The Rise of Nationalism in Europe is an important chapter 1 in Class 10 History that explains how the idea of nationalism developed and led to major political and social changes in Europe. Through topics like the French Revolution, the making of nation-states, and the role of culture and symbols, students understand how modern countries were formed.
The Rise of Nationalism in Europe Class 10 MCQ
1. Which of the following prepared the series of four prints in 1848 showing democratic and social republics?
a. Giuseppe Mazzini
b. Frédéric Sorrieu
c. Otto von Bismarck
d. Metternich
2. In Sorrieu’s first print, Liberty is shown as _________.
a. Male soldier with sword
b. Female figure with torch and charter
c. Angel holding a flag
d. Christ with saints
3. Which two countries lead the procession in the print?
a. France and Germany
b. United States and Switzerland
c. Italy and Poland
d. England and Ireland
4. Which of the following flags carried by the German people symbolized liberal hopes of unity in 1848?
a. Black, Red, Gold
b. Red, White, Blue
c. Green and White
d. Black and White
5. Why is Sorrieu’s vision called utopian?
a. It was a realistic plan for Europe.
b. It was too ideal to exist in reality.
c. It was a military strategy.
d. It was a religious prophecy.
6. After the French Revolution, sovereignty was transferred from:
a. The monarchy to the citizens
b. The Pope to the clergy
c. The nobles to the army
d. None of the above
7. What do you mean by the ideas of la patrie and le citoyen emphasize?
a. Religious unity
b. A united community with equal rights
c. Economic reforms
d. None of the above
8. Which of the following flags replaced the royal standard after the French Revolution?
a. Black-Red-Gold
b. Tricolour (French flag)
c. Union Jack
d. None of the above
9. What do you mean by the Civil Code of 1804 introduced by Napoleon called?
a. The Jacobin Code
b. The Napoleonic Code
c. The Revolutionary Code
d. None of the above
10. Which of the following is NOT a part of the Napoleonic Code?
a. Right to property
b. Privileges based on birth
c. Equality before law
d. None of the above
11. In the mid-eighteenth century, which of the following is not known as a nation-state?
a. Germany, Italy, Switzerland
b. France, England, Spain
c. Portugal, Russia, Britain
d. None of the above
12. Which of the following empires was described as a “patchwork of many different regions and peoples”?
a. Ottoman Empire
b. Habsburg Empire (Austria-Hungary)
c. Russian Empire
d. British Empire
13. Which language is spoken by the aristocracy in Bohemia?
a. Magyar
b. Polish
c. German
d. Italian
14. In revolutionary France, who had the right to vote?
a. All adult males
b. Property-owning men only
c. Women and men equally
d. Nobles only
15. What was the Zollverein (1834)?
a. A political union of German states
b. A customs union abolishing tariff barriers
c. A military alliance
d. A confederation of aristocrats
16. Who hosted the Congress of Vienna in 1815?
a. Napoleon Bonaparte
b. Duke Metternich (Austria)
c. Otto von Bismarck
d. Giuseppe Mazzini
17. What was the main aim of the Treaty of Vienna (1815)?
a. To restore monarchies and create a conservative order
b. To spread democracy in Europe
c. To unify Germany and Italy
d. To abolish feudalism
18. Who was known by Metternich as “the most dangerous enemy of our social order”?
a. Napoleon Bonaparte
b. Giuseppe Mazzini
c. Friedrich List
d. Andreas Rebmann
19. The July Revolution of 1830 in France led to __.
a. Restoration of the Bourbon monarchy
b. Installation of Louis Philippe as constitutional monarch
c. Establishment of a republic
d. Napoleon’s return to power
20. Which of the following countries got independence after the July Revolution?
a. Poland
b. Belgium
c. Greece
d. Hungary
21. When the Greek struggle for independence started.
a. 1821
b. 1830
c. 1848
d. 1815
22. How Greece was recognized as an independent nation.
a. Treaty of Vienna, 1815
b. Treaty of Constantinople, 1832
c. Treaty of Paris, 1848
d. Treaty of Frankfurt, 1871
23. Which of the following Polish composers introduced folk dances like the polonaise and mazurka to promote nationalism?
a. Chopin
b. Karol Kurpinski
c. Liszt
d. Wagner
24. Which of the following is a reason for the Silesian weavers’ revolt (1845)?
a. Heavy taxation
b. Low wages and exploitation by contractors
c. Political repression
d. Religious discrimination
25. Who rejected the crown offered by the Frankfurt Parliament?
a. Napoleon III
b. Friedrich Wilhelm IV, King of Prussia
c. Otto von Bismarck
d. Metternich
26. Who was the chief minister of Prussia and architect of German unification?
a. Metternich
b. Otto von Bismarck
c. Friedrich Wilhelm IV
d. William I
27. Which of the following social groups supported the monarchy and military in repressing the 1848 liberal initiative in Germany?
a. Peasants
b. Junkers (large landowners)
c. Industrialists
d. Clergy
28. During the mid-19th century, Italy was divided into how many states?
a. Five
b. Seven
c. Ten
d. Twelve
29. Who founded Young Italy and promoted a unitary Italian Republic?
a. Garibaldi
b. Mazzini
c. Cavour
d. Victor Emmanuel II
30. The Act of Union (1707) led to the formation of:
a. United Kingdom of Great Britain
b. United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland
c. British Commonwealth
d. Anglo-Scottish Confederation
31. What were the attributes of Marianne?
a. Red cap, tricolor, cockade
b. Crown of oak leaves
c. Sword and olive branch
d. Broken chains
32. Which female allegory represented Germany?
a. Marianne
b. Germania
c. Italia
d. Britannia
33. What does the broken chain symbolize?
a. Being freed
b. Strength
c. Readiness to fight
d. Beginning of a new era
34. Nationalist rivalry in the Balkans eventually led to:
a. The Crimean War
b. The First World War
c. The Napoleonic Wars
d. The Franco-Prussian War
35. Match the following and Choose the correct option:
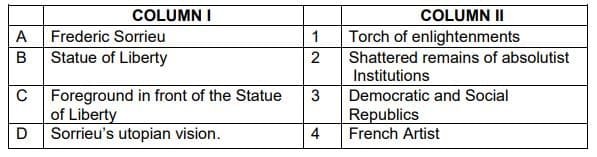
a. A-4, B-1, C-2, D-3
b. A-2, B-4, C-4, D-1
c. A-1, B-2, C-4, D-3
d. A-4, B-1, C-3, D-4
36. Napoleon in the given picture is depicted as a postman. What do each letter falling from his bag represent?

a. Number of wars he fought
b. Letters he posted to the monarchs
c. Territories lost by him
d. Areas conquered by him
37. Which of the following symbol does the “broken chains “stand for?
a. Freedom.
b. Strength
c. Willingness to make peace.
d. Heroism
38. When many countries of Europe came together to form the European Union, was chosen as its headquarters.
a. Brussels
b. Paris
c. London
d. Zurich
39. Identify the painting from the options given below.

a. Frankfurt Parliament
b. Reichstag
c. Duma
d. The House of Parliament
40. Which of the following does the symbol “crown of oak leaves “stand for?
a. Freedom
b. Shows readiness to fight.
c. Willingness to make peace.
d. Heroism.
41. Who among the following was the founder of ‘Young Europe’ underground secret society in Berne?
a. Giuseppe Garibaldi
b. Giuseppe Mazzini
c. Count Cavour
d. Otto von Bismark
42. Which of the following was the result of the Act of Union, 1707?
a. Unification of Germany
b. Unification of the kingdom of Great Britain
c. Unification of Italy
d. Unification of Vietnam
43. Identify the correct statement with regard to the ‘Zollverein’ from the following options:
a. It was a coalition of Prussian states formed to manage political alliances.
b. Its aim was to bind the Prussia politically into an association.
c. It was a Custom Union at the initiative of Prussia.
d. It helped to awaken and raise national sentiment in Europe.
44. Which of the following countries were involved in the Three Wars with Prussia and ended with victory and unification of Germany?
a. Austria, Poland and France
b. Austria, Denmark and France
c. Austria, Turkey and France
d. Austria, England and France
45. Identify the ideology under which people demanded freedom of markets in earlynineteenth-century Europe.
a. Romanticism
b. Liberalism
c. Socialism
d. Rationalism
46. Following image is the personification of Germany commonly associated with the Romantic Era and the Revolutions of 1848. Identify its name from among the following options.

a. Marianna
b. Philip Viet
c. Germania
d. La Italia
47. Identify the name of the Prussian King who was proclaimed German Emperor in a ceremony held at Versailles.
a. William I
b. William II
c. Henry VII
d. Louis IV
48. Which of the following option(s) is/are correct about Balkan nationalism?
- I. The Balkan region became part of the conflict because of the Ottoman Empire.
- II. The region comprised of ethnic groups included Greeks, Serbs, Montenegro, etc.
- III. British and ethnic nationalities struggled to establish their identity.
a. I & II
b. II & III
c. Only II
d. Only 1
49. Why did the weavers in Silesia revolt against contractors in 1845? Identify the appropriate reason from the following options.
a. Contractors did not pay their dues
b. Contractors appointed few on high posts
c. Contactors used government policies
d. Contractors gave them loans on high interests
50. Identify the major aspect that helped in the formation of a nation-state in Britain.
a. In 1688, the monarch of Britain fought war with English Parliament.
b. The Parliament through a bloodless revolution seized power from the monarchy.
c. The British nation was formed as a result of a war with Ireland and Wales.
d. The formation of a nation-state in Britain was the result of many revolts.
51. Which one of the following regions became a part of unified Italy in 1866?
a. Sardinia-Piedmont
b. Venetia
c. Sicily
d. Papal State
52. Arrange the following in chronological order and choose the correct option:
- I. The Treaty of Constantinople
- II. The defeat of Napoleon
- III. The granting of more autonomy to Hungarians by the Habsburg rulers
- IV. The Napoleonic Civil Code
a. III, I, II, IV
b. II, III, IV, I
c. I, IV, III, II
d. IV, II, I, III
53. From which of the following countries Giuseppe Garibaldi belonged to?
a. Austria
b. Italy
c. Greece
d. Spain
54. Two statements are given below. They are Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read both the statements and choose the correct option.
Assertion (A): The most serious source of nationalist tension in Europe after 1871 was Balkan.
Reason (R): A large part of the Balkan was under the control of Ottoman Empire.
Options:
a. Both, (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
b. Both, (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
c. (A) is true but (R) is false.
d. (A) is false but (R) is true.
55. Arrange the following events in chronological order and choose the correct option from the following:
I. Treaty of Constantinople
II. Defeat of Napoleon
III. Unification of Italy
IV. Unification of Germany
Options:
a. I, II, IV and III
b. II, III, I and IV
c. II, I, III and IV
d. IV, I, III and II
56. Choose the correct option from the following regarding nineteenth century ‘liberalism’:
a. Monarchy, social hierarchy and property must be maintained.
b. The abolition of state-imposed restrictions on the movement of goods and capital.
c. Criticised the glorification of reason and science.
d. Not tolerating dissent and imposing censorship.
57. Look at the picture given below and select the correct option from the following:

Which of the following aspects best signifies this image of ‘Germania’?
a. As a protector of Germany
b. As a protector of her child
c. As a protector of German Rhine
d. As a guardian of women’s rights
58. Match the following attributes of allegory of Germania with its significance and choose the correct option:
| Attributes | Significance |
|---|---|
| a. Broken Chains | I. Heroism |
| b. Breast-Plate with eagle | II. Readiness to fight |
| c. Crown of oak leaves | III. Strength |
| d. Sword | IV. Being free |
a. a-I, b-II, c-III, d-IV
b. a-IV, b-III, c-I, d-II
c. a-II, b-I, c-IV, d-III
d. a-III, b-IV, c-II, d-I
59. Which one of the following ideologies were the European Governments driven by after the defeat of Napoleon in 1815?
a. Socialism
b. Conservatism
c. Liberalism
d. Romanticism
Disclaimer: We have provide you with the accurate handout of “The Rise of Nationalism in Europe Class 10 MCQ“. If you feel that there is any error or mistake, please contact me at anuraganand2017@gmail.com. The above CBSE study material present on our websites is for education purpose, not our copyrights.
All the above content and Screenshot are taken from Social Science Code 087 Class 10 NCERT Textbook, CBSE Sample Paper, CBSE Old Sample Paper, CBSE Board Paper and CBSE Support Material which is present in CBSEACADEMIC website, NCERT website This Textbook and Support Material are legally copyright by Central Board of Secondary Education or NCERT. We are only providing a medium and helping the students to improve the performances in the examination.
Images and content shown above are the property of individual organisations and are used here for reference purposes only. To make it easy to understand, some of the content and images are generated by AI and cross-checked by the teachers. For more information, refer to the official CBSE textbooks available at cbseacademic.nic.in.
