Data Literacy Class 9 ai notes – The CBSE has changed the previous textbook and the syllabus of Std. IX. The new notes are made based on the new syllabus and based on the New CBSE textbook. All the important Information are taken from the Artificial Intelligence Class IX Textbook Based on CBSE Board Pattern.

Data Literacy Class 9 ai notes
Every data set has a story; the ability to understand, explore, and communicate with data is known as data literacy. Data-literate people have the ability to derive meaningful information from data. Data literacy helps to analyse complex data or big data in summarised form.
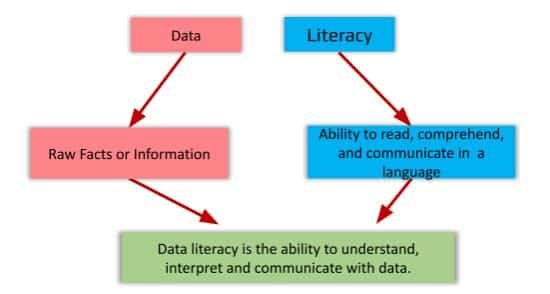
Let’s see one example—
Identify the following table. How the data is arranged, you can see in the below table that the data is arranged properly, but there is no meaningful information. Here the data-literate person will analyze and give some meaningful information.
| Roll No | Student Name | Address | Job Title | Working Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Rajesh Kumar | Mumbai | Supervisor | 9 AM – 5 PM (8 hrs) |
| 2 | Anil Kumar Sinha | Pune | Attender | 10 AM – 6 PM (8 hrs) |
| 3 | Ram Kumar Rawani | Delhi | Clerk | 8 AM – 4 PM (8 hrs) |
Here, the data literacy person will help to extract the data in a proper manner and give some meaningful information from it. Data Literate is a person who can interact with data to understand the world around them.
Benefits of data literacy in organization –
- Better decision making in organization
- Improved business outcomes
- Better customer understanding
- Enhanced collaboration
- Filter the category as per the requirement
How to become Data Literate?
To become data literate, you have to understand, interpret, and effectively use the data in decision-making. To become data literate, then develop the following things in you.
- Understand the Basics of Data
- Develop Statistical & Analytical Skills
- Learn to Work with Data Tools
- Interpret Data Accurately
- Develop Critical Thinking
What is a Data Literacy Framework?
The data literacy framework provides a structured method to work efficiently with data. The data literacy framework includes data collection, data analysis, data organisation, data visualisation, and evaluation.
What is a data pyramid?
The data pyramid is a method to convert the raw data to the meaningful data; the data pyramid is also known as the DIKW pyramid, where “D” means data, “I” means information, “K” means knowledge, and “W” means wisdom. To convert raw data to meaningful information, we use the DIKW pyramid. The DIKW pyramid is a hierarchical model that represents the relationship between different levels of data.
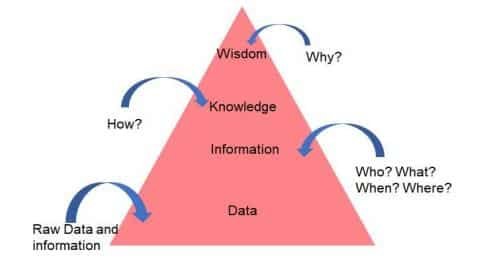
The flow of the DIKW pyramid starts from the bottom to the top.
- Data – The first stage is raw data; this stage of data is unprocessed data that is collected from the various sources. This data can have a number or text.
- Information – Data will become information when the data is processed and organised; raw data can become information using four relevant questions: “Who? What? When? Where?” These questions help to derive valuable knowledge from the data.
- Knowledge – Knowledge is an understanding that comes from information through interpretation and analysis. “How?” is a question that adds more meaning and value to the information, which helps to identify “How can we apply the information?”.
- Wisdom – Wisdom is the top level of the DIKW pyramid, which applies knowledge and experience to make the decisions. “Why?” is a question that is used to convert into action.
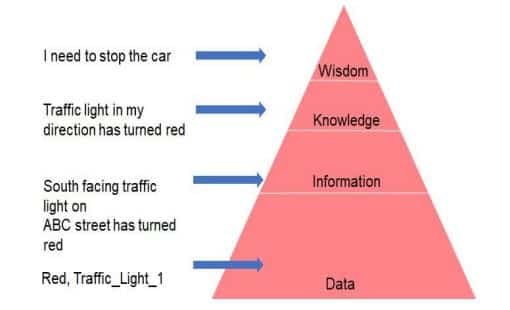
Let’s understand Data Pyramid with a simple Traffic Light example:
Differentiate between Data Privacy and Security?
Data privacy and data security are the two important components of the data.
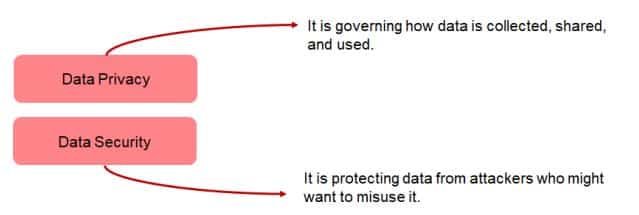
Data privacy refers to the protection of the personal data and other confidential data, data privacy ensures that the data is handled in a proper way on computers, which preserve the data protection rights of the individuals. The data privacy act in India is the Digital Personal Data Protection Act (DPDPA). This act ensures that every individual data can be used lawfully, fairly, and responsibly.
Data security is the protection of data against unauthorised access. Data security also protects data from loss or corruption. Data security uses a wide range of security measures, for example, authentication, network security, encryption, or access controls.
The potential risks associated with data are:
- Data loss – Data loss can be caused by virus attacks, hardware failure, or human error.
- Phishing Attacks – The most common way of unauthorised access is phishing attacks, which involve irrelevant login credentials or clicking on malicious links.
- Password attacks – Cybercriminals used various techniques to crack the password.
Learn measures to protect data privacy and enhance data security
The measures to protect data privacy and enhance data security are:
- Use strong, unique passwords with a mix of characters for each account.
- Activate Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) for added security.
- Download software from trusted sources and scan files before opening.
- Prioritize websites with “https://” for secure logins.
- Keep your browser, OS, and antivirus updated regularly.
- Adjust social media privacy settings for limited visibility to close contacts.
- Always lock your screen when away.
- Connect only with trusted individuals online.
- Use secure Wi-Fi networks.
- Report online bullying to a trusted adult immediately.
Acquiring Data, Processing, and Interpreting Data
What is Data?
Data is a representation of facts or instructions about an entity that can be processed or conveyed by a human or a machine, such as numbers, text, pictures, audio clips, videos, and so on.
What are the different types of Data?
Data serving is a foundation of artificial intelligence; the data is classified into two types:
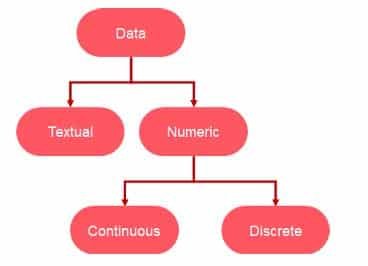
| Textual Data (Qualitative Data) | Numeric Data (Quantitative Data) |
|---|---|
| It is made up of words and phrases | It is made up of numbers |
| It is used for Natural Language Processing (NLP) | It is used for Statistical Data |
| Search queries on the internet are an example of textual data | Any measurements, readings, or values would count as numeric data |
| Example: “Which is a good park nearby?” | Example: Cricket Score, Restaurant Bill |
Data Acquisition/ Acquiring Data
Data acquisition is a process where real-world data can be collected and converted into a digital form with the help of computers and software. For example, if you want to predict the salary of any employee based on the previous salaries, then you have to acquire the data from the different reliable sources, or you can feed the data directly to the machine. Once the data is collected, then the machine can predict the next salary efficiently. The previous salary data is known as training data, and the next salary prediction is known as testing data.
The data acquisition involves searching for datasets suitable for training AI models. The process typically comprises three key steps:
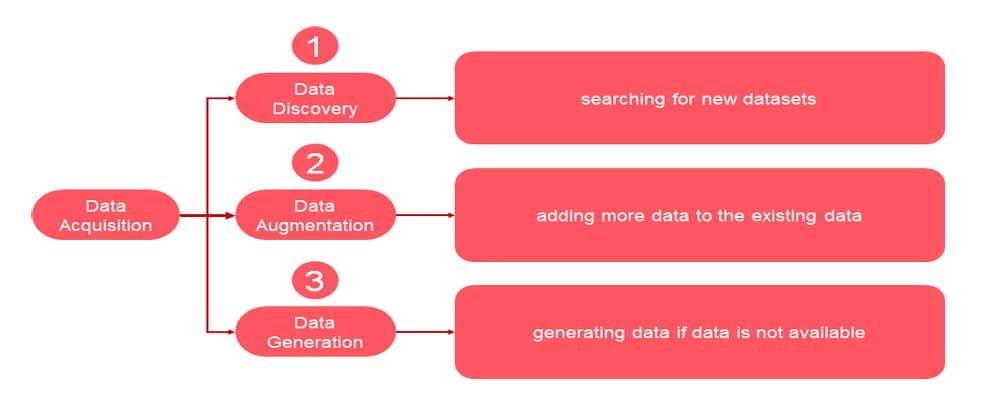
- Data discovery – Data discovery is a method that helps to extract meaningful data from the image and patterns. This data can be extracted from different data sources for visual analysis.
- Data augmentation – Data augmentation is an AI-based technique that uses existing data to create new data to improve machine learning models.
- Data Generation – When the large amount of data is processed and simplify using computer software, using algorithm or using sensors, it is known as data generation, for example, temperature reading.
What are the different sources used for acquiring data?
There are two methods used to acquire data from the various sources.
Primary Data Source – If the data is collected from the original source, it is known as a primary data source. This data is original data and more reliable data. This data is used for research purposes. Some of the sources for primary data include surveys, interviews, experiments, etc. The data generated from the experiment is an example of primary data.
Secondary data source – This type of data is collected from someone else for other purposes or from external sources and is known as a secondary data source. It is not real-time data, as the research has already been done on this type of data. Some of the sources for secondary data sources include government websites, published journals, reviews, etc. Some sources for secondary data collection include:

Best Practices for Acquiring Data
To acquire the data from the different sources, you have to understand the difference between good data and bad data.
| Good Data | Bad Data |
|---|---|
| Information is well structured | Information is scattered |
| It is accurate | Contains a lot of incorrect values |
| It is consistent | Contains missing and duplicate values |
| It is cleanly presented | It is poorly presented |
| Contains information which is relevant to our requirement | Contains information which is not relevant to our requirement |
Ethical concerns in data acquisition
Ethical concerns in data acquisition mean knowing the difference between right and wrong, always trying to do the thing in the right manner and protecting the privacy of individuals. Some of the ethical concerns in data acquisition are:

What is Data Preprocessing?
Data preprocessing refers to the process of making the data in an organized format using structuring, cleaning, and accuracy from the raw data to ensure that the quality and consistency will remain the same. There are three primary factors determining the usability of data.
Structure – Define how data is stored. Data should be stored in a structured method; if data is not structured, then it will be difficult for machines to understand the data.

Cleanliness – Clean data is always useful for data analysis; clean data is free from duplicate values, missing values, outliers, and other anomalies that may affect its reliability.
Accuracy – Accuracy helps to indicate how well the data matches with the real world, which helps the quality and trustworthiness of the dataset; accurate data closely reflects actual values without errors.
Features of data and Data Preprocessing
Data features are the most important steps in machine learning; they describe each and every piece of information present in the data. They are just like characteristics or properties of the data. For example, in a table of student records, features could include things like the student’s name, age, or grade. In a photo dataset, features might be the colors present in each image. These features help us understand and analyze the data.
In AI models, we need two types of features: independent and dependent.
- Independent – Independent features help to predict the outcome based on input data given to the model.
- Dependent – Dependent features help to predict the outcome based on what we are trying to predict; dependent features can be manipulated.
What is Data Interpretation?
Data interpretation is the process of making sense out of data that has been processed, the interpretation of data helps us answer critical questions using data.
Methods of Data Interpretation
There is two ways to interpret data –
- Qualitative Data Interpretation
- Quantitative Data Interpretation
Qualitative Data Interpretation – The Qualitative data used for text data for interpretation; qualitative data tells us about the emotions, thoughts, experiences and feelings of the people. Qualitative data focused on insights and motivations of people. There are two types of qualitative data. Nominal data and ordinal data: ordinal data is much easier than nominal data interpretation.
Data Collection Methods – Qualitative Data Interpretation
- Record keeping: Record keeping method is the most important method for collecting qualitative data from the data source; it is just like going to a library.
- Observation: The observation method helps to identify the behavior and emotions of the participant carefully.
- Case Studies: In this method, data is collected from case studies.
- Focus groups: In this method, data is collected from a group discussion on a relevant topic.
- Longitudinal Studies: This data collection method is performed on the same data source repeatedly over an extended period.
- One-to-One Interviews: In this method, data is collected using a one-to-one interview.
Quantitative Data Interpretation – Quantitative data interpretation is a process for analyzing numerical data using statistical methods. It helps us answer questions like “when,” “how many,” and “how often.” For example, how many numbers of likes on the Instagram post?
Data Collection Methods – Quantitative Data Interpretation
- Interviews: Quantitative interviews play an important role in collecting information.
- Polls: A poll is a type of survey that asks simple questions of respondents. Polls are usually limited to one question.
- Observations: Quantitative data can be collected through observations in a particular time period.
- Longitudinal Studies: A type of study conducted over a long time
- Survey: Surveys can be conducted for a large number of people to collect quantitative data.
Difference between Qualitative & Quantitative Data Interpretation
| Qualitative Data Interpretation | Quantitative Data Interpretation |
|---|---|
| Categorical | Numerical |
| Provides insights into feelings and emotions | Provides insights into quantity |
| Answers how and why | Answers when, how many or how often |
| Methods – Interviews, Focus Groups | Methods – Assessment, Tests, Polls, Surveys |
| Example question – Why do students like attending online classes? | Example question – How many students like attending online classes? |
Types of Data Interpretation
There are three ways in which data can be presented:
- Textual Data Interpretation – In this data interpretation, the data is mentioned in the form of text, usually in a paragraph. Textual data interpretation is used when the data is not large and easy to comprehend by reading. It is not suitable for large data.
- Tabular Data Interpretation – In this data interpretation, the data is represented in the form of rows and columns. where the title contains the description and information contained in columns.
- Graphical Data Interpretation – In this data interpretation, the data is represented in the form of graphs like bar graphs, pie charts, line graphs, etc.
What is data visualization?
Data visualization is the graphical representation of the data. Data visualization uses visual elements like charts, graphs, and maps for understanding the data.
Discover different methods of data visualization
There are different methods of data visualization techniques that help to display data in a graphical form. Some of the important data visualization techniques are
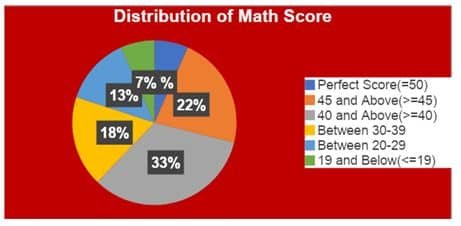
Pie Chart – Pie charts have the shape of a pie, and each slice of the pie represents the portion of the entire pie allocated to each category. It is a circular chart divided into various sections (think of a cake cut into slices). Each section of the pie chart is proportional to the corresponding value.
Bar Chart – Bar charts are used to compare the data and help to show the distribution of the data. In a Bar Graph, data is represented using vertical and horizontal bars.

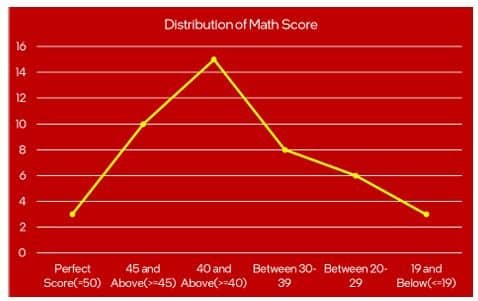
Line Graphs – A line graph is created by connecting various data points; it shows the change in quantity over time.
Updated Class 9 AI Notes
Subject Specific skills Notes (40 Marks)
- Unit 1: AI Reflection, Project Cycle and Ethics
- Unit 2: Data Literacy
- Unit 3: Math for AI (Statistics & Probability)
- Unit 4: Introduction to Generative AI
- Unit 5: Introduction to Python
Employability skills Notes ( 10 Marks )
- Unit 1 – Communication Skills
- Unit 2 – Self-Management Skills
- Unit 3 – Basic ICT Skills
- Unit 4 – Entrepreneurial Skills
- Unit 5 – Green Skills
Old Subject Specific skills Notes (For revision)
- Unit 1 – Introduction to Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Unit 2 – AI Project Cycle
- Unit 3 – Neural Network
- Unit 4 – Introduction to Python
Disclaimer: We have taken an effort to provide you with the accurate handout of “Data Literacy Class 9 AI notes“. If you feel that there is any error or mistake, please contact me at anuraganand2017@gmail.com. The above CBSE study material present on our websites is for education purpose, not our copyrights. All the above content and Screenshot are taken from Artificial Intelligence Class 9 CBSE Textbook and Support Material which is present in CBSEACADEMIC website, This Textbook and Support Material are legally copyright by Central Board of Secondary Education. We are only providing a medium and helping the students to improve the performances in the examination.
For more information, refer to the official CBSE textbooks available at cbseacademic.nic.in

I love this. Tysm.
Very good
nice