Teachers and Examiners (CBSESkillEduction) collaborated to create the Java Class 12 Notes. All the important Information are taken from the NCERT Textbook Information Technology (802) class 12.
Java Class 12 Notes
Java Programming Class 12
Java is a high-level, class-based, object-oriented programming language. Java Interpreter java program to Java Bytecode. This method has the advantage that once a Java programme has been converted to bytecode, it can be executed on any platform (such as Windows, Linux, or Mac), provided the platform is running the JVM. Because of this, Java programmes are extremely portable and cross-platform.
Variables and Datatypes in Java
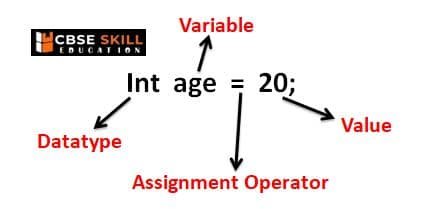
What is Variable?
Variables will be used to store the program’s data. A variable is a placeholder for information whose value may change as a result of a program’s execution. In a computer, a variable is the name of a memory region that stores data. All data variables in Java have to be declared and initialized before they are used.
What is Datatype?
When declaring variables, we have to specify the data type of information that the member will hold – integer, fractional, alphanumeric, and so on. The type of a variable tells the compiler, how much memory to reserve when storing a variable of that type.
Java Datatype is divided into two types –
- Primitive data types – includes byte, short, int, long, float, double, boolean and char.
- Non-primitive data types – such as String, Arrays and Classes.
Primitive data types
A reserved term is used to identify a primitive type, which is predefined by the language. The Java programming language’s support eight primitive data types.
| Data Type | Type of values | Size |
|---|---|---|
| byte | Integer | 8-bit |
| short | Integer | 16-bit |
| int | Integer | 32-bit |
| long | Integer | 64-bit |
| float | Floating Point | 32-bit |
| double | Floating Point | 64-bit |
| char | Character | 16-bit |
| boolean | True or False | 1-bit |
Java Variables Naming rules
- Variable names can begin with either an alphabetic character, an underscore (_), or a dollar sign ($).
- Variable names must be one word. Spaces are not allowed in variable names. Underscores are allowed. “total_marks” is fine but “total marks” is not.
- There are some reserved words in Java that cannot be used as variable names, for example – int.
- Java is a case-sensitive language. Variable names written in capital letters differ from variable names with the same spelling but written in small letters.
- It is good practice to make variable names meaningful. The name should indicate the use of that variable.
- You can define multiple variables of the same type in one statement by separating each with a comma.
String Variable
String variables, also known as alphanumeric variables or character variables, treat their values as text. As a result, string variables may have values that are made up of letters, numbers, or symbols.
Example –
String first_name = “Mayank”;
String last_name = “Saxena”;
Operators
In a programming language, operators are special symbols that carry out certain operations.
- Arithmetic Operators
- Relational Operators
- Assignment Operators
- Logical Operators
Athematic Operator
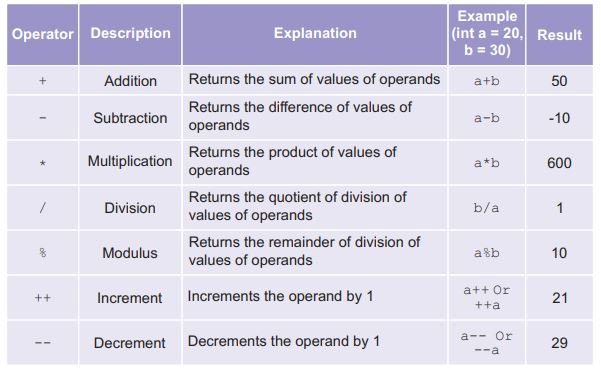
Relational Operators
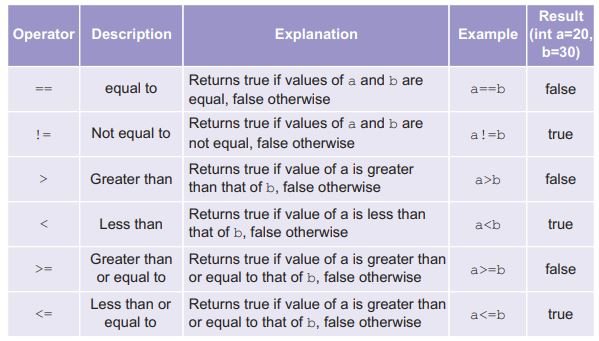
Assignment Operators
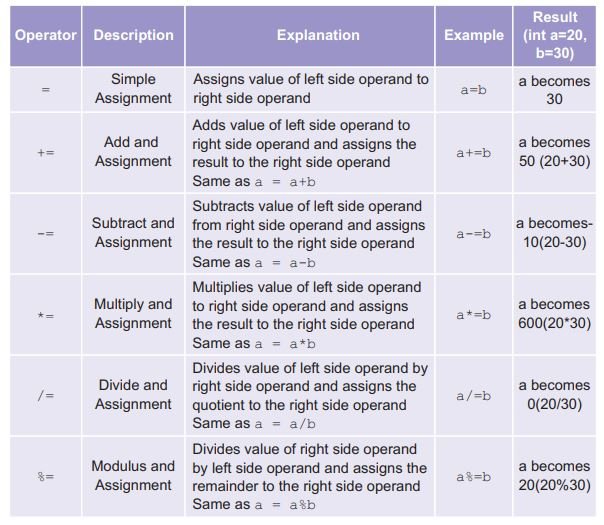
Logical Operator

Selection Structures
In real life, you often select your actions based on whether a condition is true or false. Similarly in a program, you may want to execute a part of the program based on the value of an expression. Java provides two statements –
- If else Statement
- Switch Statement
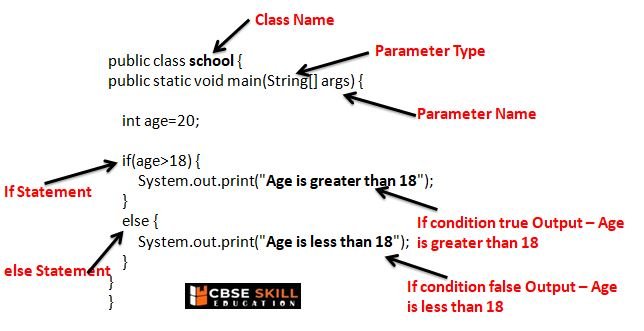
The if Else Statement
The if else statement in Java lets us execute a block of code depending upon whether an expression evaluates to true or false. The structure of the Java if statement is as below –
Syntax –
if (expression) {
statements
}
else
{ }
Question > Write a Java program to check weather age is grater then 20 not?
The Switch Statement
The switch statement is used to execute a block of code matching one value out of many possible values. The structure of the Java switch statement is as follows –
Syntax –
switch (expression) {
case 1:
System.out.println(“Case 1”);
case 2:
System.out.println(“Case 2”);
case 3:
System.out.println(“Case 3”);
default:
System.out.println(“Default case”);
}
Question > Java programme to display a Switch statement example.
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int number=30;
switch(number){
case 10:
System.out.println(“10”);
break;
case 20:
System.out.println(“20”);
break;
case 30:
System.out.println(“30”);
break;
default:
System.out.println(“Not in 10, 20 or 30”);
}
}
}
Repetition Structures
In real life you often do something repeatedly, for example, consider a task such as reading a book, first you open the book, and then repeatedly – read a page; flip the page – until you get to the end of the book, then close the book.
Difference between Entry control loop and Exit control loop
| Entry Control Loop | Exit Control Loop |
|---|---|
| In entry control loop condition is checked first | In exit control loop condition is checked last |
| If the condition is false, loop body will not execute | If the condition is false, loop body will execute at least once |
| Example of entry control loop – For & While | Example of exit control loop – Do-while |
The While Statement
The while statement evaluates the test before executing the body of a loop. The structure of the Java while statement is as shown –
Syntax –
while (expression)
{
statements
}
Question > Write a Java program to print the number from 1 to 5 using while statement.
public class WhileDemo {
public static void main (String[ ] args) {
int number = 1;
while (number <= 5) {
System.out.print (“number);
number++;
} } }
The Do While Statement
The do while statement evaluates the test after executing the body of a loop. The structure of the Java do while statement is as shown –
Syntax –
do
{
statements
} while (expression);
Question > Write a Java program to print the number from 1 to 5 using do-while statement.
public class DowhileDemo {
public static void main (String[ ] args) {
int number = 1;
do {
System.out.print (“number);
number++;
} while (number <= 5);
} }
The for Statement
The for loop is the most widely used Java loop construct. The structure of the Java for statement is as below:
Syntax –
for (counter=initial_value; test_condition;change counter)
{
statements
}
Question > Write a Java program to print the number from 1 to 5 using for statement.
public class WhileDemo {
public static void main (String[ ] args) {
int number;
for (number=1; number <= 5; number++) {
System.out.print (“number);
} } }
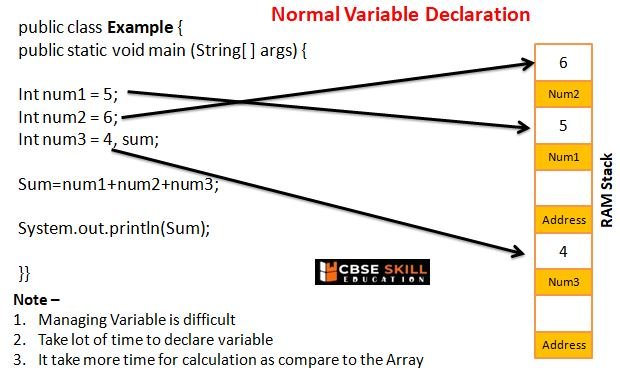
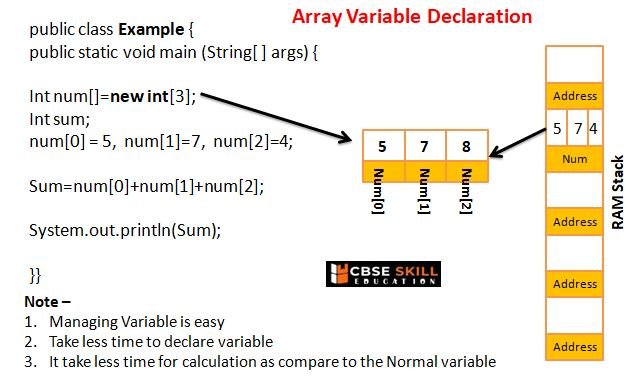
Arrays in Java
Arrays are variables that can hold more than one value, they can hold a list of values of the same type.
For example,
Normal Variable Declaration
Array Variable Declaration
User Defined Methods
A method in Java is a block of statements grouped together to perform a specific task. A method has a name, a return type, an optional list of parameters, and a body. The structure of a Java method is as below –
Syntax –
return_type method_name(list of parameters separated by commas)
{
statements
return statement
}
Example – Let us write a method that given the length and breadth of a rectangle as parameters returns the area of the rectangle.
static double rectangle_area (double length, double breadth)
{
return (length * breadth);
}
Object Oriented Programming
A computer programming paradigm known as object-oriented programming (OOP) arranges the architecture of software around data or objects rather than functions and logic. An object is a data field with particular characteristics and behaviour.
What is Class?
A class is a collection of objects with similar characteristics. It serves as a model or blueprint from which things can be made. It makes sense as a whole. It cannot be bodily.
A class in Java can contain:
- Fields
- Methods
- Constructors
- Blocks
- Nested class and interface
Syntax to declare a class:
class <class_name>{
field;
method;
}
What is Object?
An object is an entity with state and behaviour, such as a chair, bike, marker, pen, table, or car. It could be intellectual or physical (tangible and intangible). The banking system is an illustration of an intangible entity.
Object Definitions:
- An object is a real-world entity.
- An object is a runtime entity.
- The object is an entity which has state and behavior.
- The object is an instance of a class.
Constructors
A special method member called the constructor method is used to initialize the data members of the class (or any other initialization is to be done at time of object creation).
The constructor has the same name as the class, has no return type, and may or may not have a parameter list. Whenever a new object of a class is created, the constructor of the class is invoked automatically. We do not call the constructor explicitly.
Access Modifiers
In object-oriented languages, the accessibility of classes, methods, and other members is controlled through the use of access modifiers . Access modifiers are a particular type of syntax used in programming languages that make it easier to encapsulate components.
Public, protected, default, and private are the four types of access modifiers in Java.
Getter and Setter Methods
A class’s private data members cannot be accessed from outside the class, but you can grant getter and setter methods controlled access to data members outside the class. The value of a data member is returned by a getter method.
For example we could define a getter method in the Bookclass for the price data member as given below –
double getPrice ( ) {
return price;
}
Java Libraries
A Java library is nothing more than a selection of already created classes. You can use those classes in your code when you download them and inform your computer about them.
Java Standard Library
- Without String, Enum, Double, etc., we cannot write any Java programme. Everything we need to write Java code is available to us through the lang library.
- Because util class contains the definitions of all data structures and collections, it is necessary in order to use data structures and collections in Java.
- We require the io library in order to deal with pipes and read data from files. It enables Java programmers to use files in their programmes.
Data Input
The data input helps to take input from the user, this input are by default string. There are three ways to read user input into a Java programme in a command-line environment: Java BufferedReader Class, Java Scanner Class, and Console Class.
Note – In class 12, Only Java Scanner input is given.
Syntax for taking input from the user –
Scanner user_input = new Scanner(System.in);
Question > Write a program to accept name from user and print them in the console.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Datainput {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner user_input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println(“Enter Your Name”);
String name = user_input.next();
System.out.println(“Your name is : ” + name);
} }
Array Manipulation
The elements of an array can be any combination of integers, floating numbers, or complex numbers, and they all share the same underlying data type. Array manipulation helps to manipulate the data using predefine function, from example “binarySearch()”.
We can search for a specific element in an array using the binarySearch() function of the Arrays class. The array to be searched and the key element to be searched are the parameters required. The method returns the array’s index, which is the location of the key. The binarySearch method gives a negative value if the key cannot be found in the array.
Example –
double[] marks = {103, 144, 256.5, 346, 387.5};
int key = 346;
int index = Arrays.binarySearch(marks,key);
String Manipulation
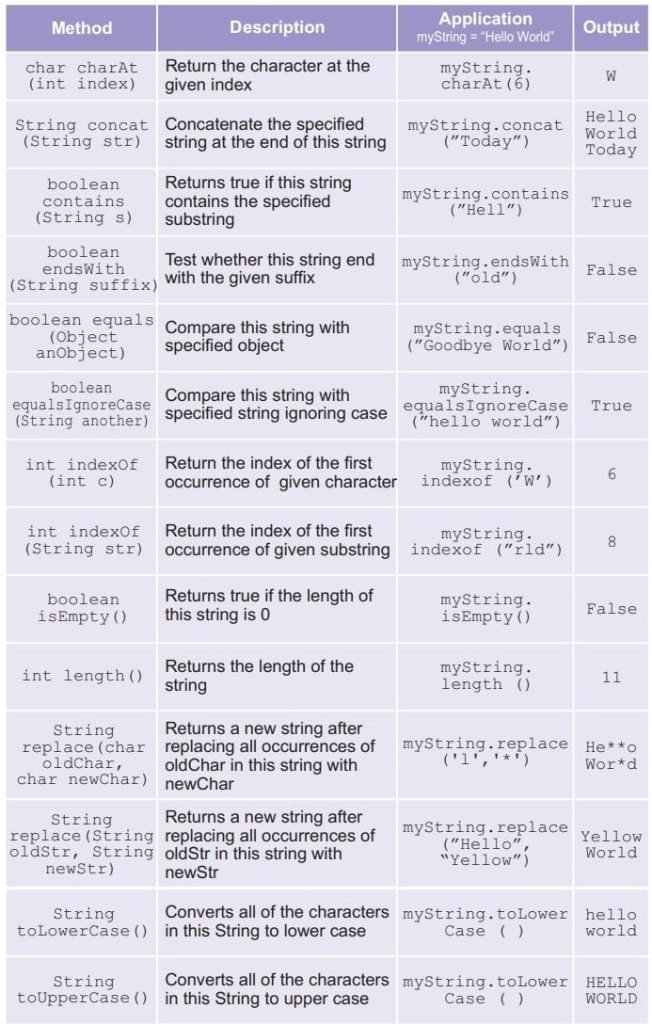
Exception Handling
Runtime issues such as ClassNotFoundException, IOException, SQLException, RemoteException, etc. can be handled through the Java Exception Handling mechanism. An exception is a disruptive occurrence that takes place at run time, or during the execution of a programme, which interrupts the regular flow of the program’s instructions.
Java provides the following keywords to handle an exception:
try – A try block surrounds the part of the code that can generate exception(s).
catch – The catch blocks follow a try block. A catch block contains the exception handler – specific code that is executed when the exception occurs. Multiple catch blocks following a try block can handle different types of exceptions.
Threads
A multithreaded programme can execute numerous tasks simultaneously for the best possible resource utilisation on the computer. A multithreaded programme is made up of two or more threads, each of which is capable of carrying out a particular task independently and concurrently.
In Java, threads can be created in two ways
1. By extending the Thread class
2. By implementing the Runnable interface
Wrapper Classes
Java’s primitive datatypes, including int, float, and others, are typically supplied by value rather than via reference. Primitive datatypes may occasionally need to be passed by reference. When that happens, you can use the Java wrapper classes.
These classes encapsulate the primitive datatype in an object. For instance, an int variable is held by the Integer wrapper class.
Employability Skills Class 12 Notes
- Communication Skills Class 12 Notes
- Self Management Skills Class 12 Notes
- Basic ICT Skills Class 12 Notes
- Entrepreneurial Skills Class 12 Notes
- Green Skills Class 12 Notes
Employability Skills Class 12 MCQ
- Communication Skills Class 12 MCQ
- Self Management Skills Class 12 MCQ
- ICT Skills Class 12 MCQ
- Entrepreneurship Class 12 MCQ
- Green Skills Class 12 MCQ
Employability Skills Class 12 Questions and Answers
- Communication Skills Class 12 Questions and Answers
- Self Management Skills Class 12 Questions and Answers
- ICT Skills Class 12 Notes Questions and Answers
- Entrepreneurship Skills Class 12 Questions and Answers
- Green Skills Class 12 Questions and Answers
Information Technology Class 12 802 Notes
- Database Concepts Class 12 Notes
- Operating Web Class 12 Notes
- Java Class 12 Notes
Information Technology Class 12 802 MCQ
Information Technology Class 12 802 Questions and Answers