Server Side Scripting – PHP is an important chapter of Information Technology (IT) Class 12 as per the MSBSHSE (HSC Maharashtra Board) syllabus. This chapter helps students understand how dynamic web pages are created using PHP, a popular server-side scripting language. Topics such as PHP basics, syntax, variables, operators, control structures, forms, and database connectivity are essential for board exams as well as practical knowledge.
Server Side Scripting PHP Class 12 Notes
PHP stands for Hypertext Preprocessor. It is a general-purpose scripting language. PHP is a server-side scripting language designed for web development, widely used to build dynamic websites and applications.
- PHP runs on various platforms (Linux, Unix, Mac OS X, Windows, etc.).
- PHP is compatible with almost all servers used today (e.g., XAMPP, Apache, NGINX, and lighttpd).
- PHP supports a wide range of databases.
- PHP is free, and one can download it from the official PHP resource: www.php.net.
- PHP is easy to learn and runs efficiently on the server side.
Server-Side Scripting
PHP is a server-side scripting language run on the server, not on the client (user) computer. The server executes the script and sends back the dynamic HTML to the browser. A few programming languages for server-side programming are:
- PHP
- Java and JSP
- Python
PHP mainly focuses on server-side scripting, which is used to collect form data, generate dynamic page content, or send and receive cookies. There are three things to make this work : the PHP parser a web server and a web browser.
Note : PHP hides the code from the user.
Features of PHP
PHP is most popular and frequently used world wide server-side scripting language and the main reason of popularity is:
- Simple: Easy to learn as compared to other scripting languages.
- Interpreted: No compilation needed; code runs directly on the server.
- Faster: Executes faster than JSP and ASP in many cases.
- Open Source: Free to download, use, and modify.
- Platform Independent: Runs on Linux, Unix, Mac OS X, and Windows.
- Case Sensitive: Variables are case-sensitive ($Name ≠ $name).
- But keywords, functions, and classes are NOT case-sensitive (echo, ECHO, and Echo all work).
- Error Reporting: Built-in constants generate warnings or error notices.
- Real-Time Access Monitoring: Can log and summarise user access activity.
- Loosely Typed Language: No need to declare data types; PHP decides at runtime.
- Example: You can add a string to an integer without error.
First sample code of PHP
A PHP file normally contains HTML tags and some PHP scripting code. The PHP code is usually enclosed in <?php and ?>. All the PHP files have the extension “.php”. A PHP script can be placed anywhere in the HTML document. Note that ‘echo’ is used to display text on a web page.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>My First PHP Page</h1>
<?php
echo "Hello World!";
?>
</body>
</html>Output
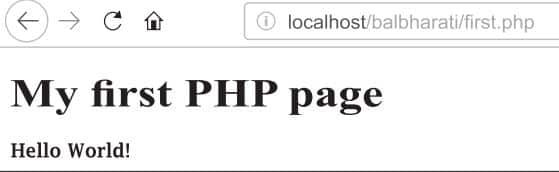
Note : The PHP code is embedded with HTML tags using <?php and ?>.
How to execute PHP program
- Type the above program and save it as”first.php”using any text editor (for e.g. notepad, gedit).
- Create folder with your name in /var/www/html. (for e.g. balbharati)
- Save the ‘first.php’ file in balbharati folder.
- Go to browser and type “http://localhost/balbharati/”inURLbar. Click on ‘first.php’.
PHP Case Sensitivity
In PHP, the variable names are case sensitive. However keywords (e.g. if, else, break, for, while, echo etc.), function and class names are case insensitive. For e.g. : The echo keyword is case insensitive in the program.
<?php
ECHO "Hello World!<br>";
echo "Hello World!<br>";
EcHO "Hello World!<br>";
?>Output

Note : In above example, HTML tag <br> is enclosed in echo output string.
PHP Variables
A variable is a container that holds a value and which can change during the execution of a program. ariables are used for storing values such as numeric values, characters, character strings, or memory addresses, so that they can be used in any part of the program.
Rules for declaring PHP Variable
- A variable starts with the $ sign, followed by the name of the variable
- A variable name must start with a letter or the underscore character
- A variable name cannot start with a number
- A variable name can only contain alpha-numeric characters and underscores (A-z, 0-9, and _ )
- Variable names are case-sensitive ($age and $AGE are two different variables)
There are three different variable scopes in PHP
- local: LOCAL SCOPE and can only be accessed within that function (variable $b).
- global: A variable declared outside a function has a GLOBAL SCOPE.
- static: A static variable inside a function remembers its value between function calls.
We can access a global variable $c from within a function using “global”keyword before the variables (inside the function).
Note : PHP also stores all global variables in an array called $GLOBALS[index]. The index holds the name of the variable
PHP Data Types
Variables can store data of different types and PHP supports the following data types:
- String
- Integer
- Float
- Boolean
- Array
- NULL
Note: One can check the data-type of variable using var_dump() method in PHP.
<?php
echo "<br> -- String --<br>";
$x = "Hello World !";
echo var_dump($x);
echo "<br> -- Decimal --<br>";
$x = "1234";
echo var_dump($x);
?>Output

Comments in PHP
Comments are the statements in PHP code, which are not visible execute in the output of the program. A Single-line comment is possible if one adds // or # before a statement in PHP. A multi-line comment is possible with /* and */ .
Control structures in PHP
If statement in PHP
if statement allows programmer to make decision, based on one or more conditions; and execute a piece of code conditionally.
Syntax:
if(condition)
{
block of statement;
}If-else statement in PHP
if-else statement allows programmer to make decision based on either this or that conditions.
Syntax:
if(condition)
{
Statement;
}
else
{
Statement;
}Loop Structure in PHP
Loops are used to execute the same block of code repeatedly as long as a certain condition is satisfied. For eg : ‘For loop’ in PHP
Syntax
for(initialisation;condition;incrementation
or decrementation)
{
Statement;
}Use of foreach loop
This loop works only on arrays, and is used to loop through each key/value pair in an array.
Syntax
foreach ($array as $value) {
code to be executed;
}Note : Use of ‘.’ in PHP. It is used for concatenation purpose.
Following are the few predefined functions in PHP to manipulate string.
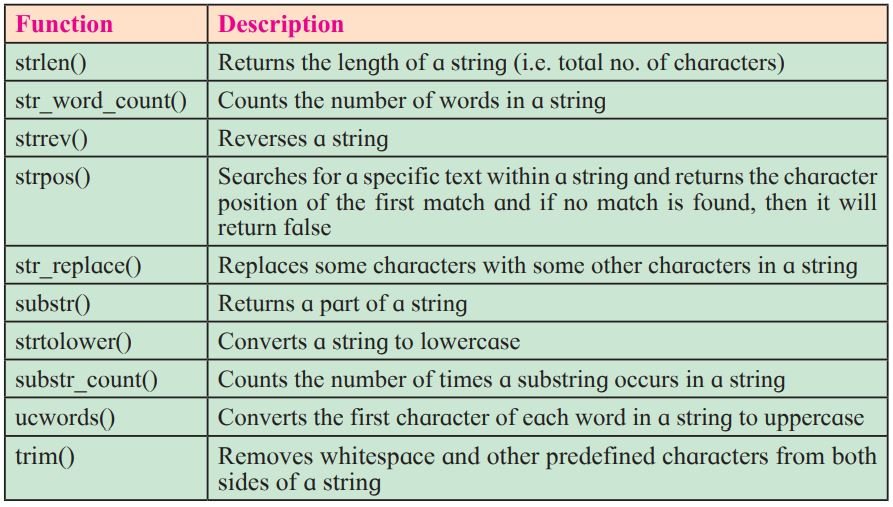
PHP String Functions
A string is series of characters. PHP has many built-in functions that can be called directly to perform a specific task.
<?php
$str="Textbooks produced by Balbharati are also published in pdf format. ";
echo "<br>String: ".$str;
echo "<br>";
echo "<br>String Length : ".strlen($str);
echo "<br>";
echo "<br>String Word Count: ".str_word_count($str);
echo "<br>";
echo "<br>Reverse String : ". strrev($str);
echo "<br>";
echo "<br>Retrun position of string
search : ".strpos($str,"Balbharati");
echo "<br>";
echo "<br>Replace string :".str_replace("Balbharati","State Board",$str);
?>Output

PHP Arrays
An array is a special variable, which can hold more than one value at a time. An array stores multiple values in one single variable. In PHP, the array() function is used to create an array.
Syntax
$a = array( values )In PHP, there are three types of arrays:
- Indexed arrays – Arrays with a numeric index
- Associative arrays – Arrays with named keys
- Multi-dimensional arrays – Arrays containing one or more arrays
In PHP, there are three types of arrays:
- Indexed arrays – Arrays with a numeric index
- Associative arrays – Arrays with named keys
- Multi-dimensional arrays – Arrays containing one or more arrays
1. Indexed arrays
The index can be assigned automatically (index always starts at 0).
Syntax
$a = array( value1, value2, ..., value n)2. PHP Associative Arrays
Associative arrays are arrays that use named keys instead of index to identify record/value. Let us see how to create associative array.
Syntax
$a = array( key1 => value1, key2 =>value2, ...,key n => value n)3. PHP Multi-dimensional Arrays
A multidimensional array is an array containing one or more arrays. PHP can handle multiple levels of multidimensional array.
<?php
$subjects = array("English","Hindi", "Marathi");
foreach ($subjects as $value)
{
echo "$value <br>";
}
?>PHP User Defined Functions
User Defined Functions (UDFs) are functions you create yourself (not built-in). It will not execute immediately when a page loads but will be executed by a call to the function. A user-defined function declaration starts with the word function.
Syntax
function functionName()
{
code to be executed;
} Note : A function name can start with a letter or underscore (not a number). Function names are NOT casesensitive.
PHP Function Arguments
Information can be passed to functions through arguments. An argument is just like a variable. Arguments are specified after the function name, inside the parentheses. The following example has a function with arguments ($rollno and $name):
<?php
function Student($rollno, $name)
{
echo "Roll No is $rollno and Name is
$name <br>";
}
Student(1,"Ashwini");
Student(2,"Raj");
Student(3,"Sonam");
?>Returning Value
To let a function return a value, use the return statement:
<?php
function sum(int $x, int $y)
{
$z = $x + $y;
return $z;
}
echo "5 + 10 = " . sum(5, 10) . "<br>";
echo "7 + 13 = " . sum(7, 13) . "<br>";
echo "2 + 4 = " . sum(2, 4);
?> PHP Form Handling
A simple HTML form with two input fields and a submit button
<html>
<body>
<form action="welcome.php" method="post">
Name: <input type="text" name="name"><br>
E-mail: <input type="text" name="email"><br>
<input type="submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>Output
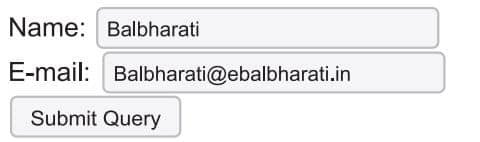
When the user fills out the form above and clicks the submit button, the form data is sent for processing to a PHP file named “welcome.php”. The form data is sent with the HTTP POST method. The code for “welcome.php” looks like this:
<html>
<body>
Welcome
<?php echo $_POST["name"]; ?> <br>
Your email address is:
<?php echo $_POST["email"]; ?>
</body>
</html>Output

$_POST[“email”] helps us to get the data of form field whose name attribute is email.
GET vs POST
In PHP, the difference between GET and POST is how data is sent from the browser to the server: GET appends data in the URL, while POST sends data in the request body.
- $_GET is an array of variables passed via the URL parameters.
- $_POST is an array of variables passed via the HTTP POST method.
When to use GET?
Use the GET method when you want to retrieve or request data from the server, especially for non‑sensitive information that can be safely shown in the URL.
- Information is sent in the URL.
- Only small amounts of data can be sent.
- Because data is in the URL, the page can be bookmarked or shared.
- Safe for search queries, filters, navigation links.
- Never use GET for passwords or sensitive information.
When to use POST?
- Passwords, personal info, payment details (hidden from URL).
- Unlike GET, POST can handle big form submissions.
- Adding, editing, or deleting records.
- Uploading images, documents, or videos.
- Because POST data isn’t stored in the URL.
Create database connection object
$conn = new PDO($servername,$username, $password);In our example, we connect PHP with PostgreSQL server. The above statement creates connectivity object ‘$conn’ with three parameters as shown below:
- Server host name or IP address and Database name
- Database username
- Database password
SQL statement and its execution
$sql = "INSERT INTO student (name, gender) VALUES ('".$name."', '".$gender."')";The above statement creates SQL string to insert values in the table named ‘student’. In the above statement ‘->’ is used to execute SQL statement using $conn as connectivity object.
$conn -> exec($sql);Cookies and session in PHP
1. Cookies
A cookie is a small text file that the server sends on the user’s computer. It is used to identify user or its machine and track activities created on the user computer. When browser requests server page, cookies are sent along with the request. PHP can be used both to create and retrieve cookie values.
Eg. Cookies store visited page on browser to optimise search.
2. Session
This is used to store user information on server to track user activites. It helps web application to maintain user
information on all the pages. Eg. If you login to gmail account, the session help us to access youtube account also.
Disclaimer: We have provide you with the accurate handout of “Server Side Scripting PHP Class 12 Notes“. If you feel that there is any error or mistake, please contact me at anuraganand2017@gmail.com. The above study material present on our websites is for education purpose, not our copyrights.
All the above content and Screenshot are taken from Information Technology Class 12 Textbook and MSBSHSE (HSC) Support Material which is present in MSBSHSE (HSC) website, This Textbook and Support Material are legally copyright by Maharashtra State Bureau of Textbook Production and Curriculum Research, Pune. We are only providing a medium and helping the students to improve the performances in the examination.
Images and content shown above are the property of individual organisations and are used here for reference purposes only. To make it easy to understand, some of the content and images are generated by AI and cross-checked by the teachers. For more information, refer to the official website.
