E-Commerce and E-Governance is an important chapter in Class 12 Information Technology that explains how digital technologies are used in business and government services. These notes are prepared in simple language as per the latest Class 12 syllabus and are useful for exam preparation and revision.
E-Commerce and E-Governance Class 12 Notes
E-Commerce stands for Electronic Commerce. Commerce is nothing but the buying and selling of goods. Commerce is an important part of a business. One of the most popular activities on the Web is shopping. E-commerce became possible in 1991 when the Internet was opened to commercial use. Since that date thousands of businesses have taken up residence at websites.
Definition of E-Commerce
E-commerce can be broadly defined as the process of buying and selling goods or services using an electronic medium such as the Internet. E-commerce is also referred to as a paperless exchange of business information using EDI, email, electronic fund transfer, etc.
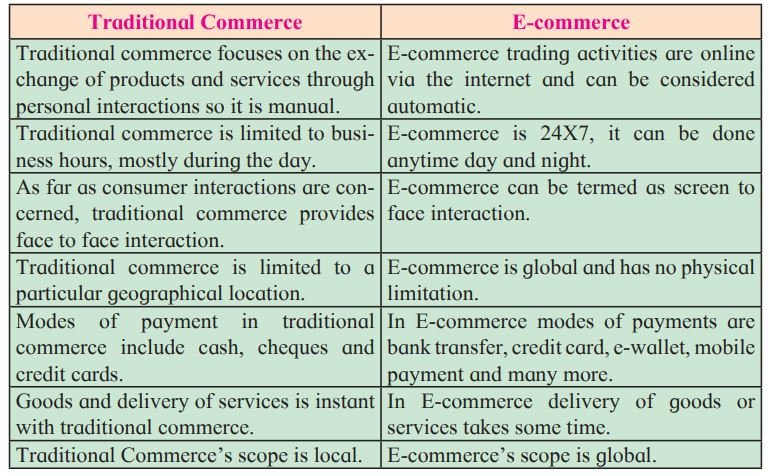
Difference between Traditional Commerce and E-Commerce
Advantages of E-Commerce
- Global scope: Now sellers and buyers can meet in the virtual world, without the barrier of place (geography).
- Electronic transaction: E-commerce reduces the paperwork and significantly lowers the transaction cost. E-commerce enables the use of credit cards, debit cards, and smart cards.
- Cost Saving: E-commerce applications provide users with more options to compare and select the cheaper and better option.
- Anytime shopping: A customer can shop 24×7. The website is functional at all times; it does not have working hours like a shop.
- No intermediaries: Electronic commerce also allows the customer and the business to be in touch directly, without any intermediaries.
- Public services: E-commerce helps the government to deliver public services such as healthcare, education, and social services at a reduced cost and in an improved manner.
Disadvantages of E-Commerce
- Setup Cost: The setup of the hardware and the software, the training cost of employees and maintenance are quite expensive.
- Physical presence: This lack of a personal touch can be a disadvantage for many types of services.
- Security: Credit card theft, identity theft, etc. remain big concerns with the customers.
- Goods Delivery: Some time after an order is placed, there can be problems with shipping, delivery, mix-ups, etc. This leaves the customers unhappy and dissatisfied.
Types of E-Commerce
The primary e-commerce types are as follows:
- Business-to-Consumer (B2C): In the B2C model, a business sells its products directly to a customer. Example: Amazon, Flipkart, etc.
- Business-to-Business (B2B): B2B refers to electronic transactions of goods and services between two businesses. For example, A manufacturer selling raw materials to another manufacturer. A wholesaler supplying products to a retailer.
- Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C): C2C refers to electronic transactions of goods and services between individual consumers. For example, selling used books, clothes, or gadgets on platforms like OLX, eBay, or Quikr. Renting property or vehicles directly to other consumers via online portals.
- Consumer-to-Business (C2B): C2B refers to electronic transactions where individual consumers offer products or services to businesses. For example, a freelancer offering web design services to a company through platforms like Upwork or Fiverr. Photographers selling stock images to companies via online marketplaces.
E-Commerce Trade Cycle
A trade cycle is the series of exchanges between a customer and a supplier during a commercial transaction. It typically has four phases:
- Pre-Sales: The first step is pre-sales, where the customer searches for a product on the website and compares it with other suppliers, checks quality and price, etc.
- Execution: In this step the customer places the order for the chosen product, and the supplier delivers the product.
- Settlement: In this step the customer receives a bill for the purchased product, and the customer pays after confirming product delivery.
- After-Sales: The low-cost maintenance during the warranty period. if the customer gives a service request handled by the supplier.
Modes of Payment
- Credit Cards : Credit cards are the most common way for customers to pay online.
- Mobile Payments : Mobile payments offer a quick solution for customers to purchase on e-commerce websites.
- Bank Transfers : Bank transfer is used when money is sent from one bank account to another.
- E-wallets : E-wallet is a type of electronic card which is used for transactions made online through a computer or a smartphone.
Forms of E-Commerce
Some common forms of E-Commerce are as follows.
- M-commerce (mobile commerce): as a form of e-commerce, m-commerce enables users to access online shopping platforms without needing to use a desktop computer. Some applications of M-Commerce are mobile banking, ticket booking, e-bill payment, online auctions, and stock market trading.
- Social Commerce: Social commerce is the use of networking websites such as Facebook, Instagram and Twitter as vehicles to promote and sell products and services.
E-Commerce Technology
Electronic commerce draws on technologies such as mobile commerce, electronic funds transfer, supply chain management, Internet marketing, online transaction processing, electronic data interchange (EDI), inventory management systems and automated data collection systems.
- Electronic Data Interchange (EDI): EDI is the electronic interchange of business information using a standardised format, a process which allows one company to send information to another company electronically rather than on paper.
E-Governance
E‑governance means the use of information technology (IT) in government processes and functions to achieve efficient, transparent, and citizen‑friendly governance. E-governance delivers SMART government. (S-Simple, M-Moral, A-Accessible, R-Responsive, T-Transparent Government)
Advantages of E-governance:
- Reduced corruption
- High transparency
- Increased convenience
- Direct participation of constituents
- Reduction in overall cost.
- Expanded reach of government
Types of E-Governance:
E-governance is of 4 types depending on the specific types of services.
- Government-to-Citizen (G2C): ‘Government-to-citizen’ refers to the government services which enable citizens to get access to a wide variety of public services. Most of the government services fall under G2C. Many services like licence renewals and paying tax are essential in G2C. It also focuses on geographic land barriers.
- Government-to-Business (G2B): The government-to-business is the exchange of services between government and business organisations. For example, online business registration, tax filing systems like the GST portal, etc.
- Government-to-Government (G2G): G2G refers to electronic interactions and information exchange between different government departments, ministries, or agencies. Sharing data between the Income Tax Department and the Passport Office for verification.
- Government-to-Employee (G2E): G2E refers to the digital relationship between the government and its employees. For example, online salary and pension portals for government employees and training and skill development platforms.
Security Measures in E-Commerce
A. Encryption
Encryption is widely used on the internet to protect user information being sent between a browser and a server. This includes passwords, payment information and other personal information that should be considered private. Encryption converts plain text (readable data) into cypher text (coded, unreadable data). Decryption converts cypher text back into plain text (original readable data).
Encryption is of two types.
- Symmetric (Shared Secret Encryption)
- Asymmetric (Public-Key Encryption)
B. Digital Signature
A digital signature is also known as an electronic signature. A digital signature guarantees the authenticity of an electronic document or message in digital communication and uses an encryption technique (asymmetric cryptography) to provide proof of original and unmodified documentation.
C. Digital Certificate
A digital certificate is an electronic “password” that allows a person or organisation to exchange data securely over the Internet using the public key infrastructure (PKI). A digital certificate is also known as a public key certificate or identity certificate.
Disclaimer: We have provide you with the accurate handout of “E-Commerce and E-Governance Class 12 Notes“. If you feel that there is any error or mistake, please contact me at anuraganand2017@gmail.com. The above study material present on our websites is for education purpose, not our copyrights.
All the above content and Screenshot are taken from Information Technology Class 12 Textbook and MSBSHSE (HSC) Support Material which is present in MSBSHSE (HSC) website, This Textbook and Support Material are legally copyright by Maharashtra State Bureau of Textbook Production and Curriculum Research, Pune. We are only providing a medium and helping the students to improve the performances in the examination.
Images and content shown above are the property of individual organisations and are used here for reference purposes only. To make it easy to understand, some of the content and images are generated by AI and cross-checked by the teachers. For more information, refer to the official website.
