Introduction to Problem Solving Class 11 Notes, Problem solving is a fundamental concept of programming language. In this chapter include algorithms, flowcharts, and logical thinking. This note will help you to develop the technical skills, and you will be able to break down complex problems into a simple step-by-step method.
Introduction to Problem Solving
Problems cannot be resolved by computers alone. We must provide clear, step-by-step directions on how to solve the issue. The process of identifying a problem, creating an algorithm to solve it, and then putting the method into practice to create a computer program is known as problem solving.
Steps for Problem Solving
To identify the best solution to a difficult problem in a computer system, a Problem Solving methodical approach is necessary. Problem Solving Steps are –
- Analysing the problem
- Developing an Algorithm
- Coding
- Testing and Debugging
- Analyzing the problem: It is important to clearly understand a problem before we begin to find the solution for it. If we are not clear about what is to be solved, then the software program will not work properly.
- Developing an Algorithm: Developing an algorithm is important before creating the program. An algorithm is a step-by-step process where we write the problem and the steps of the programmes.
- Coding: After the algorithm is completed, it must be translated into a form of program. This program can be written using any programming language to produce the desired outcome.
- Testing and Debugging – The developed programme needs to pass different parameters to produce accurate output. This parement can be tested using the testing and debugging method.
What is the purpose of Algorithm?
Before creating any code, the programmer first creates a roadmap for the software. Without a roadmap, a programmer will not be able to visualise the problem, and the software will not work properly as per the requirement. Here, the roadmap is known as an algorithm.
Representation of Algorithms
There are two common methods of representing an algorithm —flowchart and pseudocode. Any one of the method can be used to represent an algorithm while keeping in mind the following:
- A flowchart is a visual represention of the logic and control flow of the program.
- Pseudocode is a structured way of writing an algorithm.
Flowchart — Visual Representation of Algorithms
A flowchart is a visual representation of an algorithm. A flowchart is a diagram made up of boxes, diamonds and other shapes, connected by arrows. Each shape represents a step of the solution process and the arrow represents the order or link among the steps.
There are standardized symbols to draw flowcharts. Some are given below –
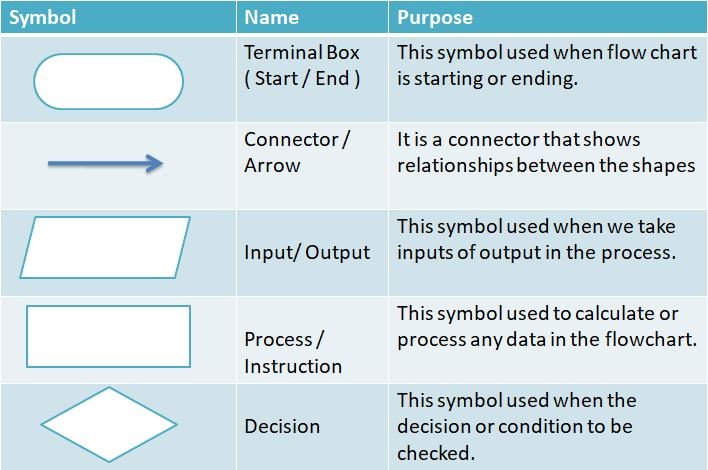
Flow Chart Syntax

Introduction to Problem Solving Class 11 Notes
How to draw flowchart
Q. Draw a flowchart to find the sum of two numbers?

Q. Draw a flowchart to print the number from 1 to 10?

Introduction to Problem Solving Class 11 Notes
What is Pseudocode?
Another way to represent an algorithm is with a pseudocode, which is pronounced Soo-doh-kohd. It is regarded as a non-formal language that aids in the creation of algorithms by programmers. It is a thorough explanation of the steps a computer must take in a specific order.
The word “pseudo” means “not real,” so “pseudocode” means “not real code”. Following are some of the frequently used keywords while writing pseudocode –
- INPUT
- COMPUTE
- INCREMENT
- DECREMENT
- IF/ELSE
- WHILE
- TRUE/FALSE
Example
Write an algorithm to display the sum of two numbers entered by user, using both pseudocode and flowchart.
Pseudocode for the sum of two numbers will be –
input num1
input num2
COMPUTE Result = num1 + num2
PRINT Result
Flowchart for this pseudocode or algorithm –

Decomposition
A problem may occasionally be complex, meaning that its solution cannot always be found. In these circumstances, we must break it down into simpler components. Decomposing or breaking down a complicated problem into smaller subproblems is the fundamental concept behind addressing a complex problem by decomposition. These side issues are more straightforward to resolve than the main issue.
Computer Science Class 11 Notes important links
- Computer Systems and Organisation
- Introduction to problem solving
- Getting Started with Python
- Flow of Control statements in Python
- String in Python
- Lists in Python
- Tuples in Python
- Dictionary in Python
- Society, Law and Ethics
Disclaimer: We have taken an effort to provide you with the accurate handout of “Introduction to Problem Solving Class 11 Notes“. If you feel that there is any error or mistake, please contact me at anuraganand2017@gmail.com. The above CBSE study material present on our websites is for education purpose, not our copyrights. All the above content and Screenshot are taken from Computer Science Class 11 CBSE Textbook, Sample Paper, Old Sample Paper, Board Paper, NCERT Textbook and Support Material which is present in CBSEACADEMIC website, This Textbook and Support Material are legally copyright by Central Board of Secondary Education. We are only providing a medium and helping the students to improve the performances in the examination.
Images and content shown above are the property of individual organizations and are used here for reference purposes only.
For more information, refer to the official CBSE textbooks available at cbseacademic.nic.in
