Teachers and Examiners (CBSESkillEduction) collaborated to create the Encoding Schemes and Number System Class 11 Notes. All the important Information are taken from the NCERT Textbook Computer Science (083) class 11.
Encoding Schemes and Number System Class 11 Notes
Encoding Schemes
A computer can only understand binary (0s and 1s) numbers. As a result, whenever a key is touched on a keyboard, is internally translated into a special code known as unique code and then converted to binary. for example, Pressing the key “A” causes is internally mapped to the value 65 (the code value), which is then translated to its corresponding binary value for the computer to comprehend. encoding helps the system to give unique number to the characters, symbols or numbers.
What is encoding?
Encoding is the process of transforming data into an encryption process that is equivalent using a particular code. Some of the well-known encoding schemes are described in the following sections. There are three most popular encoding in computer system.
a. American Standard Code for Information Interchange (ASCII)
b. Indian Script Code for Information Interchange (ISCII)
c. Unicode ( Most popular coding method)
American Standard Code for Information Interchange (ASCII)
For the purpose of standardizing character representation, ASCII was created. The most widely used coding technique is still ASCII. ASCII represented characters using 7 bits. There are just 2 binary digits 0 and 1. Consequently, the total amount of distinct characters on the 27 = 128 on an English keyboard can be represented by a 7-bit ASCII code.
| Character | Decimal Value | Character | Decimal Value | Character | Decimal Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Space | 32 | @ | 64 | ` | 96 |
| ! | 33 | A | 65 | a | 97 |
| “ | 34 | B | 66 | b | 98 |
| # | 35 | C | 67 | c | 99 |
| $ | 36 | D | 68 | d | 100 |
| % | 37 | E | 69 | e | 101 |
| & | 38 | F | 70 | f | 102 |
| ‘ | 39 | G | 71 | g | 103 |
| ( | 40 | H | 72 | h | 104 |
| ) | 41 | I | 73 | i | 105 |
Encoding Schemes and Number System Class 11 Notes
Indian Script Code for Information Interchange (ISCII)
A standard for coding Indian scripts it is develop in the middle of the 1980s, India developed a system of characters known as ISCII. It is an 8-bit representation of Indian languages. which means it can represent 28=256 characters.
Unicode
Every character in the Unicode Standard has a specific number, independent of the platform, gadget, programme, or language. As a result of its wider adoption by modern software vendors, data may now be sent without corruption across a wide range of platforms, gadgets, and programmes.
The most popular method for identifying characters in text in almost any language is now Unicode. Unicode uses three different encoding formats: 8-bit, 16-bit, and 32-bit.
| अ | आ | इ | ई | उ | ऊ | ऋ | ऌ |
| 0905 | 0906 | 0907 | 0908 | 0909 | 090A | 090B | 090C |
Encoding Schemes and Number System Class 11 Notes
Number System
What is Number System?
A way to represent (write) numbers is called a number system. There are a specific set of characters or literals for each number system. It is the mathematical notation for consistently employing digits or other symbols to represent the numbers in a particular set.
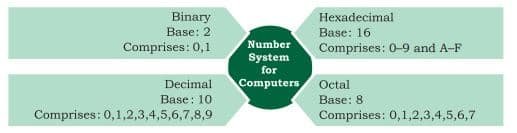
There are four different types of number system
a. Decimal Number System
b. Binary Number
c. Hexadecimal Number
d. Octal Number
Encoding Schemes and Number System Class 11 Notes
Decimal Number System
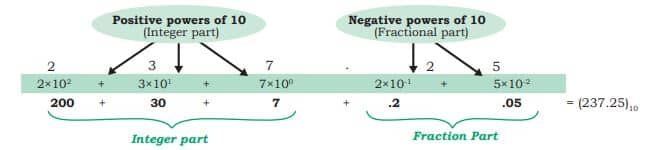
Decimal is single digit number system in computer. The decimal number system consists of ten single-digit numbers 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 and 9. This number system is also known as based-10 number.
Binary Number System
Binary Number is used in computer system because computer only understands the language of the two digits 0 and 1 (low/high). Binary number is also known as the base-2 system. Examples of binary numbers include 111111.01, 1011101, and 1001011.
| Decimal | Binary |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 10 |
| 3 | 11 |
| 4 | 100 |
| 5 | 101 |
| 6 | 110 |
| 7 | 111 |
| 8 | 1000 |
| 9 | 1001 |
Encoding Schemes and Number System Class 11 Notes
Octal Number System
Sometimes, a binary number is so large that it becomes difficult to manage. Octal number system was devised for compact representation of the binary numbers. Octal number system is called base-8 system.
| Octal Digit | Decimal Value | 3 -bit Binary Number |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 000 |
| 1 | 1 | 001 |
| 2 | 2 | 010 |
| 3 | 3 | 011 |
| 4 | 4 | 100 |
| 5 | 5 | 101 |
| 6 | 6 | 110 |
| 7 | 7 | 111 |
Hexadecimal Number System
Hexadecimal numbers are also used for compact representation of binary numbers. It consists of 16 unique symbols (0–9, A–F), and is called base16 system. In hexadecimal system, each alphanumeric digit is represented as a group of 4 binary digits because 4 bits (24=16) are sufficient to represent 16 alphanumeric symbols.
| Hexadecimal Symbol | Decimal Value | 4-bit Binary Number |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0000 |
| 1 | 1 | 0001 |
| 2 | 2 | 0010 |
| 3 | 3 | 0011 |
| 4 | 4 | 0100 |
| 5 | 5 | 0101 |
| 6 | 6 | 0110 |
| 7 | 7 | 0111 |
| 8 | 8 | 1000 |
| 9 | 9 | 1001 |
| A | 10 | 1010 |
| B | 11 | 1011 |
| C | 12 | 1100 |
| D | 13 | 1101 |
| E | 14 | 1110 |
| F | 15 | 1111 |
Encoding Schemes and Number System Class 11 Notes
Applications of Hexadecimal Number System
Every byte’s memory location is described using the hexadecimal number system. For computer professionals, these hexadecimal numbers are also simpler to read and write than binary or decimal numbers.
Memory Address example using hexadecimal Number System
| Decimal Number | Binary Number | Hexadecimal Number |
|---|---|---|
| 76 | 01001100 | 37FD00 |
| 38 | 00100110 | 37FD02 |
Color code example using hexadecimal Number System
| Colour Name | Decimal | Binary | Hexadecimal |
|---|---|---|---|
| Black | (0,0,0) | (00000000,00000000,00000000) | (00,00,00) |
| Yellow | (255,255,0) | (11111111,11111111,00000000) | (FF,FF,00) |
Conversion between Number Systems
Although digital computers understand binary numbers, humans most often utilise the decimal number system. Octal and hexadecimal number systems are used to make the binary representation easier for us to understand. Lets see some of the number conversion system –
Conversion from Decimal to other Number Systems
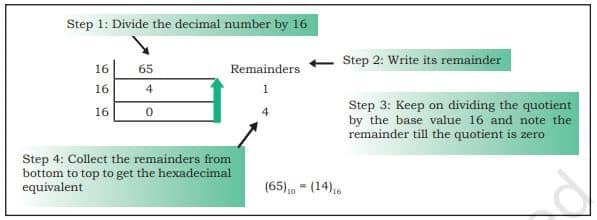
To convert a decimal number to any other number system (binary, octal or hexadecimal), use the steps
given below.
Step 1: Divide the given number by the base value (b) of the number system in which it is to be converted
Step 2: Note the remainder
Step 3: Keep on dividing the quotient by the base value and note the remainder till the quotient is zero
Step 4: Write the noted remainders in the reverse order (from bottom to top)
Encoding Schemes and Number System Class 11 Notes
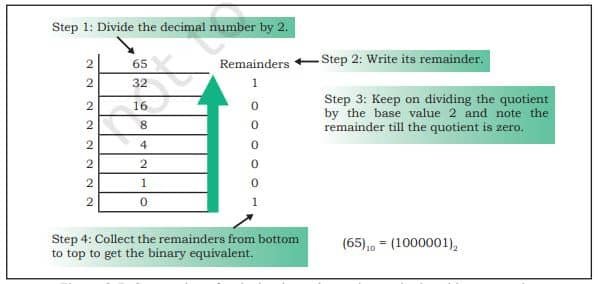
Decimal to Binary Conversion
Binary equivalent of 65 is (1000001)2. Let us now convert a decimal value to its binary representation and verify that the binary equivalent of (65)10 is (1000001)2.
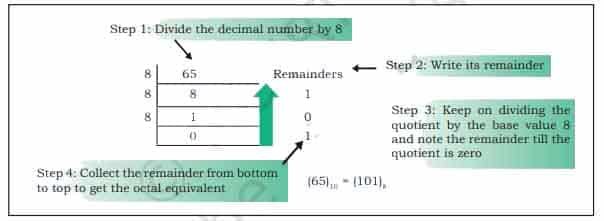
Decimal to Octal Conversion
Since the base value of octal is 8, the decimal number is repeatedly divided by 8 to obtain its equivalent octal number. The octal equivalent of letter “A” by using its ASCII code value (65)10 is calculated in below figure –
Decimal to Hexadecimal Conversion
Since the base value of hexadecimal is 16, the decimal number is repeatedly divided by 16 to obtain its equivalent hexadecimal number. The hexadecimal equivalent of letter ‘A’ using its ASCII code (65)10 is calculated as shown below –
Conversion from other Number Systems to Decimal Number System
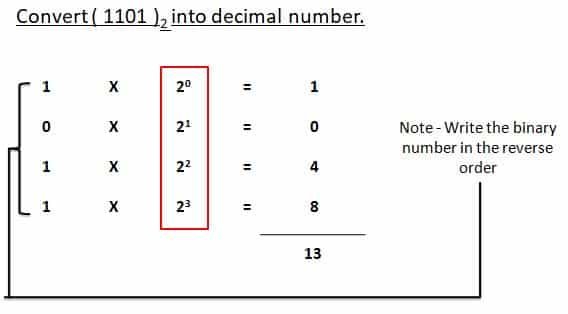
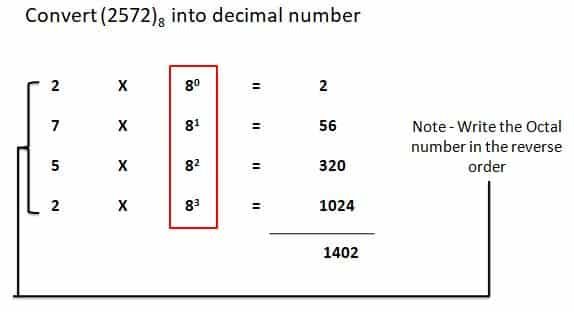
We can use the following steps to convert the given number with base value b to its decimal equivalent, where base value b can be 2, 8 and 16 for binary, octal and hexadecimal number system, respectively.
Step 1: Write the position number for each alphanumeric symbol in the given number
Step 2: Get positional value for each symbol by raising its position number to the base value b symbol in the given number
Step 3: Multiply each digit with the respective positional value to get a decimal value
Step 4: Add all these decimal values to get the equivalent decimal number
Encoding Schemes and Number System Class 11 Notes
Binary Number to Decimal Number
Binary number system has base 2, the positional values are computed in terms of powers of 2. Using the above mentioned steps we can convert a binary number to its equivalent decimal value as shown below –
Octal Number to Decimal Number
The following example shows how to compute the decimal equivalent of an octal number using base value 8.
Hexadecimal Number to Decimal Number
For converting a hexadecimal number into decimal number, use steps given in this section with base value 16 of hexadecimal number system. Use decimal value equivalent to alphabet symbol of hexadecimal number in the calculation, as shown below –

Computer Science Class 11 Notes
- Unit 1 : Basic Computer Organisation
- Unit 1 : Encoding Schemes and Number System
- Unit 2 : Introduction to problem solving
- Unit 2 : Getting Started with Python
- Unit 2 : Conditional statement and Iterative statements in Python
- Unit 2 : Function in Python
- Unit 2 : String in Python
- Unit 2 : Lists in Python
- Unit 2 : Tuples in Python
- Unit 2 : Dictionary in Python
- Unit 3 : Society, Law and Ethics
Computer Science Class 11 MCQ
- Unit 1 : Basic Computer Organisation
- Unit 1 : Encoding Schemes and Number System
- Unit 2 : Introduction to problem solving
- Unit 2 : Getting Started with Python
- Unit 2 : Conditional statement and Iterative statements in Python
- Unit 2 : Function in Python
- Unit 2 : String in Python
- Unit 2 : Lists in Python
- Unit 2 : Tuples in Python
- Unit 2 : Dictionary in Python
- Unit 3 : Society, Law and Ethics
Computer Science Class 11 NCERT Solutions
- Unit 1 : Basic Computer Organisation
- Unit 1 : Encoding Schemes and Number System
- Unit 2 : Introduction to problem solving
- Unit 2 : Getting Started with Python
- Unit 2 : Conditional statement and Iterative statements in Python
- Unit 2 : Function in Python
- Unit 2 : String in Python
- Unit 2 : Lists in Python
- Unit 2 : Tuples and Dictionary in Python
- Unit 3 : Society, Law and Ethics
It so good notes, please add another very summarized, thanks