Teachers and Examiners collaborated to create the Basic ICT Skills Class 9 Notes. All the important Information are taken from the NCERT Textbook Employability Skills as per the board pattern. The CBSE Employability Skills Class 9 Notes is a useful resource for students studying in class 9. The page offers notes and other study materials that can help students prepare for exams, including the CBSE and other competitive exams. It is a good idea for students to regularly visit the page and stay up to date with the latest information and resources.
Basic ICT Skills Class 9 Notes
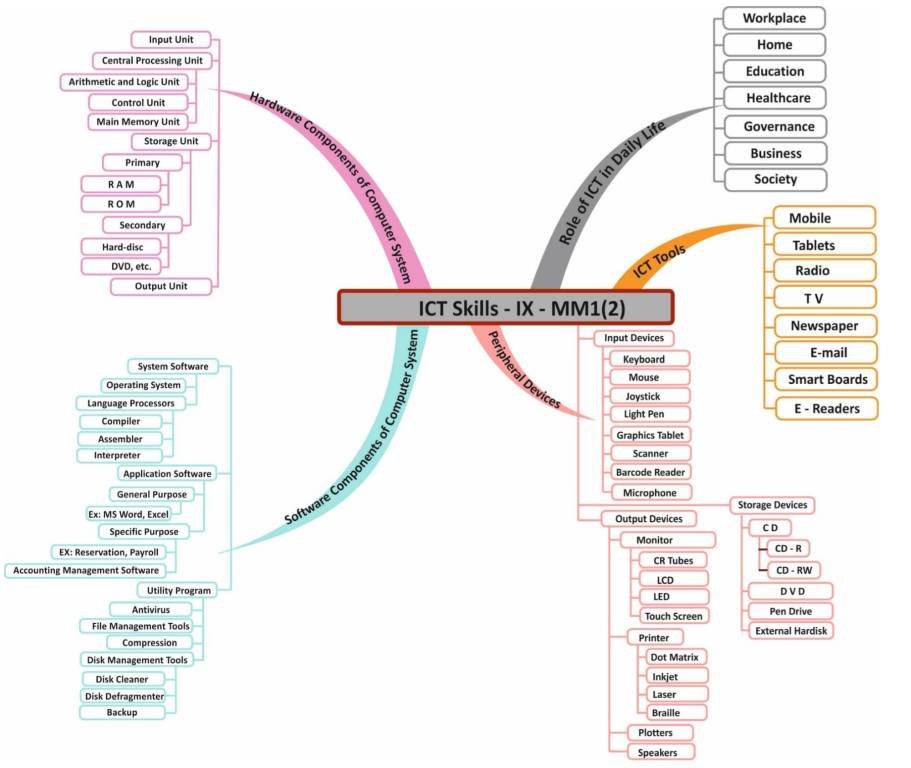
Information and communication technology, or ICT, is the field that deals with using electronic devices like computers, smartphones, iPads, etc.
Information technology refers to the processes of gathering, controlling, storing, and transferring data. It encompasses all available information management technologies.
Using ICT tools can lead to
• higher order thinking skills
• provide creative and individualized options for students to express their understandings
• Students are better prepared to deal with ongoing technological change in society and the workplace.
Basic ICT Skills Class 9 Notes
Some of the advantages of ICT in education are:
• Complex topics can be easily explained to the students with the help of pictures, videos, presentations, etc.
• Images and videos used for teaching improves the retention memory of the students.
• Presentations can make the lessons interesting.
• Practical demonstration can be given to the students.
• If the teaching process in the class is interactive, it will make the lesson more enjoyable.
• An e-learning program allows students to learn at their own pace, at any convenient time, and from any place.
ICT in different sectors
ICT in Healthcare
ICT plays an important role in healthcare. Some of the uses of ICT in health care are:
• Through the right communication media, a doctor can easily deliver treatment and care to the patient who is located far away. Doctor can also continuously monitor the patient’s history, diagnostic report, and track the current health condition. The Doctor can also interact with patient, recommend to take medical
examination and prescribe medicine.
• Using the ICT tool or a suitable communication system, government can make efforts to create awareness among the public about the communicable diseases, prevention measures and various current diagnostic & etc.
• ICT in healthcare research helps to find the possible prevention measures to eradicate and reduce the spread of diseases.
• Through ICT, the traditional healthcare systems can be eliminated and new models can be formed for effective quality care.
• Hospitals can use different electronic media to store medical data. This helps to retrieve the information easily. This data can be transferred to the patient or to the Doctors for consultation.
• Computer based machines are used for MRI, CT-scan, ultrasound are done in hospitals, diagnostic centres, to diagnose the diseases.
• Life support systems are provided to the patients
• You can search information on any disease, medicines, etc. on the internet.
Basic ICT Skills Class 9 Notes
ICT in Governance
ICT in governance can be help:
• Deliver government services efficiently
• E-governance sites enable people to perform various tasks such as filling a form, applying for passport, paying bills, property tax, etc. even sitting at home.
Basic ICT Skills Class 9 Notes
ICT in Business
ICT in business can be used for the following purposes:
• Keep records of the stock
• Prepare accounts and balance sheets
• Maintain database of staff and customers
• E-commerce enables people to buy and sell products online. This service is available 24 x 7.
• E-banking facility helps to make banking transactions at any time of the day .
Impact of ICT on society
ICT has divided the society into two groups:
1. Persons who can do their personal and professional work efficiently. They are efficient in using services like, e-banking, e-learning, e-governance sites, etc.
2. People who do not have access to a computer and internet. They also do not have knowledge to use facilities available on the internet.
Basic ICT Skills Class 9 Notes
ICT in our daily life
ICT has a great impact in our daily life. Some of the uses of ICT in our daily life are given below:
• We can read newspapers online.
• We can get connected with our friends, relatives or even family members far away from us using email, messenger, video conferencing etc.
• With the introduction of video conferencing, business meetings are now easier.
• Nowadays people use mobile phone apps to meet and connect with new and old friends.
• Social networks like Facebook.com have played a big role in connecting both old and new relationships.
• We can access a full library of educational material via a mobile app or website on any smartphone or iPad.
• Technology has also made the buying and selling of goods and services flexible and a lot safer.
• Most banks now offer online banking facilities. People make use of this service daily to manage their finances.
• Most businesses use online banking facility to pay employees and transfer money.
Basic ICT Skills Class 9 Notes
ICT Tools
Mobile
The simplest and most convenient form of communication is via a mobile phone. It is portable, lightweight, and tiny in size. You can always and everywhere keep in touch with your friends and family.
Tablets
Small personal computers with a touch screen are called tablets. Users of tablets can enter data and commands using a keyboard or mouse.
Radio
Radio is the oldest tool used to provide entertainment and information to people. You can listen to music, radio shows, etc. on radio.
TV
Television is another important ICT tool. You can watch music, view programs, etc. on television.
Newspaper
Newspaper is another most important ICT tool. News related to all the issues , national, international, sports, space, etc, are printed in newspapers.
Email is the most common way of communication in today’s world. It is the official way of communication. Some of the advantages of using email are:
• You don’t have to pay anything extra for sending or receiving email. You just pay for the internet connection.
• You can send bulk mails
• The receiver may not be online when you send the email.
• You can send documents, presentations, images, videos, etc. as an attachment to email.
• When you send an email, it reaches, the receiver at any part of the world in few seconds.
Basic ICT Skills Class 9 Notes
Interactive White Boards
These boards a allow to project computer . Also handwritten notes can be taken on the board and saved for later use.
E-readers
E-readers are electronic devices that can hold hundreds of books in digital form. E-readers are portable, have a long battery life.
Identify the Various Components of Computer System
BAISC COMPONENTS OF COMPUTER SYSTEM
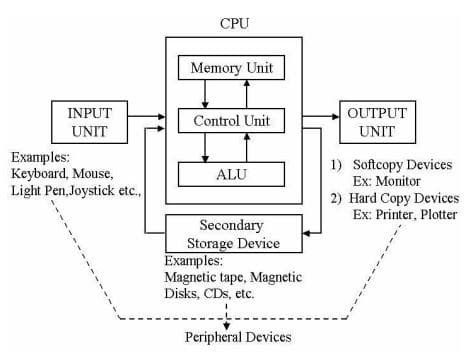
A computer is an electronic device that has devices to enter data, store data and process raw facts and figures according to the given instructions and give the desired result on an output device.
HARDWARE AND SOFTWARE
A computer system comprises of hardware and software.
• Computer hardware – Physical parts of a computer such as Input devices, output devices, central processing unit and storage devices are called computer hardware.
• Computer software – Software are the programs or applications that run on computer. For example, MS Word, MS PowerPoint, Operating systems, etc.
Basic ICT Skills Class 9 Notes
Computer hardware
The physical components of a computer system are called hardware. A computer basically consists of
following physical components:
• Input unit
• Processing unit
• Storage unit
• Auxiliary storage
• Output unit
Input Devices
Input devices are used for entering data or instructions into the computer.
The Central Processing Unit
The Central Processing Unit is the brain of the computer system.
Functions of Central Processing Unit are:
• It controls the sequence of operations within the computer
• It gives commands to other parts of the computer
• It controls the use of main memory for storing data and instructions
It consists of the following main units:
• Arithmetic and Logic unit (ALU)
• Control Unit (CU)
• Main Memory Unit
Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU)
All the calculations and comparisons are done in this unit.
The ALU performs all the following arithmetic operations:
+ (addition)
– (subtraction)
*(multiplication)
/(Division)
^(Exponent)
The ALU also performs the following logical operations:
< (less than)
<(greater than)
<= (less than or equal to)
>= (greater than or equal to)
<> (not equal to)
Registers
These are temporary storage areas found in CPU of modern computers.
Basic ICT Skills Class 9 Notes
Computer Software
Software is a set of computer programs that perform a particular task.
Following are the categories of softwares:
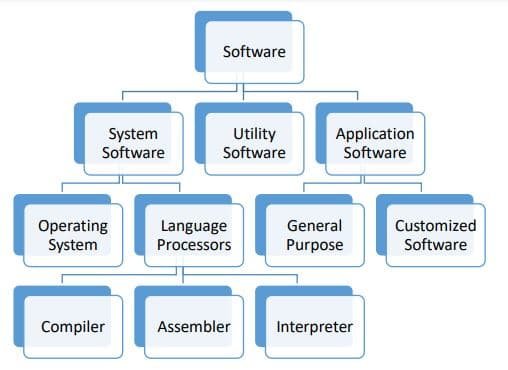
System Software
System software is a set of one or more programs designed to control the operation of a computer
system. Operating systems and language processors come under the category of system software.
Operating System
Operating system is a master control program that runs the computer. When the computer is switched on, operating system is the first program loaded into the computer’s memory. Examples of operating system are Windows, UNIX, MS-DOS, Mac OS, Solaris, etc.
Language Processors
A computer can understand commands expressed as machine code, such as 0 and 1. The source code for the programmes is written in a high level language similar to English. To run, the source code needs to be translated into machine language. Language processor refers to the programme used to translate source code written in high level languages into machine code. The object programme is the programme that has been converted into machine code.
Basic ICT Skills Class 9 Notes
Language processor is of three types:
1. Assembler:- It is a program that translates an assembly language program into machine language.
2. Compiler:-It is a program that translates a high-level language program into machine language. For example C++ compiler.
3. Interpreter:-It is a program that translates a high-level language into machine language program line by line. For example, Visual basic Interpreter.
Application Software
Application software is a computer program that is designed to perform a certain type of work. This type of software pertains to one specific application. For example, software written to calculate salary of the school employees cannot be used to prepare school result.
Utility Program
A utility program is used to perform maintenance work on a system or on the components of the computer.
Antivirus software:- This program helps in detecting and removing viruses. For example, Norton antivirus, McAffee virus scan, etc.
File management tools:-These tools help in storing, searching, and sorting files and folders on the system. For example, Windows Explorer.
Compression:- This program helps in compression of large files so that they take less storage space. For example, WinZip.
Disk Management Tools:- These programs include
- Disk Cleaner:-This utility scans for the files that have not been used since long. These files may be occupying large amount of space. It prompts the user to delete such files to create more disk space.
- Disk Defragmenter:-It rearranges the files and free space on the computer so that files are stored in contiguous and free space is consolidated in one contiguous block. This speeds up the disk access.
- Backup:- backup means making a duplicate of the files and data stored on the computer. This program is used to take backup copy of the data. In case the original data is lost, the backed up data can be used.
Basic ICT Skills Class 9 Notes
PRIMARY AND SECONDARY MEMORY
The storage unit consists of the following components:
• Primary storage
• Temporary Storage
Primary Storage
The primary storage is also called the primary memory. It is directly accessible by the CPU. It can be:
• RAM (Random Access Memory)
• ROM (Read Only Memory)
Functions of primary memory are:
• Here data is fed and held until it is ready to be accessed.
• It is used to hold the data being processed and the intermediate results of processing.
• It holds the result of the processing.
• It holds the processing instructions.
Basic ICT Skills Class 9 Notes
Memory Units
Units of computer memory are:- Bit (Binary Digit), Byte (Kilobyte, Megabyte, GigaByte, TeraByte,
PetaByte, ExaByte, ZettaByte, YottaByte)
The elementary unit of memory is a bit. A group of 4 bits is called a nibble and a group of 8 bits is
called a byte.
One byte is the minimum space required to store one character.
1 Byte = 8 bits
One kilobyte (KB) = 1024 bytes
One Megabyte (MB) = 1024 KB = 1024 x 1024 bytes
One Gigabyte (GB) = 1024 MB =1024 x 1024 x 1024 bytes
One Terabyte (TB) = 1024 GB = 1024 x 1024 x 1024 x 1024 bytes
One petabyte (PB) = 1024 TB=1024 x 1024 x 1024 x 1024 x 1024 bytes
One ExaByte (EB)=1024 PB=1024 x 1024 x1024 x 1024 x 1024 x 1024 bytes
One ZettaByte (ZB)=1024 EB)= 1024 x 1024 x 1024 x1024 x 1024 x 1024 x 1024 bytes
Basic ICT Skills Class 9 Notes
Random Access Memory (RAM)
RAM is utilised to store active data and instruction information. RAM stands for random access memory because information is stored there in a random order. It is only a passing recollection. RAM is also referred to as volatile memory because it is lost when the power is switched off. It is also referred to as read/write memory since data may be read from and written to RAM. It is possible to overwrite or erase data kept in RAM.
Read-Only memory (ROM)
The primary memory of a computer includes ROM. It is used to store the manufacturer’s instructions for checking the system’s hardware basics and loading the operating system from the proper storage device.
Until it is written over, data and instructions stored in ROM are permanent.
If the power is turned off, the contents of the ROM are not lost. ROM is referred to as non-volatile memory for this reason.
Secondary Storage
The secondary memory is used because the computer’s primary memory only temporarily saves the data and information. The majority of information is stored in secondary memory. Secondary memory is also a non-volatile memory because the data it contains is not lost when it is used. Since data is stored on these devices until it is removed, they are non-volatile. Hard drives, CDs, DVDs, Pen drives, and other secondary storage media are examples.
INPUT, OUTPUT AND STORAGE DEVICES
Input devices
Input devices are used for entering data or instructions into the computer.
Output Devices
The output unit comprises of devices such as Monitor, Printer, speaker, etc. to display information to the user.
Storage Devices
All computers have a hard disk drive installed in them. It is used to store files of Operating system, softwares and other files.
Basic ICT Skills Class 9 Notes
Identify Various Peripheral Devices
VARIOUS PERIPHERAL DEVICES AND THEIR USES
An internal or external device that is directly connected to a computer but does not support the computer’s main task, such as computing, is referred to as a peripheral device. It facilitates end users’ access to and usage of a computer’s features.
Different peripheral devices, fall into following three general categories:
1. Input devices, such as a mouse and a keyboard
2. Output devices, such as a monitor and a printer
3. Storage devices, such as a hard drive or flash drive
EXAMPLES OF PERIPHERAL DEVICES
Input Devices
Keyboard
Different types of keys of the keyboard are:
• Alphanumeric keys are used to type alphabets, numbers and special symbols like $, %, @, A etc.
• Special keys such as Shift, Ctrl, Alt, etc. are used for special functions.
• Function keys such as Fl, F2, F3 etc. are used to give special commands and these commands may be different for different softwares.
• Cursor Movement keys. These keys are used to move the cursor in a document. These include the arrow keys, PAGE UP, PAGE DOWN, etc.
Mouse
On a computer monitor, a mouse is used as a pointing device to move the mouse cursor. The mouse pointer on the computer screen goes in the same direction as the mouse when it is moved on a flat surface.
Joystick
A Joystick is used to play games on the computer. It consists of a vertical stick that is moved to control objects on the computer screen.
Light pen
A light pen is a pointing device. It is used to draw directly on the screen. It can also be used to point to an object or option directly on the computer screen.
Graphics Tablet
Digital drawings are made using a graphic tablet by manually drawing images using a special pen on a flat surface known as the tablet. Stylus is the name of this particular pen.
Scanner
A scanner is a device that is sued to convert text or image into a digital file.
Barcode Reader
Vertical lines that are both thick and thin make up a barcode, which can be found on items. The product and the manufacturer are identified by the bar code. A tool called a barcode reader can read these barcodes.
Microphone
A microphone is a device used to record your voice and save it in the form of a digital file in the computer.
Basic ICT Skills Class 9 Notes
Output Devices
Computer Monitor
A computer monitor, resembles a TV screen and can display both text and images. The output displayed on computer screen is called the soft copy.
Printer
A printer is a device used to print the files stored on the computer on paper. The output produced on paper is called the hard copy. Commonly used printers are:
• Dot matrix printer – It is the most commonly used character printer, i.e, it prints one character at a time. Most of the dot matrix printers are bidirectional, i.e., they print one line of text from left to right and then the next line from right to left.
• Inkjet printer – These printers use a continuous stream of ink drops to print on paper
• Laser printer – These printers print one page at a time and are very fast.
Storage Devices
CDs/DVDs
Compact Disc (CD) and Digital Versatile disc (DVD) are optical media that is used to record data from computer. Data can then be read from the CD. To read data from the CD, we need to have a CD Drive in our computer.
There are two variations of CD-
• CD-R and
• CD-RW
Pen Drive/Flash Drive
A pen drive is a tiny, portable device used to store computer data. Additionally, it can be used to access and move data. Pen drives come in a variety of sizes, including 1 GB, 8 GB, 16 GB, and 32 GB.
External hard disk
A storage device called an external hard drive is one that is attached to a computer using a USB cable or wirelessly. When compared to flash drives, an external hard drive has a larger storage capacity and is typically used to back up essential data and computer files. There are external hard drives with capacities of up to 1 TB and 2 TB.
Basic ICT Skills Class 9 Notes
USE ANY TYPING TUTOR SOFTWARE TO PRACTICE TYPING AND LEARN USING DIFFERENT KEYS OF THE KEYBOARD.
Tux Typing tutor is a software used to teach typing to children and even adults. Regular practice will help you to increase typing speed and reduce the mistakes while typing. Before learning typing, you should learn how to place your fingers properly on the keyboard.
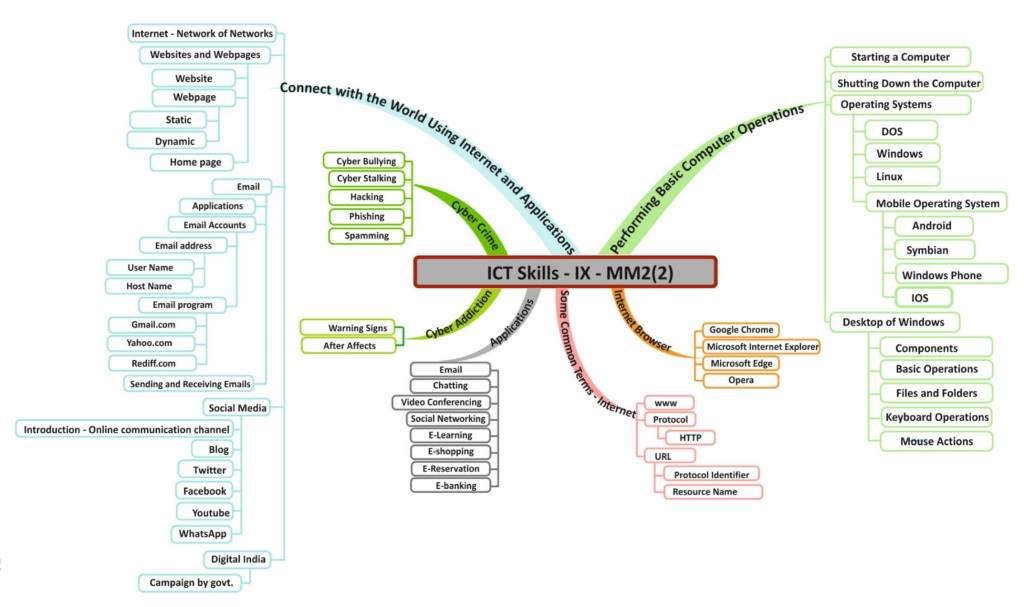
Performing Basic Computer Operations
The computer must be started correctly, and it must be shut down correctly when you are done with it. The operating system and the files may become corrupted if the computer’s power is turned off while you haven’t closed any open documents.
Operating Systems
The foundational programme that manages a computer is called an operating system. It acts as a conduit for communication between the user and the computer.
Some of the functions of Operating system are:
• It manages all the devices of a computer and keeps track of the status of the device, whether it
is busy or not.
• It also checks whether the device is functioning properly or not.
• It also controls software resources of the computer.
• t manages the computer memory and keeps track of which memory space is in use by which
program and which space is free.
• It manages the structure of the files and directories on a computer system.
• It keeps track of the amount of disk space used by a specific file.
• It allows you to create, copy, move and delete files.
Basic ICT Skills Class 9 Notes
TYPES OF OPERATING SYSTEMS
DOS – DOS (Disk Operating System) is an operating system for a personal computer. Early computers were able to run one program at a time. It had a command line interface in which a user has to remember the commands to run the program and do other operating system tasks. For example, the DOS command, dir, will display the list of files in the current directory.
Windows – It is an operating system developed by Microsoft. Some popular versions of Windows operating system are- Windows 98, Windows, 2000, Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, and Windows 10.
Linux – It is an operating system designed for personal computers. It is a free and open-source software, which means it can be modified and redistributed.
Mobile operating Systems
Android – It is an operating system used in mobile phones and tablets. It is owned and maintained
by Google and is an open-source operating system. The android releases were nicknamed after sweets
or dessert items like Cupcake (1.5), Donout (1.6), Éclair (2.0), Frozen Yogurt (2.2), Honeycomb (3.0)
and Jelly Bean (4.1), Kitkat (4.4), marshmallow (6.0),
Symbian – It is an operating system used in mobile phones. Symbian was developed and sold by
Symbian Ltd. It is primarily used by Nokia. It is also used by Japanese mobile phone manufacturers for
handsets sold in Japan.
Windows Phone – It is a mobile operating system developed by Microsoft for smart phones and pocket PCs. Windows Mobile. Windows 8.1 is the latest release of this operating system. iOS It is a mobile operating system developed by Apple Inc. for iPhones, iPads, and iPods. It is supported only by Apple hardware. iOS 9 is the latest release of this operating system.
Basic ICT Skills Class 9 Notes
Connect with the World Using Internet and its Applications
INTRODUCTION TO INTERNET
Internet is a network of networks. It is an interconnection between several computers of different types belonging to various networks all over the world. The Internet is a medium of communication and exchange of information.
Exploring information on the web is called web surfing.
WWW (World Wide Web) – WWW stands for world wide web is a network of world wide computers.
Protocol – Protocol is a set of rules to be followed while communicating or transferring data on internet.
HTTP (Hyper Text Transfer Protocol) – This protocol defines the rules to be followed while transferring the
information. The information may be in the form of text, images, videos, etc.
URL (Uniform Resource Locator) – Each web page has a unique address which identifies its location on the network. This unique address is called the URL.
The URL has two parts:
• Protocol identifier: It identifies the name of the protocol used.
• Resource name: It specifies the complete address to the resource on the Internet.
Basic ICT Skills Class 9 Notes
APPLICATIONS OF INTERNET
Some of the services provided by internet are:
• Email
• Chatting
• Video conferencing
• Social networking
• E-learning
• E-shopping
• E-reservation
• E-banking, etc.
Basic ICT Skills Class 9 Notes
Email
E-mail stands for electronic mail. It is a message in an electronic form that is sent or received from one
computer to another.
Chatting
Chatting on internet refers to textual communication that offers a real-time transmission of text
messages from one person to another. These messages are generally short.
Video Conferencing
Video conferencing using internet is a visual communication between two or more persons who may
be present at different locations.
Social Networking
Social networking is the use of internet based social media sites that is used by people to stay
connected with friends, family, etc.
E-learning
E-learning or online learning refers to a learning system that is done using an electronic device with
internet connection.
E-shopping
Buying products online, i.e., using an electronic device with internet connection is called e-shopping. Customer can buy products from the comfort of their home. It saves time and effort. You can even compare products, even cancel the transactions. Most important, this facility is available 24 X 7 and 365 days.
E-reservation
E-reservation means booking of tickets online. You can book airline tickets, train tickets, movie tickets and even hotel rooms and tour packages online.
Basic ICT Skills Class 9 Notes
INTERNET BROWSER
A programme used to access websites is known as a web browser or internet browser. It serves as a conduit between the web server and the internet. Google Chrome, Microsoft Internet Explorer, Microsoft Edge, opera, etc. are some examples of widely used web browsers.
A web browser performs the following tasks:
1. It connects to the web server and sends a request for the information.
2. It displays the information on the computer
WEBSITES AND WEBPAGES
Web site
A web site is a collection of two or more related web pages. Web pages of a web site are linked together through hyperlinks.
Web page
An individual page of a web site is called a web page. It is written in a special computer language
called HTML (Hyper text markup Language).
There are two types of web pages:
• Static web pages
• Dynamic web pages
Basic ICT Skills Class 9 Notes
EMAIL APPLICATIONS
Some of the advantages of e-mail are:
• It is fast and easy to use.
• It is the fastest means of communication. A message can reach any part of the world in a fraction of a second.
• You can send text message, pictures, sound messages across the globe.
• Message can consist of few lines or more. It is not charge by weight.
• You don’t have to pay anything extra for the sending or receiving the email. You just pay for the internet connection.
• You need not be on your computer or online to receive the e-mail.
• E-mails are eco-friendly as no paper is used.
• You can also send bulk messages to a large number of people at the same time.
EMAIL ACCOUNTS
To send or receive email messages, you first need to open your email account and have your email address.
Email address
An email address has two main parts:
• User name
• Host name
These two parts are separated by @ symbol.
For example, consider the following email address: myemail@gmail.com
In the above email address, myemail is the user name and gmail.com is the host name.
Basic ICT Skills Class 9 Notes
SENDING AND RECEIVING EMAIL
Some of the options while composing an email are:
To – This option allows you to write the email address of the person you want to send the message to.
Cc – It stands for carbon copy. This option allows you to send the same message to several persons at the same time and every recipient will know all the recipients of this mail. The multiple email addresses are separated by semicolon.
BCc – It stands for Blind Carbon copy. This option allows you to send the same message to several persons at the same time but a recipient will not know who the other recipients of this message are.
Subject – This option allows you to write in few words about the content of the message. Attachment This icon helps you to attach files such as, documents, presentations, images, videos, etc with your email message.
Basic ICT Skills Class 9 Notes
INTRODUCTION TO SOCIAL MEDIA
The benefits of social networking websites are:
• These sites provide a way to connect with people around the world.
• Social Networking site, like Facebook can be used to stay in touch with the family, and connecting with old friends has become very easy
• These sites help us to learn about current events.
• These sites also work as a platform to launch new business ides, or for advertisers to market their products and services to their subscribers.
• Social networking sites can be used to disarm social stigmas.
Disadvantages of Social Networking websites
• These sites expose people to a lot of information, which may or may not be authentic.
• If you share your current location over social media, you can easily become a target.
• Peer pressure and cyberbullying are also important issues.
• Online interactions have now substituted the face-to-face interactions and this has reduced the social skills.
• Social networking has become a distraction for most of the people. Students who use social networking too often have lower grades.
• Using social networking for long hours in a day can lead to a sedentary lifestyle.
• Social networking sites can spread false or unreliable information quickly.
The following actions keep you safe on social networking websites:
• Do not post and share private information like mobile phone number, home address, etc. on social networking websites.
• You should be familiar with the privacy policy of the social networking sites. You can adjust your privacy settings on social networking websites, so as to control who can access your information.
• Use a strong password. Longer password is more secure than a shorter one.
• Use a different password for each social media account.
• Be selective with friend requests. Don’t accept the friend request if you don’t know the person personally.
• Be careful while clicking at any link or any pop-up window.
• Protect your computer with anti-virus software and keep it updated.
• Always Log Off when you are done.
Basic ICT Skills Class 9 Notes
CYBER CRIME
Introduction to Cyber Crime
Cyber crime refers to any crime done using computer or any electronic device with internet connection. Some of the cyber crimes are:
• Cyber Bullying
• Cyber Stalking – It refers to harassing an individual or an organization using internet. This may include making false accusation or defaming, threatening, damaging data, etc.
• Hacking – If someone tries to get into computer systems in order to steal, corrupt or illegitimately view data, then it is called hacking. The person who does hacking is called a hacker.
• Phishing – Phishing means an attempt to acquire a sensitive information such as username, password, etc.
• Spamming – Spam refers to unsolicited email which is sent in large quantities to a large number of users.
Cyber Bullying
Cyberbullying is when a student posts text and images on any electronic device, such as a computer, smart phone, tablet, etc. with the goal to harm, humiliate, threaten, or embarrass the victim. Cyberbullying typically entails posting or transmitting rumours, abusive, or nasty messages in an effort to harm a person’s reputation or relationships with others.
Basic ICT Skills Class 9 Notes
Cyber Addiction
The internet has grown to be a necessity in our lives. We use the internet for a variety of things, including communication, knowledge enhancement, shopping, bill payment, in schools, at home, and at work.
Some of the factors responsible for cyber addiction are:
• Lack of family interaction
• Change in life style
• Lack of social circle
• To compete with latest up comings and technology to keep updated.
• Mostly both the parents are working and doesn’t have time for kids and want their kids to be busy on computer or mobiles.
Some warning signs of cyber addiction
• Loss of control when trying to stop or limit the amount of time on the internet.
• Breaking promises to self or others
• Feeling of depression or anxiety when someone stops or interrupts while working on the computer.
• Feeling of guilt over excessive use of internet
After Effects of Cyber Addiction
Over use of internet may lead to:
• Headaches
• Back aches
• Irregular eating habits
• Sleep disturbances
• Neglect of family and friends
• Dry eyes and eye problem
• Feeling of depression, irritation
Excellent blog post. I absolutely appreciate this website. Thanks!
bookmarked!!, I love your website!