File Handling in Python Class 12 Notes: File handling is the process of saving data in a file using Python program. The Python file can be stored in a text file or in a binary file. There are six different types of modes available in the Python programming language which is used for reading, writing, and appending files in Python.
File Handling in Python Class 12 Notes | Computer Science
File Handling in Python
File handling is the process of saving data in a file using Python program. The Python file can be stored in a text file or in a binary file. There are six different types of modes available in the Python programming language which is used for reading, writing, and appending files in Python.
Note: The Python file can be stored in a text file or in a binary file.
| Text File Mode | Binary File Mode | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ‘r’ | ‘rb’ | Read |
| ‘w’ | ‘wb’ | Write |
| ‘a’ | ‘ab’ | Append |
| ‘r+’ | ‘rb+’ | Read and write |
| ‘w+’ | ‘wb+’ | Write and read |
| ‘a+’ | ‘ab+’ | Write and read |
File Handling Steps
- Open the file
- Write and Read operation
- Close the file
1. Open a file in Python
For reading, writing, or editing a file in Python, you have to open the file first using the open() method.
Syntax:
<file_object_name> = open(<filename>, <mode>)

2. Write and Read operation
Write operation in Python
When the file is opened in write mode and if a new file does not exist in the specific location on the disk, then the write mode creates the file automatically; otherwise, if it is found in the location, then the same file will be used. The function used to write in the file is filename.write().
Syntax:
file_object.write(<text which you want to write>)
file = open("example.txt", "w") # Open the file in write mode
file.write("Hello, World!") # Writing content to the fileRead operation in Python
The read() function is used to read content from a text file. It is basically used when we want to fetch data from a file that is opened in read mode (‘r).
Syntax:
file_object.read()
file = open("example.txt", "r") # Open the file in read mode
content = file.read() # Read the content of the file
print(content)3. Close the file
The close() method is important to close the operation on the file after execution. It defines that the file is properly closed after performing the operation, like reading, writing, or appending, which will help to prevent the file corruption.
Syntax:
close()
# Writing to the file
file = open("example.txt", "w")
file.write("Hello, World!")
file.close() # Close the file
# Reading from the file
file = open("example.txt", "r")
content = file.read()
print(content)
file.close() # Close the fileReading a Text File
The reading of the text file can be done using 3 different methods as per the requirement.
- read(): Reads entire content from a file or a specific number of bytes.
- readline(): Reads one line from the file at a time.
- readlines(): Reads all lines from the file and returns them as a string.
1. read() method
The read() method is used to read the entire content from a file; it can handle large files but takes lots of memory. The read() method can be used in text files and binary files both such as ‘r’ (text read mode) or ‘rb’ (binary read mode).
Example,

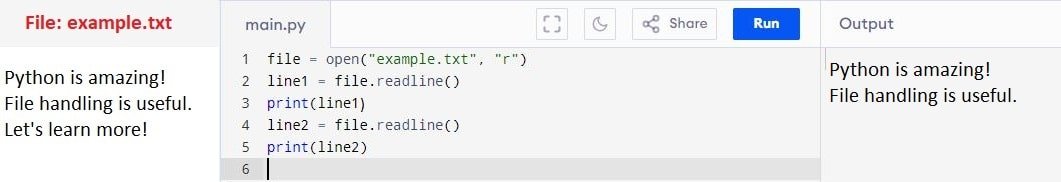
2. readline() method
Reads one line from the file at a time. This method is useful for reading files line by line, especially in loops.
Example,
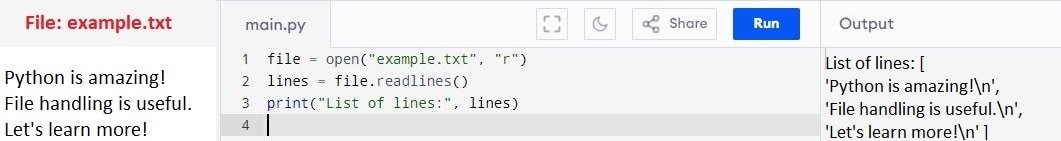
3. readlines() method
Reads all lines in the file and returns them as a list of strings; each string in the list ends with a newline (\n). Ideal for small to medium sizes of files.
Example,
Writing into a Text File
The writing of the content on the text can be done using two methods:
- write(): Writes a single string to a file at a time; does not add newline characters automatically.
- writelines(): Writes multiple strings to a file; does not add newline characters automatically.
1. write() method
Writes a single string to a file at a time; does not add newline characters automatically.
file = open("example.txt", "w")
file.write("Hello, World!\n") # Writes a single string to the file
file.write("Python is great for file handling!\n") # Adds another line2. writeline() method
Writes multiple strings to a file; does not add newline characters automatically.
file = open("example.txt", "w")
lines = [
"Line 1: File handling in Python.\n",
"Line 2: This is the second line.\n",
"Line 3: Let's write multiple lines!"
]
file.writelines(lines)Appending into a Text File
Append mode helps to add new data in the file without erasing the previous one; this new data is added at the end of the existing data. To use this append mode, you need to set “a” as append in the open() function.
file = open("example.txt", "a")
file.write("Hello, World!\n") # The new data will be added at the end of the existing data.Binary File Handling
Binary files are made up of non-human-readable data in the form of bytes. The pickle module is used to convert Python objects like lists, tuples, and dictionaries into a byte stream called pickling or serialization using the dump() method. To restore or to retrieve the data in original form is known as unpickling, which can be done using load() method.
Writing into a binary file
The dump() function is used in Python for writing an object into a binary file.
import pickle
data = {
"name": "Anil",
"age": 25,
"skills": ["Python", "Data Science", "Machine Learning"]
}
# Writing data into a binary file
pickle = open("data.bin", "wb")
pickle.dump(data, binary_file) # Serialize and write the dataReading a binary file
The load() method is used to read the binary file in Python. This method unpickles the data from the binary file, which helps to convert the binary stream into the original object.
unpickle = open("data.bin", "rb")
data = pickle.load(binary_file) # Deserialize the data (unpickling)
print(data)What is csv file?
A CSV, which stands for comma-separated values, is just like a text file that stores data in a tabular format. A CSV file is used to store high-volume data in a database.
Writing into a csv File
Python has a built-in module called CSV. CSV is a universal format, and CSV is just like a text file, which is easier to read and edit. While working on a CSV file, there are two methods used to write data: write() and writerow(). To write content in a CSV file, the mode “w” must be specified in the file path. After opening the file, the writer() or writerow() method is used to write content in the file.
Note: The file extension is .csv.
| write() | writerow() |
|---|---|
| Required format rows, commas, quotes etc | Not requried formatting, handled automatically |
| Less user friendly | User friendly |
| Handle manually | Automatically escapes characters like , or “ |
write() method
data = [["Name", "Age", "City"], ["Rakesh", 25, "New Delhi"], ["Amit", 30, "Mumbai"]]
file = open("example.csv", "w")
for row in data:
formatted_row = ",".join(map(str, row)) + "\n"
file.write(formatted_row)
file.close() writerow() method
import csv
header = ["Name", "Age", "City"]
data = ["Alice", 25, "New York"]
file = open("writerow_example.csv", "w", newline="")
writer = csv.writer(file)
writer.writerow(header)
writer.writerow(data)
file.close()Reading From a csv File
To read data from a CSV file, the file should be opened in the same method, and the mode ‘r’ is used for reading the file. After opening the file, the reader() method will be used.
import csv
file = open("example.csv", mode="r")
reader = csv.reader(file)
for row in reader:
print(row)
file.close()Disclaimer: We have taken an effort to provide you with the accurate handout of “File Handling in Python Class 12 Notes | Computer Science“. If you feel that there is any error or mistake, please contact me at anuraganand2017@gmail.com. The above CBSE study material present on our websites is for education purpose, not our copyrights.
All the above content and Screenshot are taken from Computer Science Class 12 NCERT Textbook, CBSE Sample Paper, CBSE Old Sample Paper, CBSE Board Paper and CBSE Support Material which is present in CBSEACADEMIC website, NCERT websiteThis Textbook and Support Material are legally copyright by Central Board of Secondary Education. We are only providing a medium and helping the students to improve the performances in the examination.
Images and content shown above are the property of individual organizations and are used here for reference purposes only.
For more information, refer to the official CBSE textbooks available at cbseacademic.nic.in
