark, exclamation mark and apostrophe are used in communication to separate parts of a sentence for better clarity of message.
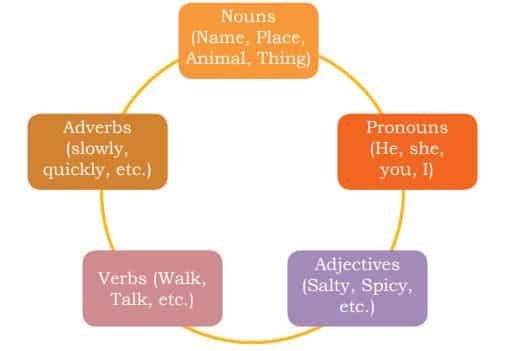
5. What are the basic parts of speech
The part of speech indicates how a particular word functions in meaning as well as grammatically within the sentence.
- Noun – Names a person, place, thing, or idea. (e.g., dog, city)
- Pronoun – Replaces a noun to avoid repetition. (e.g., he, she, it)
- Verb – Expresses action or state of being. (e.g., run, exist)
- Adjective – Describes or modifies a noun. (e.g., happy, tall)
- Adverb – Modifies a verb, adjective, or another adverb. (e.g., quickly, very)
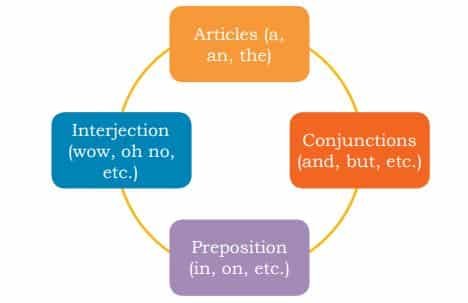
6. What are the different supporting parts of speech?
- Article – A type of adjective that defines a noun as specific or unspecific. (e.g., a, an, the)
- Conjunction – Connects words, phrases, or clauses. (e.g., and, or, but)
- Preposition – Indicates the relationship between a noun and another word. (e.g., in, on, under)
- Interjection – Expresses strong emotions but is not grammatically related to the rest of the sentence. (e.g., wow, oh)
Session 7: Writing Skills—Sentences
1. What is sentence?
A sentence is a group of words that conveys a complete thought. It consists of a subject (the main actor or topic) and a predicate (the action or what the subject does). A sentence can be simple, compound, or complex, and it is the basic unit of communication in written and spoken language.
2. What are the different parts of a sentence.
There are basically three different parts of sentence –
- Subject – The person or thing performing the action.
- Verb – Describes the action carried out by the subject.
- Object – The person or thing that receives the action.
3. What are the different types of objects?
In a sentence, there can be two types of objects — Direct and Indirect.
Direct Object:
- Receives the action directly from the verb.
- Answers the question “what” or “whom.”
- Example: She ate an apple.
Indirect Object:
- Indirectly affected by the action, often preceded by a preposition.
- Answers the question “to whom” or “for whom.”
- Example: He gave a gift to her.
4. What are the different types of sentences?
- Statement or Declarative Sentence
- Question or Interrogative Sentence
- Emotion/Reaction or Exclamatory Sentence
- Order or Imperative Sentence
5. What do you mean by Active and Passive Sentences?
Active Sentence:
- The subject performs the action.
- Example: The cat (subject) chased the mouse (object).
Passive Sentence:
- The subject receives the action.
- The object becomes the focus.
- Example: The mouse (object) was chased by the cat.
6. What do you mean by paragraph?
A paragraph is a collection of sentences centered around a single idea. It starts with a topic sentence, followed by supporting details, and often ends with a concluding sentence. This structure enhances organization and readability in written communication.
Important link of employability skills class 10 notes
- Communication Skills Class 10 Notes
- Self-Management Skills Class 10 Notes
- Basic ICT Skills Class 10 Notes
- Entrepreneurial Skills Class 10 Notes
- Green Skills Class 10 Notes
Disclaimer: We have taken an effort to provide you with the accurate handout of “Communication Skills Class 10 Notes“. If you feel that there is any error or mistake, please contact me at anuraganand2017@gmail.com. The above CBSE study material present on our websites is for education purpose, not our copyrights. All the above content and Screenshot are taken from Employability Skills Class 10 CBSE Textbook and Support Material which is present in CBSEACADEMIC website, This Textbook and Support Material are legally copyright by Central Board of Secondary Education. We are only providing a medium and helping the students to improve the performances in the examination.
For more information, refer to the official CBSE textbooks available at cbseacademic.nic.in
Notes of communication skills class 10 – All the important information is taken from the employability skills class 10 textbook and created communication skills class 10 notes. Class 10 communication skills notes are based on the CBSE examination. If you want to score higher marks in class 10, then please read the above information on communication skills notes class 10; class 10 computer chapter 1 communication skills notes is based on the CBSE textbook. All the information is taken from the CBSE textbook.
If you want to download communication skills class 10 notes PDF format, then you can send an email to me; I will provide the Communication Skills Class 10 PDF. Communication skills class 10 notes or communication skills 2 class 10 notes handwritten are not available on our site, but the information given above is based on handwritten notes only and collects the most important information from the textbook and handwritten notes. Unit 1 communication skills Class 10 PDF free download is available, but you have to send a message through mail.

Best notes ever 💯💯💯💯💯💯💯💯💯😄💯😄💯💯😄💯😄💯😄💯💯😄😄💯😄💯💯😄😄💯💯💯💯💯