These Advanced JavaScript Class 12 Notes are prepared strictly according to the latest HSC Maharashtra syllabus. The notes are written in simple, student-friendly language with proper examples, making them useful for board exam preparation, practical exams, and last-minute revision. This chapter builds a strong foundation for advanced web development and future IT careers.
Advanced Javascript Class 12 Notes
JavaScript is a lightweight, interpreted programming language used to make web pages interactive and dynamic. It runs directly in the browser, enabling features like animations, form validation, interactive maps, and real-time updates without needing extra software.
Features of JavaScript
- JavaScript is lightweight because it does not include all the features of object-orientated programming languages.
- No special software is required to run a JavaScript programme.
- JavaScript is an object-orientated scripting language.
- JavaScript is a case-sensitive language.
- JavaScript helps the browser to perform input validation without wasting the user’s time by the Web server access.
- JavaScript avoids unnecessary communication with the server.
- It can handle date and time very effectively.
- Functions can be created within scripts using the function keyword.
- JavaScript is platform-independent and runs on any device, like mobile, laptop, desktop and tablet.
Type of JavaScript
There are two types of scripting: server-side scripting and client-side scripting.
- Client-side Scripting: In this type, the script resides on the client computer (browser) and can run on the client. Basically, these types of scripts are placed inside an HTML document.
- Server-side Scripting: In this type, the script work on a web server. To execute the script, it must be activated by the client, and then it is executed on the web server.
Difference between Server side scripting and client side scripting
| Server Side Scripting | Client Side Scripting |
|---|---|
| Runs at the backend on the web server. Source code is hidden from the user. | Runs at the frontend in the browser. Code is visible to the user. |
| More secure because the code is hidden on the client side. | Less secure because users can view/modify the script. |
| Requires communication with the server to process requests. | Executes directly in the browser without server interaction. |
| The server-side scripting language involves such as PHP, ASP.net, Ruby, ColdFusion, Python, C# etc. are server side scripting languages. | The client-side scripting language involves languages such as HTML5, JavaScript etc. |
| Customizes web pages, handles dynamic content, database operations, authentication. | Used mainly for input validation, UI interactivity, animations, reducing server load. |
| Special software (web server software) is required to execute server-side script. | Client side scripts requires web browser as an interface. |
Switch case and Looping Structures
Switch Case statement
JavaScript has a built-in multiway decision statement known as ‘switch’. When a match is found, the corresponding block of code runs until a break statement is encountered. If no match is found, the default block executes.
Syntax:
switch(expression)
{
case value1:
statement block 1;
break;
case value2:
statement block 2;
break;
…………....
case value n:
statement block n;
break;
default:
statement block ;
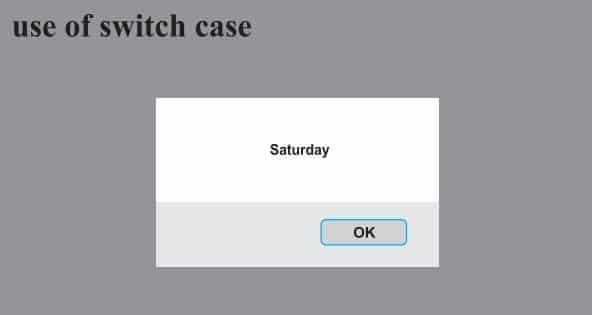
}Program example –
<!DOCTYPE html>
<head><title>Javascript Program
</title></head>
<body>
<h1> use of switch case </h1>
<script type="text/javascript">
var day=6;
switch(day)
{
case 1: alert("Monday"); break;
case 2: alert("Tuesday"); break;
case 3: alert("Wednesday"); break;
case 4:alert("Thursday"); break;
case 5: alert("Friday"); break;
case 6: alert("Saturday"); break;
case 7: alert("Sunday"); break;
default: alert("Invalid day");
}
</script>
</body>
</html>Output
Looping Statement
Looping statements in JavaScript are used to execute a block of code repeatedly until a condition is met. The condition should be boolean condition. Some commonly used JavaScript looping statements are:
for…….loop
This loop executes statements as long as condition becomes true, control comes out from the loop when condition becomes false. Benefit of for-loop is that it combines initialization, condition and loop iteration (increment or decrement) in single statement.
Syntax
for(initialization; condition; iteration)
{
statement block;
}Program example
Q. Write a program to print the number from 1 to 5
for(i=1;i<=5;i++)
{
document.writeln(i);
}
Output
1
2
3
4
5Q. Write a program to print the number from 5 to 1
for(i=5; i>=1; i--)
{
document.writeln(i);
}
Output
5
4
3
2
1While…..loop
This loop executes statements as long as the condition is true. As soon as condition becomes false control comes out of the loop.
Syntax
initialization;
while(condition)
{
statement block;
}Program example
Q. Write a program to print the number from 1 to 5
var i=1
while(i<=5)
{
document.writeln(i);
i=i+1;
}
Output
1
2
3
4
5Break and continue statements
Break statement is used to jump out of loop. It is used to make an early exit from a loop. When keyword break is encountered inside the loop, control automatically passes to the next statement after the loop.
Sometimes in looping it may be necessary to skip statement block and take the control at the beginning for next iteration. This is done by using ‘continue’ statement in JavaScript.
Break statement example
for (let i = 1; i <= 10; i++)
{
if (i === 5)
{
break; // Exit the loop when i equals 5
}
console.log("Iteration: " + i);
}
Output
Iteration: 1
Iteration: 2
Iteration: 3
Iteration: 4Continue statement example
for (let i = 1; i <= 5; i++)
{
if (i === 3)
{
continue; // Skip when i equals 3
}
console.log("Iteration: " + i);
}
Output
Iteration: 1
Iteration: 2
Iteration: 4
Iteration: 5
Objects in JavaScript
JavaScript is an object-based scripting language. In JavaScript everything is an object. A JavaScript object is an entity having state (properties) and behaviour (methods). Objects can group data and functions together. For example, think of a car as an object; properties (state) are the name, model, weight, and colour of the car. Methods (behaviour) like start/stop, brake/drive, etc. All the cars share the same properties and method, but the values and performance differ.
Properties and methods of objects are accessed with the ‘.’ operator. JavaScript supports 2 types of objects: built-in objects and user-defined objects.
- Built-in objects such as Math, String, Array, Date, etc.
- JavaScript gives the facility to create user-defined objects as per user requirements. The ‘new’ keyword is used to create a new object in JavaScript.
Syntax
d= new Date();
// ‘d’ is new instance created for Date object.DOM (Document Object Model)
When an HTML document is loaded into a web browser, it becomes a document object. The DOM defines the logical structure of the document and provides a way to access and modify its content. It acts as a programming interface for both HTML and XML documents.
The standardisation of DOM was founded by W3C (World Wide Web Consortium), which works for the standardisation of web technologies. According to W3C:
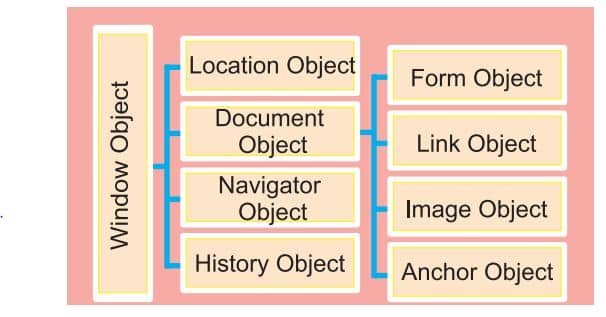
The following diagram shows the hierarchy of DOM objects:
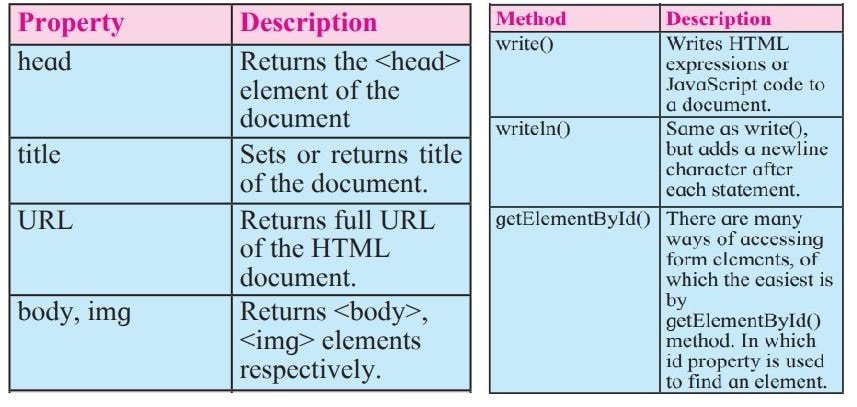
Following are some of the predefined methods and properties for DOM object.
The innerHTML Property
The innerHTML property is useful for getting html element and changing its content. The innerHTML property can be used to get or change any HTML element, including <html> and <body>.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script type="text/javascript">
function changeText3()
{
var style="<h2 style= 'color:green'>";
var text="Welcome to the HTML5 and Javascript";
var closestyle="</h2>";
document.getElementById('para').innerHTML =style+text+closestyle;
}
</script></head>
<body style="backgroundcolor:cyan">
<h1 align="center">
<p id="para">Welcome to the site</p>
<input type="button"onclick=" "changeText3()" value="click this button to change above text">
</h1>
</body>
</html>Window Object
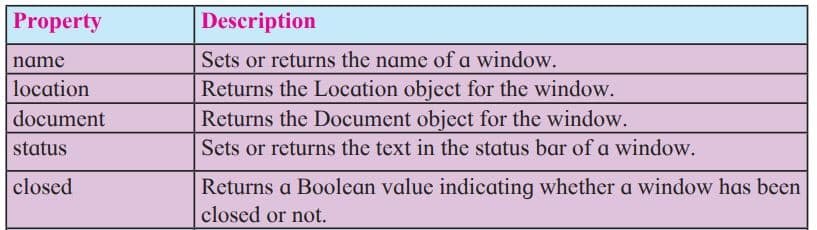
Window object is parent object of all other objects. It represents an open window in a browser. An object of window is created automatically by the browser. Following table shows some of the methods and properties for window object.
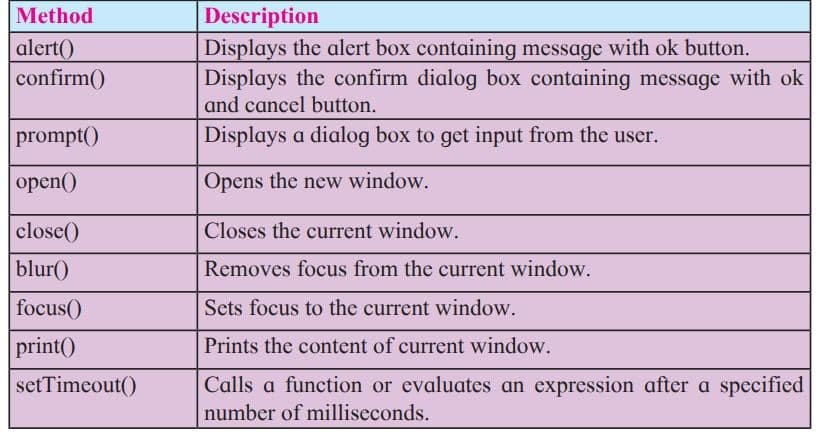
JavaScript Event
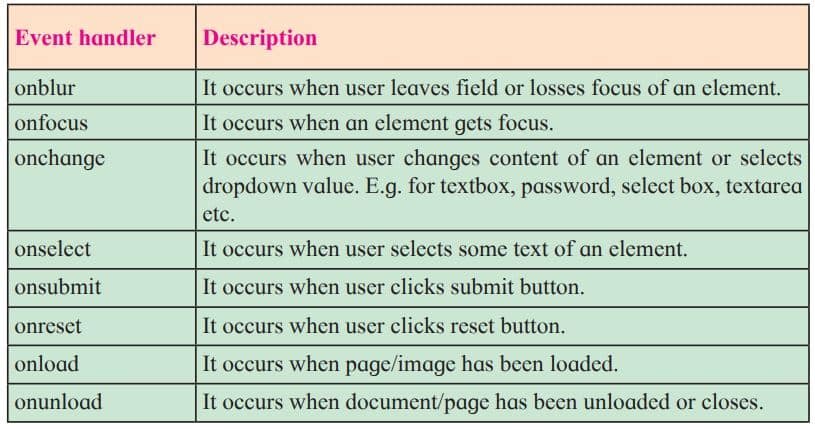
Events are actions done by the user or an application that occurs on the webpage. In previous year we studied different keyboard events (onKeypress, onKeydown, onkeyup) and mouse events (onClick, onMousemove, onMouseout, onMouseover). Similarly there are some more events used with form objects.
JavaScript Built-in Objects
JavaScript has several built-in or core language objects. These built-in objects are available regardless of window content and operates independently of whatever page browser has loaded. These objects provide different properties and methods that are useful while creating live web pages.
String Object :
String is used to store zero or more characters of text within single or double quotes. String object is used to store and manipulate text.
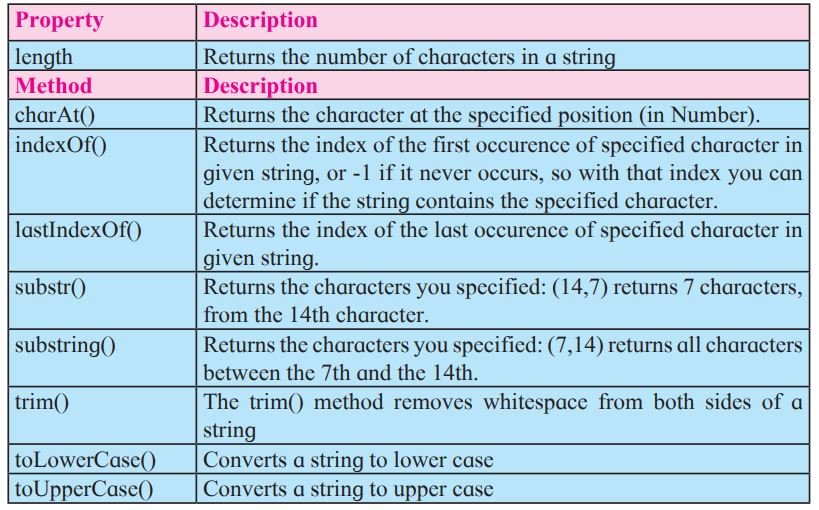
Example
var str="Information Technology";
document.write ("length of string is :-" + str.length);
document.write ("Substring is :-" + str.substr (12,10));
Output
Length of string is :-22
Substring is :- TechnologyMath Object
The built-in Math object includes mathematical constants and functions. You do not need to create the Math object before using it. Following table contains list of math object methods: e.g. var x=56.899; alert(Math.ceil(x));

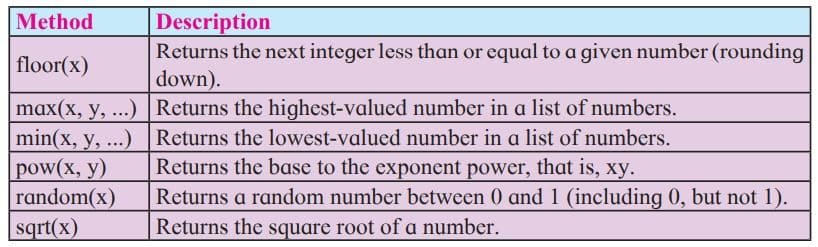
Date Object
The date object is used to create date and time values. It is created using new keyword. There are different ways to create new date object.
var currentdate=new Date();
var currentdate=new Date(milliseconds);
var currentdate=new Date(dateString);
var currentdate=new Date(year, month, day, hours, minute, seconds, milliseconds);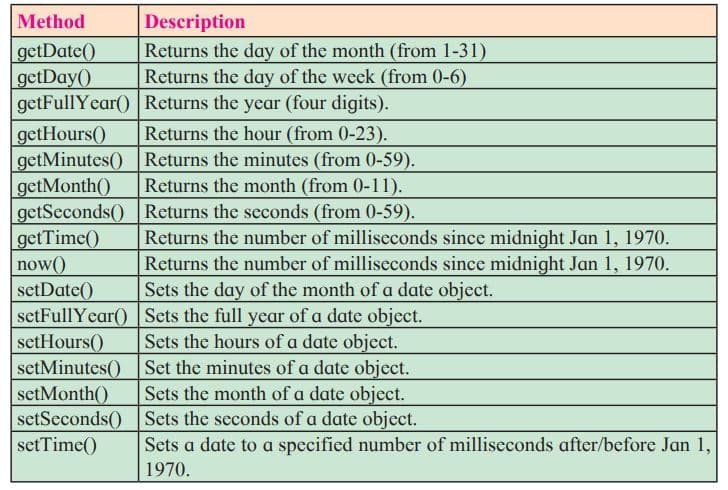
Number Object
It helps us to work with numbers. Primitive values (like 34 or 3.14) cannot have properties and methods, but with JavaScript it is available with primitive values.
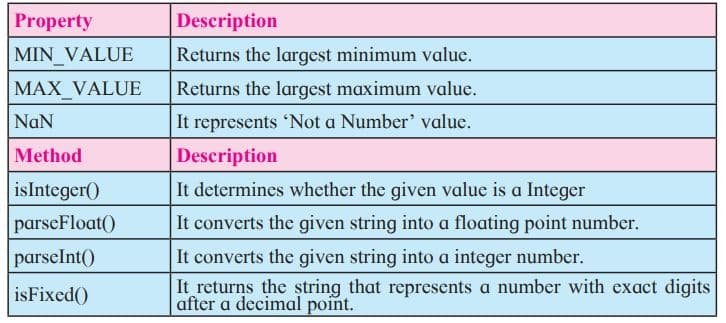
Array Object
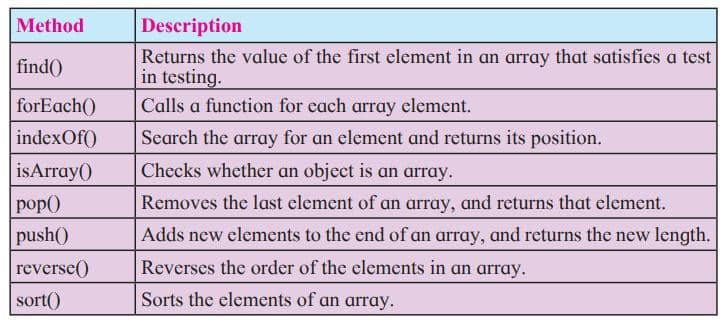
An array is a special type of object in JavaScript. It can store multiple values in a single variable. Useful for handling large amounts of data of the same type.
// Using array literal
var fruits = ["Mango", "Apple", "Orange", "Grapes"];
// Using Array constructor
var fruits = new Array("Mango", "Apple", "Orange", "Grapes");You can access and set the items in an array by referring to its indexnumber and the index of the first element of an array is zero. arrayname[0] is the first element, arrayname[1] is second element and so on.
var fruitname=fruits[0];
document.getElementById("demo").inner HTML=fruits[1];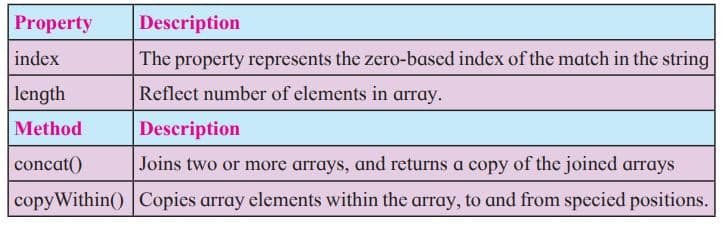
Disclaimer: We have provide you with the accurate handout of “Advanced Javascript Class 12 Notes“. If you feel that there is any error or mistake, please contact me at anuraganand2017@gmail.com. The above study material present on our websites is for education purpose, not our copyrights.
All the above content and Screenshot are taken from Information Technology Class 12 Textbook and MSBSHSE (HSC) Support Material which is present in MSBSHSE (HSC) website, This Textbook and Support Material are legally copyright by Maharashtra State Bureau of Textbook Production and Curriculum Research, Pune. We are only providing a medium and helping the students to improve the performances in the examination.
Images and content shown above are the property of individual organisations and are used here for reference purposes only. To make it easy to understand, some of the content and images are generated by AI and cross-checked by the teachers. For more information, refer to the official website.
