AI For Everyone Class 11 Notes – The CBSE has updated the syllabus for St. XI. The new notes are made based on the updated syllabus and based on the updated CBSE textbook. All the important information is taken from the Artificial Intelligence Class XI Textbook Based on the CBSE Board Pattern.
AI For Everyone Class 11 Notes
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Definition: Artificial intelligence (AI) refers to the ability of a machine to learn patterns and make predictions.
Artificial Intelligence is a field that combines computer science and robust datasets to enable problem-solving. AI does not replace human decisions; instead, AI adds value to human judgment. For example, AI can:
- Understand Language: AI can understand and respond to what you say, like virtual assistants such as Siri or Alexa.
- Recognize Images: AI can look at pictures and recognize what is in them, like identifying animals in photos.
- Make Predictions: AI can analyze data to make predictions, like predicting the weather or suggesting what movie you might like to watch next.
- Play Games: AI can play games and learn to get better at them, like playing chess or video games.
- Drive Cars: AI can help cars drive themselves by sensing the road and making decisions to stay safe.
What is not AI?
When we talk about machines, not all of them are considered Artificial Intelligence (AI). Here are some examples:
- Traditional Rule-Based Systems: These machines follow set rules without learning from data.
- Simple Automation Tools: Basic tools like timers or calculators do specific tasks but do not think or learn.
- Mechanical Devices: Machines like pulleys or gears work based on physics but do not learn or think.
- Fixed-Function Hardware: Devices like microwave ovens perform tasks without learning or thinking.
- Non-Interactive Systems: Machines that do not change based on new information, like a basic electric fan.
- Basic Sensors: Sensors collect data but do not analyze or understand it
Evolution of AI
The modern era of AI began in the mid-20th century with significant developments and milestones:
- 1950 – 1950 was a landmark year for the question of machine intelligence because of Alan Turing’s famous paper “Computing Machinery and Intelligence.” In this paper, Turing proposed a thought experiment called the “imitation game” (later known as the Turing test).
- 1956 – The Dartmouth Conference was organized by McCarthy that marked the birthplace of AI as a field. The term “Artificial Intelligence” was coined by John McCarthy. McCarthy, along with Turing, Minsky, and Simon, laid the foundation for AI.
- 1960-1970 – Significant progress in AI research that led to the development of expert systems, early neural networks, exploration of symbolic reasoning, and problem-solving techniques.
- 1980-1990 – Mixed optimism and skepticism about AI with breakthroughs in machine learning, and neural networks led to “AI winter”.
- 21st Century – Resurgence of interest and progress in AI with advancements in computing power, data availability, and algorithmic innovation. Also, there were breakthroughs in machine learning, deep learning, and reinforcement learning. That led to transformative applications of AI in healthcare, finance, transportation, and entertainment.
Types of AI
Computer scientists have identified three levels of AI based on predicted growth in its ability to analyze data and make predictions.

Narrow AI:
- Focuses on single tasks like predicting purchases or planning schedules.
- Rapidly growing in consumer applications, such as voice-based shopping and virtual assistants like Siri.
- Capable of handling specific tasks effectively, but lacks broader understanding.
Broad AI:
- Acts as a midpoint between Narrow and General AI.
- More versatile than Narrow AI, capable of handling a wider range of related tasks.
- Often used in businesses to integrate AI into specific processes, requiring domain-specific knowledge and data.
General AI:
- Refers to machines that can perform any intellectual task a human can.
- Currently, AI lacks abstract thinking, strategizing, and creativity like humans.
- Artificial Superintelligence (ASI) may emerge, potentially leading to self-aware machines, but this is far from current capabilities.
Domains of AI
The AI domains are classified into three types.
- Data Science
- Natural Language Processing
- Computer Vision
1. Data Science
Data Science deals with numerical, alphabetical, and alphanumeric data inputs. It involves the collection, analysis, and interpretation of large volumes of data to extract insights and patterns using statistical methods, machine learning algorithms, and data visualization techniques. For example:
What is Data?
Data might be facts, statistics, opinions, or any kind of content that is recorded in some format. This could include voices, photos, names, and even dance moves! It surrounds us and shapes our experiences, decisions, and interactions. For example:
- Social media activity, cloud storage, textbooks, and more are all forms of data.
- Your search recommendations, Google Maps history are based on your previous data.
- Amazon’s personalized recommendations are influenced by your shopping habits.
Data is categorize in three types.
- Structured Data – Structured data is like a neatly arranged table, with rows and columns that make it easy to understand and work with. It includes information such as names, dates, addresses, and stock prices.
- Unstructured Data – Unstructured data lacks any specific organization, making it more challenging to analyze compared to structured data. Examples of unstructured data include images, text documents, customer comments, and song lyrics.
- Semi-structured Data – Semi-structured data falls somewhere between structured and unstructured data. While not as organized as structured data, it is easier to handle than unstructured data. Semi-structured data uses metadata to identify certain characteristics and organize data into fields, allowing for some level of organization and analysis. An example of semi structured data is a social media video.
2. Natural Language Processing
NLP focuses on processing text and speech inputs to enable computers to understand, interpret, and generate human language. It involves tasks such as language translation, sentiment analysis, text summarization, and speech recognition, facilitating communication between humans and machines through natural language interfaces.
Differences Between NLP, NLU, and NLG?
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): This is the broad umbrella term encompassing everything related to how computers interact with human language. Think of it as the “what” – what computers can do with human language. It is like the whole library – filled with different tools and techniques for working with language data.
- Natural Language Understanding (NLU): This is a subfield of NLP that focuses on understanding the meaning of human language. It analyzes text and speech, extracting
information, intent, and sentiment. NLU helps computers understand the language and what it means. Imagine finding a specific book in the library. - Natural Language Generation (NLG): This is another subfield of NLP, but instead of understanding, it focuses on generating human language. It takes structured data as input and turns it into coherent and readable text or speech. Think of this as writing a new book based on the information gathered in the library.
3. Computer Vision
Computer Vision is like giving computers the ability to see and understand the world through digital images and videos, much like how humans use their eyes to perceive their surroundings. In this domain, computers analyze visual information from images and videos to recognize objects.
When we take a digital image, it is essentially a grid of tiny colored dots called pixels. Each pixel represents a tiny portion of the image and contains information about its color and intensity.
Resolution is expressed as the total number of pixels along the width and height of the image. For example, an image with a resolution of 1920×1080 pixels has 1920 pixels horizontally and 1080 pixels vertically. Higher resolution images have more pixels, providing more detail.
Cognitive Computing (Perception, Learning, Reasoning)
Cognitive Computing is a branch of Artificial Intelligence (AI) that aims to mimic the way the human brain works in processing information and making decisions. It involves building systems that can understand, reason, learn, and interact with humans in a natural and intuitive way.
- This is a platform based on Artificial Intelligence and Signal processing.
- The platform (Cognitive computing) uses Machine Learning, Reasoning, Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Computer Vision to compute results.
- Cognitive computing improves human decision making.
- Cognitive computing tries to mimic the human brain.
Examples of cognitive computing software: IBM Watson, Deep mind, Microsoft Cognitive service etc.
AI Terminologies
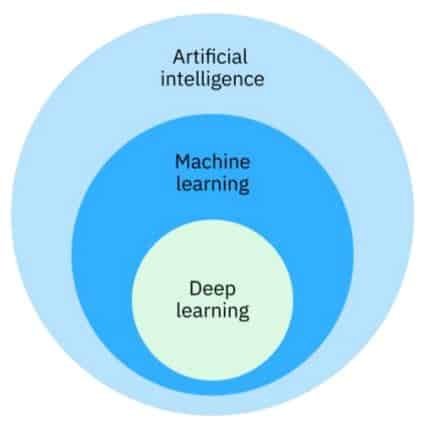
Artificial intelligence (AI) refers to the ability of a machine to learn patterns and make predictions. Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence (AI) that focuses on developing algorithms and models that enable computers to learn from data and make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed. Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that imitates the working of the human brain in processing data and creating patterns for use in decision making.
- The structure of Deep Learning is inspired by the structure of the neurons and neuron connections in the human brain.
- Neural networks, also known as Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs), are a subset of Machine Learning and the core heart and concept of Machine Learning.
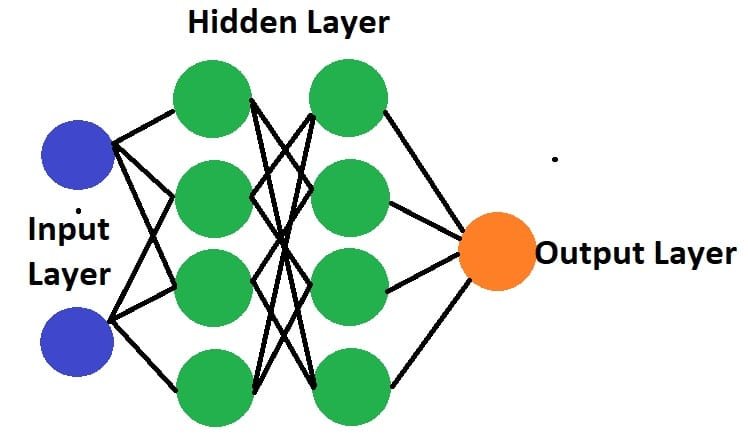
- They comprise of node layers, containing an input layer, one or multiple hidden layers, and an output layer.
- If the output of any node is above a specified threshold, that node is activated, sending data to the next layer of the network.
- Otherwise, no data is passed along to the next layer of the network.
- If the number of Layers including the Input and Output Layer is more than three, then it is called a Deep Neural Network.
Deep Neural Network diagram
Difference between machine learning and deep learning
| MACHINE LEARNING | DEEP LEARNING |
|---|---|
| Works on small dataset for accuracy | Works on Large dataset |
| Dependent on Low-end machine | Heavily dependent on high-end machine |
| Divides the tasks into sub-tasks, solves them individually and finally combine the results | Solves problem end to end |
| Takes less time to train | Takes longer time to train |
| Testing time may increase | Less time to test the data |
Types of Machine Learning
Machine learning is often divided into three categories – Supervised, Unsupervised and Reinforcement learning.
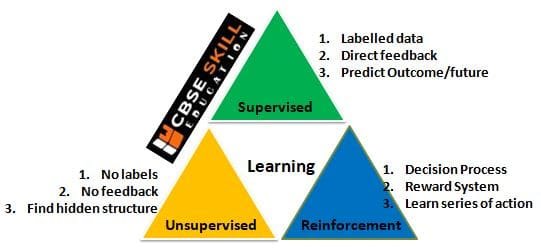
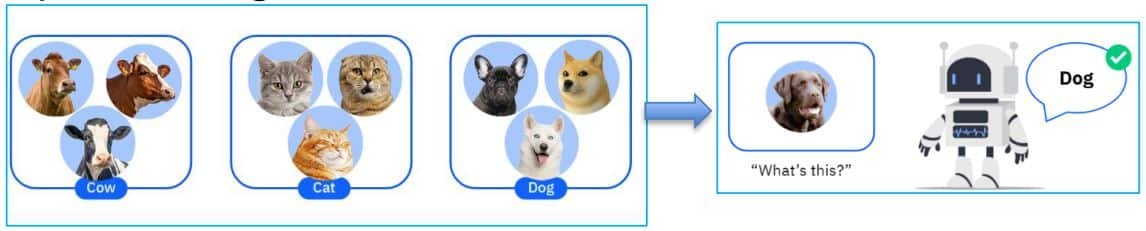
Supervised Learning – Supervised learning is a type of machine learning where the model learns from labelled data, which means that the input data is accompanied by the correct output. Examples of supervised learning algorithms include linear regression, logistic regression, decision trees, support vector machines (SVM), and neural networks.
Unsupervised learning – Unsupervised learning is a type of machine learning where the model learns from unlabelled data, which means that the input data is not accompanied by the correct output. Examples of unsupervised learning algorithms include k-means clustering, hierarchical clustering, principal component analysis (PCA), and autoencoders.
Reinforcement learning – Reinforcement learning is a type of machine learning where an agent learns to make decisions by interacting with an environment to maximize cumulative rewards. Examples of reinforcement learning algorithms include Q-learning, deep Q-networks (DQN), policy gradients, and actor-critic methods.
Benefits and limitations of AI
BENEFITS:
- Increased efficiency and productivity: AI automates tasks, analyzes data faster, and optimizes processes, leading to increased efficiency and productivity across various sectors.
- Improved decision-making: AI analyzes vast amounts of data and identifies patterns that humans might miss, assisting in data-driven decision-making and potentially leading to better outcomes.
- Enhanced innovation and creativity: AI tools can generate new ideas, explore possibilities, and automate repetitive tasks, freeing up human resources for more creative pursuits and innovation.
- Progress in science and healthcare: AI aids in drug discovery, medical diagnosis, and personalized medicine, contributing to advancements in healthcare and scientific research.
LIMITATIONS:
- Job displacement: Automation through AI raises concerns about job displacement and the need for workforce retraining and upskilling.
- Ethical considerations: Concerns exist around bias in AI algorithms, potential misuse for surveillance or manipulation, and the need for ethical guidelines and regulations.
- Lack of explainability: Some AI models, particularly complex ones, lack transparency in their decision-making, making it difficult to understand how they arrive at their outputs.
- Data privacy and security: Large-scale data collection and use for AI development raise concerns about data privacy and security vulnerabilities.
Disclaimer: We have taken an effort to provide you with the accurate handout of “AI For Everyone Class 11 Notes“. If you feel that there is any error or mistake, please contact me at anuraganand2017@gmail.com. The above CBSE study material present on our websites is for education purpose, not our copyrights. All the above content and Screenshot are taken from Artificial Intelligence Class 11 CBSE Textbook and Support Material which is present in CBSEACADEMIC website, This Textbook and Support Material are legally copyright by Central Board of Secondary Education. We are only providing a medium and helping the students to improve the performances in the examination.
Images shown above are the property of individual organizations and are used here for reference purposes only.
For more information, refer to the official CBSE textbooks available at cbseacademic.nic.in

2 thoughts on “AI For Everyone Class 11 Notes”