
Introduction: Communication Skills Class 9 Notes can help the students to understand how communication skills are involved in day-to-day life. Nowadays, good communication skills are required in every organisation. In this chapter you are going to learn what communication is and its importance, the elements of the communication, perspectives in communication, what 7C communication is, types of communication, 3Ps public speaking, and parts of speech.
Communication Skills Class 9 Notes
Session 1: Introduction to communication
What is Communication?
The word ‘Communication’ comes from the Latin word commūnicāre, meaning ‘to share’. communication is the exchange of information through signs, signals, speech, writing, or other forms of media.
Importance of communication
Communication is an ability to communicate clearly and share thoughts, feelings and ideas to others, some of communication skills are needed –
- Inform: You may be required to give facts or information to someone.
- Influence: You may be required to influence or change someone in an indirect but usually important way.
- Express feelings: Talking about your feelings is a healthy way to express them.
What are the different elements of communication?
Communication is a two-way exchange of information, i.e., giving and receiving. Speaking and writing to someone are examples of giving information.
- Sender – The communication process starts with a sender.
- Message – A sender sends a message (giving or asking for information).
- Channel – A Channel (for path), such as phone/ face-to-face (talk/writing) is used to transfer the message
- Receiver – The message is received by the receiver.
Perspectives in communication
Perspectives are ideas, views, or fixed ways of thinking. These sometimes affect our communication. For example, if your teacher or father is strict, even when they are being friendly, you may think they are scolding you even though they are polite.
Factors affecting perspectives in communication
- Language – In case of use of incorrect words, unfamiliar language and lack of detail, language can act as a barrier.
- Visual Perception – Visual perception is the brain’s ability to make sense of what we see through our eyes. For example, partially drawn pictures.
- Past Experience – Letting our earlier experience stop us from understanding or communicating clearly. For example, “This shopkeeper cheated me last time.
- Prejudice – Fixed ideas, such as thinking “No one in my class likes me” may stop a student from communicating openly in the class.
- Feelings – Our feelings and emotions, such as lack of interest or not trusting the other person affect communication. For example, “I am not feeling well”.
- Environment – Noise or disturbance in the surroundings may make communication difficult.
- Personal factors – Personal factors include your own feelings, habits and ways of thinking.
- Culture – Signs’ which have a different meaning in different cultures, such as showing a thumb may mean ‘good job’ done for some people but may be insulting to others.
What are the principles of effective communication?
Effective communication can happen if we follow the basic principles of professional communication skills, It is also known as 7c communication.
- Clear – Be clear about what you want to say.
- Concise – Use simple words and say only what is needed.
- Concrete – Use exact words and phrases.
- Correct – Use correct spellings, language and grammar.
- Coherent – Your words should make sense and should be related to the main topic.
- Complete – Your message should have all the needed information.
- Courteous – Be respectful friendly and honest.
Session 2: Verbal Communication
What is verbal communication?
Verbal communication is the sharing of information by using words. It is what most people use as a method of communication and is most important because if you do not use the right words, you will cause confusion, and you will not be able to communicate what you want.
There are two different types of verbal communication –
- Oral or Spoken Communication – exchange the information and ideas using spoken words.
- Face-to-face conversation
- Talking on a phone
- Classroom teaching
- Business discussion and public speeches
- Written Communication – convey the information through written words like emails, letters, notes etc.
- Writing letters, notes, email, etc.
- SMS (Short Message Service)
- Using email to share news, thoughts, documents and files (including photos, videos, music, etc.)
- Books and newspapers
Advantages of verbal communication
Verbal communication is easy and quick. It is an easier form of communication when you have to exchange ideas. You keep changing your communication as per the other person’s reply.
Disadvantages of verbal communication
The most common disadvantage of verbal communication is the cultural differences between the sender and receiver of the information. Verbal communication depends on words, sometimes the meanings become confusing and difficult to understand if the right words are not used.
What do you mean by public speaking?
Speaking in front of a large group is known as public speaking; the most difficult part in public speaking is fear and nervousness behind the large people. You can use the 3Ps (Prepare, Practice, Perform) method to get over your fears and become a confident and effective speaker.
3Ps of Public Speaking
- Prepare –
- Think about your topic
- Think about what your listeners need to know about the topic
- Think about the best way to make your listeners understand your topic
- Write what you plan to say
- Practice –
- Practice by yourself first,
- Talk in front of a mirror
- Talk in front of your family and friends and ask them what they think
- Speak clearly, loudly and at the right speed (not very fast nor very slow)
- Perform –
- Take a few deep breaths if you are feeling nervous
- Think about what you have prepared and start speaking confidently
Session 3: Non-Verbal Communication
What is Non-Verbal Communication?
Non-verbal communication is the message we send to others without using any words. In nonverbal communication, we communicate through signals, expressions, gestures, and body postures or using a body language.
Importance of non-verbal communication
In our day-to-day communication, it is observed that most of the communication is done using body movements (face, arms, movements, etc.) and voice control (voice, tone, pauses, etc.). The maximum communication is done using nonverbal communication. Please check the figure below.
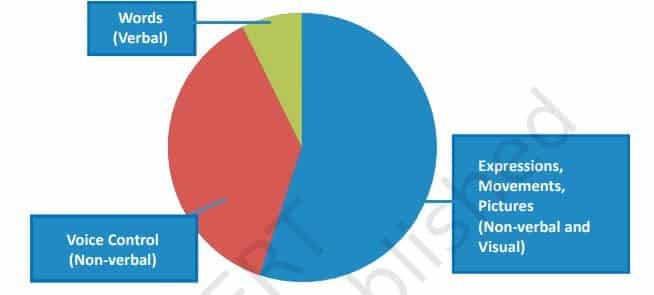
Different types of Non-Verbal Communication?
Non-verbal communication makes our message stronger. Using the right gestures while speaking makes our message more effective. The different types of Non-Verbal communication are –
- Facial Expression – A facial expression shows the feelings of a person.
- Posture – Postures are positions of the body. They show our confidence and feelings.
- Gestures or Body Language – Gestures describe movements of parts of the body, especially hands or head, to express an idea or meaning.
- Tourch – We communicate a great deal through our touch, such as shaking hands patting on the back.
- Space – Maintain proper space between two persons depending on the closeness with the person with whom you are talking.
- Eye Contact – Maintaining an eye contact with the person you are talking indicates interest, whereas, looking away can make the other person feel ignored.
- Paralanguage – Paralanguage is the tone of our voice, speed and volume that makes a difference in the meaning of the communication.
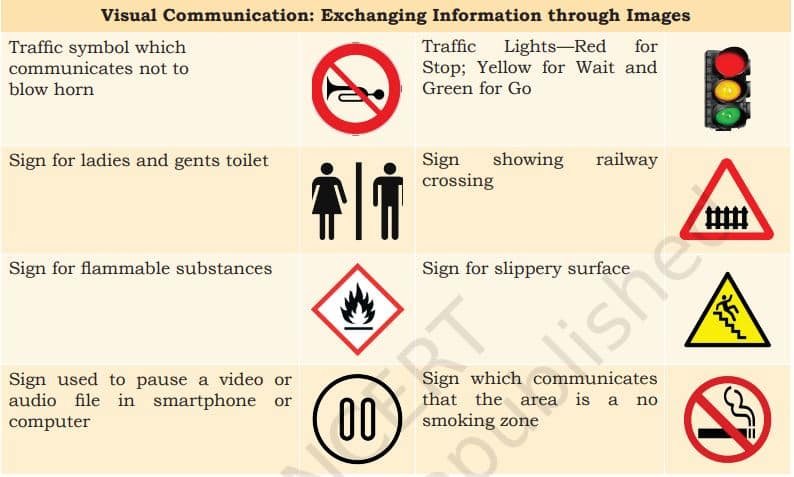
What is Visual communication?
Visual communication involves sending and understanding messages only through images or pictures. The main advantage of this type of communication is –
- Easy to understand.
- It can convey the message to large audience.
Examples of Visual Communication
Session 4: Writing Skills: Parts of Speech
What is sentence and phrase?
- Sentence – A sentence is a group of words that communicates a complete thought (Example: Raju goes to school).
- Phrase – A group of words, which does not make complete sense, is known as a phrase (Example: Raju goes).
A sentence always begins with a capital letter, and it always ends with a question mark, full stop or exclamation mark.
Using capitals
We know that all sentences begin with capital letters. These capitalization rules can easily be understood using ‘MINTS’: ‘MINTS’ is a set of simple rules that help you capitalize words correctly.
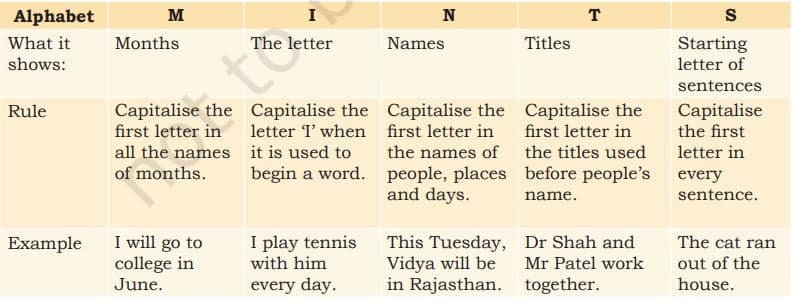
Punctuation
It is a set of marks, such as the full stop and the comma, which help us separate parts of a sentence and explain its meaning. Some common punctuation marks are –
| Punctuation name | Sign | Use |
|---|---|---|
| Full stop | ( . ) | Shows the end of a sentence. |
| Comma | ( , ) | Sometimes, we use a comma to indicate a pause in the sentence. |
| Question mark | ( ? ) | We use a question mark at the end of a question. |
| Exclamation mark | ( ! ) | We use an exclamation mark at the end of a word or a sentence to indicate a strong feeling. |
| Apostrophe | ( ‘ ) | We use an apostrophe followed by an ‘s’ to show that something belongs to someone. |
Basic parts of speech
There are eight basic parts of speech in the English language. These are noun, pronoun, verb, adjective,
adverb, preposition, conjunction and interjection.
| Parts of Speech | What they do | Example sentences |
|---|---|---|
| Noun | Nouns are words that refer to a person, place, thing or idea. These are ‘naming words.’ | – ‘Reema wrote a letter.’ – Both Reema and letter are nouns. |
| Pronoun | A pronoun is a word used in place of a noun. | – “Reema wrote a letter. She is tired.” – ‘She’ is used in place of the noun Reema, it is a pronoun. |
| Adjectives | Adjectives are words that describe other words | – “Reema wrote a long letter.” – Long is an adjective that describes the noun ‘letter’. |
| Verbs | Verbs are words that show action | – “Reema wrote a letter.” – Wrote is the verb. It tells what action Reema did. |
| Adverbs | Adverbs are words that add meaning to verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. | – “Reema quickly wrote a letter.” – – Quickly is an adverb. It tells us how Reema did the action (writing). |
Supporting parts of speech types
Along with the main ‘Parts of Speech’, there are some more words we need for making a sentence.
| Supporting Parts of Speech | Use | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Articles | The words ‘a’, ‘an’ and ‘the’ are known as articles. Articles are generally used before nouns. | The car stopped suddenly because a cat ran in front of it. – A book – An apple – An umbrella – The sun |
| Conjunctions | Conjunctions are words that join two nouns, phrases or sentences. Some common conjunctions are ‘and’, ‘or’ and ‘but’. | Do you want oranges or apples? |
| Prepositions | Prepositions connect one word with another to show the relation between them. They usually answer the questions ‘where’, ‘when’ and ‘how’. | Some common prepositions are ‘on’, ‘at’, ‘under’ and ‘in’. – The cat is on the roof. |
| Interjections | These words express strong emotions, such as happiness, surprise, anger or pain. They have an exclamation mark at the end. | Wow! Oh! Oh no! Thanks! Help! |
Session 5: Writing Skills: Sentences
What is subject, verb and object?
All English sentences have a subject and a verb. Some also have an object.
- Subject – A subject is the person or thing that does an action.
- Verb – A verb describes the action.
- Object – Object is the person or thing that receives the action.
For example, “Divya reads a book”.
- Subject – Divya
- Verb – Reads
- Object – a book
Different types of objects?
The object in a sentence can be either direct or indirect. Direct objects are the ones directly ‘acted on’ by the action word (verb). An indirect object answers questions, such as ‘to whom’ and ‘for whom’.
For example, what did Abdul give? The gift. To whom did Abdul give the gift? To his mother. Here, ‘gift’ is the direct object and ‘his mother’ is the indirect object.
Different types of sentences?
A sentence is a group of words that communicates a complete thought. There are two different types of sentences Active voice and Passive voice.
- Active voice – Sentences where the subject does an action are known to be in the Active voice.
- Passive voice – Sentences in which the subject receives an action are known to be in the Passive voice.
Types of sentences according to their purpose
| Statement or Declarative Sentence | This is the most common type of sentence. It provides information or states a fact. It always ends with a ‘full-stop’ (‘.’). |
| Question or Interrogative Sentence | This type of sentence asks a question. It always ends with a question mark (‘?’). |
| Emotion/Reaction or Exclamatory Sentence | An exclamatory sentence expresses a strong emotion, such as joy, sadness, fear or wonder. It always ends with an exclamation mark (‘!’). |
| Order or Imperative Sentence | These sentences show an order, command, request, or advice. It can end with a full stop or an exclamation mark (‘.’ or ‘!’). |
What do you mean by paragraphs?
A group of sentences forms a paragraph, or paragraph is a group of sentences focused on single topic. While writing a paragraph, make sure the sentences have a common idea.
Session 6: Pronunciation Basics
What is pronunciation?
Pronunciation is the way you say a word; correct pronunciation will help you express yourself in a clear and confident manner. It will also help others to understand your words easily.
What is phonetics?
Phonetics is the study of the sounds that we make when we speak, we use more than 26 sounds when we speak English. For example, the word dog is made of three sounds put together: d-o-g.
All English words are made of three basic types of sounds as shown in below table –
| Vowels | Diphthongs (combination sound of two vowels) | Consonant |
|---|---|---|
| The English alphabet has five vowels (a, e, i, o and u) but 12 vowel sounds. This means most vowels can be pronounced in different ways. We make a vowel sound when we read a vowel in a word. | We make a diphthong sound when we combine two vowels. Diphthongs start as one vowel sound and go to another. | A consonant sound is any sound that is neither a vowel nor a diphthong sound. |
Session 7: Greetings and Introductions
What is greeting?
There are many ways to greet a person, greeting is a polite method to acknowledge someone when you meet them.
Different types of greetings?
There are two types of greetings formals greetings and Informal greetings.
- Formal greetings – Formal greetings are used if you do not know the person. for example, like greetings to teachers or customers. This is used more often in schools, colleges and offices.
- Informal greetings – Informal greetings are used when you talk to friends, family or a known person.
Session 9 & 10: Asking Questions I & II
What is asking questions?
A question is a sentence, phrase, or word that either asks for information or is used to test someone’s
knowledge. We always use a question mark (?) at the end of a question.
Different types of questions?
There are two different types of questions, Open ended questions and Close ended questions.
- Open ended questions – When we ask a question, we expect an answer with more details is known as open ended questions. For example, if the answer is “I like to watch movies on TV.” here the answer is not limited or closed.
- Close ended questions – Questions that can be answered with a “yes” or a “no” are called close-ended question. For example, when we ask “Do you have a TV at home?”, the answer could be either “Yes” or “No”.
Summary: Communication helps to share thoughts, feelings and ideas clearly. Communication is a two-way exchange of information. In the communication cycle, there are four elements: sender, message, channel and receiver. Effective communication can be done with 7c. Communication means the communication should be clear, concise, concrete, correct, coherent, complete and courteous. There are three types of communication: verbal, non-verbal and visual. To communicate between large groups, students should follow the principle of the 3Ps method: prepare, practice and perform. A sentence is a group of words that communicates a complete thought. A group of words, which does not make complete sense, is known as a phrase.
Download Your Free PDF: Click the link below to download your Class 9 Communication Skills Notes PDF, Share this notes with your classmates and leave a comment below if you have any questions!
Employability Skills Class 9 Notes
- Communication Skills Class 9 Notes
- Self Management Skills Class 9 Notes
- Basic ICT Skills Class 9 Notes
- Entrepreneurial Skills Class 9 Notes
- Green Skills Class 9 Notes
Employability Skills Class 9 MCQ
- Communication Skills Class 9 MCQ
- Self Management Skills Class 9 MCQ
- Basic ICT Skills Class 9 MCQ
- Entrepreneurship Skills Class 9 MCQ
- Green Skills Class 9 MCQ
Employability Skills Class 9 Questions and Answer
- Communication Skills Class 9 Questions and Answers
- Self Management Skills Class 9 Questions and Answers
- Basic ICT Skills Class 9 Questions and Answers
- Entrepreneurial Skills Class 9 Questions and Answers
- Green Skills Class 9 Questions and Answers
Disclaimer: We have taken an effort to provide you with the accurate handout of “Communication Skills Class 9 Notes“. If you feel that there is any error or mistake, please contact me at anuraganand2017@gmail.com. The above CBSE study material present on our websites is for education purpose, not our copyrights. All the above content and Screenshot are taken from Employability Skills Class 9 CBSE Textbook and Support Material which is present in CBSEACADEMIC website, This Textbook and Support Material are legally copyright by Central Board of Secondary Education. We are only providing a medium and helping the students to improve the performances in the examination.
For more information, refer to the official CBSE textbooks available at cbseacademic.nic.in

bro i am a backbencher as well as a topper, and in my school there no NCERT was provided but i topped in AI just because of this… that is damn helpful
It is very helpful
Thanks it was very helpful
Very helpful for exam
Better than reading ncert
good tbh
Nice 👍🏻🙂
Very helpful content . Explained easily…….
This has saved me in exam and also it is better than NCERT book
Very nice website 💯💯
its great, tho i feel that they could be deeper and have more in-context stuff with a simpler lingo…otherwise its great
Thank you for your information ☺️☺️
So easy and really easy to understand the language, very easy question ilove this website….. ❣️????????❤????
Really helpful thanks
It is very important for exam study
????????Thanks a lot for the notes and questions????????
Thanks this was helpful for my exam ????????
Absolutely smash !
not failing exam after this!
fr though amazing webpage better than Books
Tysm, saving me on my exam. This is much better than the NCERT book
Got here due to …..
very nice notes helped a lot
Thanks it helped a lot ☺️
Good ???????? ???????? ???????? ???????? ???????? ???????? ????????