These Advanced Web Designing Class 12 Notes are prepared according to the latest HSC / MSBSHSE syllabus, using simple language and clear examples. The notes help students understand website structure, styling, scripting, and responsive design, which are essential for board exams, practical exams, and real-world web development skills.
Advanced Web Designing Class 12 Notes
HTML stands for Hyper Text Markup Language. HTML is the language used to create web pages; HTML is the mother language of web pages. HTML5 is the latest version of HTML and is used for creating mobile-friendly websites. HTML5 is supported by major browsers like Chrome, Firefox, Edge, Safari and Opera.
Basic Code of HTML5
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>My First HTML5 Page</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello World!</h1>
<p>This is my first HTML5 webpage.</p>
</body>
</html>Output
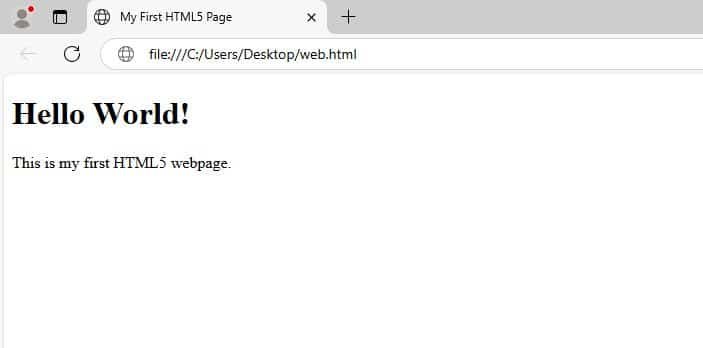
- <!DOCTYPE html> : This tells the browser that the version you are using is HTML 5.
- <html> …. </html> : It is root tag which defines the start and end of an HTML document, and everything inside these tags is a part of the webpage.
- <head> …. </head> : This contains information about the page, including <title>, CSS styles, scripts and meta tags. It helps the search engine optimisation (SEO).
- <title> …. </title> : This helps to show the text in the title bar. For example, if you write <title> Welcome </title,> the “Welcome” will be shown on the browser title bar.
- <body> …. </body> : It contains everything that is visible to the user in the browser, like text, images, links, forms, tables, etc.
Forms in HTML5
A form is basically used for collecting user input like name, address, choice, etc. There are different types of controls related to form, like text, radio, checkbox, submit button, reset button, textarea, etc. For example, when you sign up for Facebook and you fill sign up form online, that’s is known as a web form.
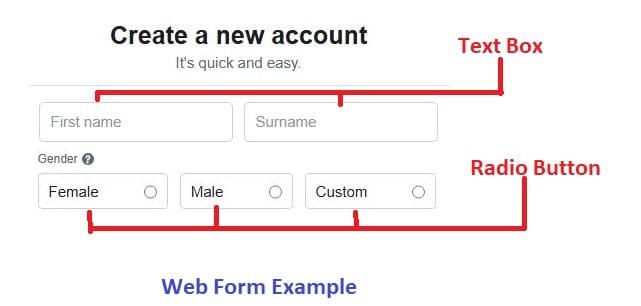
HTML 5 has special input boxes that automatically check if the user typed the right kind of information or not. This method is called validation. For example, if suppose you want to sign in gmail and the user type just hello insted of email id in the input box then the error will genrate automaticly due to invalid email and this is known as validation.
HTML 5 advanced elements
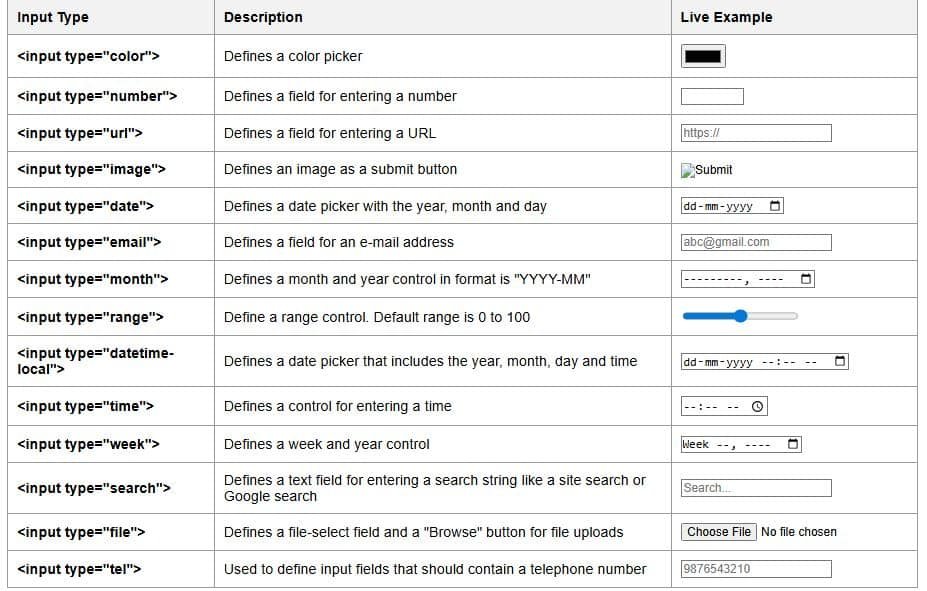
Input Restrictions
Input restrictions are rules you give to the form field in HTML. Input restrictions tell the browser how the user is allowed to type or enter data; this helps to improve user experience. It also helps to prevent invalid or incomplete submissions in the HTML form.

Attributes used in the form element
- Name: It gives a name to the form.
- Action: Tells where to send the form data.
- Method: Tells how to send the data. There are two methods to send data: GET and POST.
- GET method: The GET method is used to send data using a URL and values are visible in the address bar.
- POST Method: The POST method will pass the values in the address bar, this method is more secure for sensitive information.
Attributes used in the input element.
- ID: Gives a unique identifier to an input field. Used by JavaScript or CSS to target that specific element. Each ID must be unique in a page.
- CLASS: Used to apply CSS styles to one or more input fields. Unlike ID, the same class can be used for multiple elements.
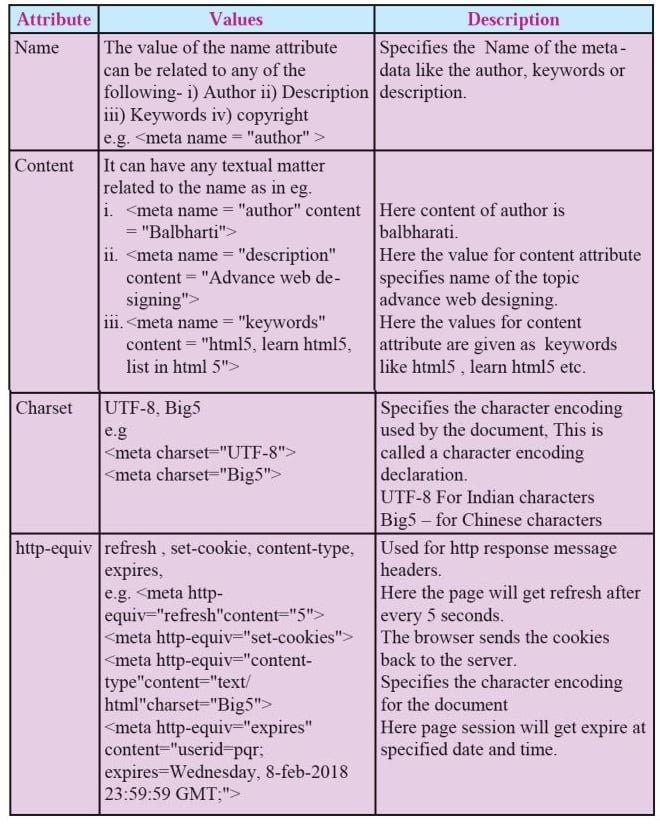
<meta> tag
The <meta> tag in HTML is used to provide metadata, which means information about the webpage, to the browser, search engines and other services.
- Metadata helps to show the data about the data.
- It helps the browser, search engines and social platforms learn about the web page.
- The <meta> tag is placed between the <head> and </head> tags.
Cascading Style Sheets in HTML 5
CSS stands for Cascading Style Sheets. It is a language used to give style and design to web pages. CSS describes how HTML elements are to be displayed on a web page. CSS is compatible with various devices, including desktop, mobile, and tablet. CSS saves a lot of work. It can control the layout of multiple web pages all at once.
CSS Syntax
A CSS rule set contains
- a selector and
- a declaration block.
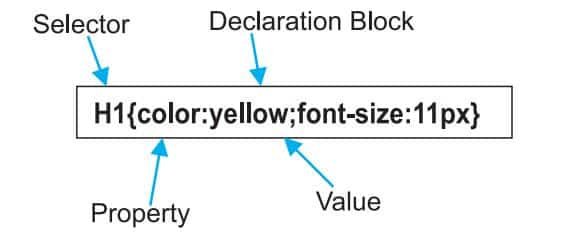
Selector: A selector is an HTML tag which points out the element you want to style.
Declaration block: The declaration block contains one or more declarations separated by semicolons and surrounded by curly braces. For the above example, there are two declarations:
- colour: yellow;
- font-size: 11 px;
Each declaration contains a property name and value, separated by a colon.
- Property: A property is a type of attribute of an HTML element. It could be colour, border, etc.
- Value: Values are assigned to CSS properties. In the above example, the value “yellow” is assigned to the colour property. Selector{Property1: value1; Property2: value2}
Types of CSS
There are three methods of implementing styling information to an HTML document.
- Inline CSS
- Embedded stylesheet or Internal CSS
- External CSS
Inline CSS
CSS written inside an HTML tag using the style attribute is known as inline CSS.
<p style="color:blue">Hello CSS</p> Internal CSS
CSS written inside the <style> tag inside the <head> section of the HTML file is known as internal CSS.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
h1{color: Red;}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1> Welcome to my page</h1>
</body>
</html>External CSS
If the CSS is written in a separate file and linked to the HTML using <link>, it is known as external CSS.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="style.css">
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is a heading</h1>
</body>
</html>File Name: Style.css
h1{color:navy;margin-left:20px}
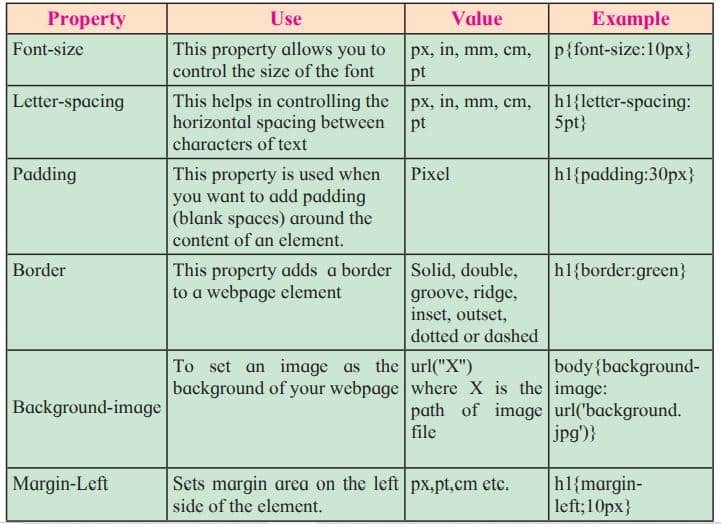
CSS Id Selector
The CSS ID selector is used to give style to a specific element. An ID is always unique within the page, so it is a unique element. It is written with the hash character (#), followed by the ID name.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
#para1{text-align: center; color: blue}
</style>
</head>
<body>
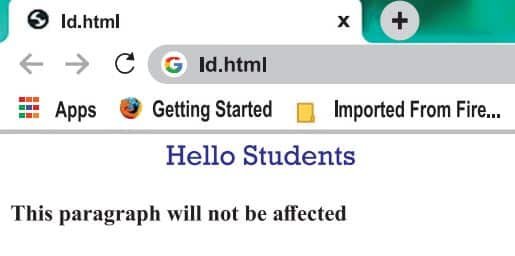
<p id="para1">Hello Students</p>
<p>This paragraph will not be affected.</p>
</body>
</html>Output
CSS Class Selector
Targets all HTML elements that have a specific class attribute. It is used with a period character ‘.’ (full stop symbol) followed by the class name. The Class selector is used when you want to change a group of elements within your HTML page.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
.intro{text-align:center;color:blue}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1 class="intro">This heading is blue and center-aligned.</h1>
</body>
</html>Output

Universal Selector
The universal selector is used as a wildcard character. It selects all the elements on the Webpages.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
* { color: green; font-size: 20px;}
</style>
</head>
<body>
This css style will be applied on Entire page.It does not check tag or plain text<br>
<h2>This css is applied to heading</h2>
<p id="para1">it is applied to first paragaraph</p>
<p>Also to second paragraph !</p>
</body>
</html>Output

Group Selector
The grouping selector is used to select all the elements with the same style definitions. It is used to minimize the code. Commas are used to separate each selector in grouping.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
h1,h2,p{text-align: center; color: blue}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello Heading 1</h1>
<h2>Hello Heading 2 (In smaller font)</h2>
<p>This is a paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>Output

Positioning in CSS
CSS helps to position the HTML elements. The position property is used to set position for an element. The element can be positioned using the top, bottom, left and right properties.
Syntax :
Selector { position: value; top: value; left: value: bottom: value; right: value}Where values in positions are fixed, absolute, relative and values of top, bottom, left, right are in pixels
There are four types of positioning in CSS
1. Static Positioning
This is a bydefault position for HTML elements. It is not affected by the top, bottom, left and right properties.
<p>This is static text (default).</p>2. Fixed Positioning
This property helps to put the text fixed on the browser. The FIXED property forces an element into a fixed position relative to the browser window. The fixed element will not move, even when the page is scrolled.
<p class="fixed">This text stays fixed!</p>
<style>
.fixed {
position: fixed;
top: 50px;
right: 10px;
color: blue;
}
</style>3. Relative Positioning
The relative positioning property is used to set the element relative to its normal position.
<p class="relative">This text is moved slightly.</p>
<style>
.relative {
position: relative;
top: 20px;
left: 30px;
color: green;
}
</style>4. Absolute Positioning
This property sets an element in a specific location and it is not affected by the flow of the page. This property positions the element at the specified coordinates relative to your screen top-left corner.
<div class="container">
<p class="absolute">This text is absolutely positioned.</p>
</div>
<style>
.container {
position: relative; /* important for absolute child */
height: 200px;
border: 1px solid black;
}
.absolute {
position: absolute;
top: 50px;
left: 50px;
color: red;
}
</style>Float Property
The CSS float property is used to position an element to the left or right of its container. The float property defines the flow of the content. The following are the types of floating properties:
- float : left : This keeps the element floating on the left side of the container.
- float : right : This keeps the element floating on the right side of the container.
- float : none : This is the default property, i.e., this shows the element as it is.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Float Example</title>
</head>
<style>
.float-left { float:left; fontsize:20px; background-color:gold}
.float-right { float: right; font-size:20px; background-color:gold}
</style>
<h2 class="float-left">Balbharati</h2>
<p>This text rearranges itself to flow around the element that is floated left.</p>
<h2 class="float-right">Balbharati </h2>
<p>This text rearranges itself to flow around the element that is floated right. </p>
</body>
</html>Output

Display property
The display property sets both the outer display type (how the element itself participates in layout) and the inner display type (how its children are laid out).
Syntax:
- Display: value;
Where values are:
- Inline: It is used to display an element as an inline element.
- Block: It is used to display an element as a block element. It starts on a new line and takes up the whole width of the browser window.
- Block-inline: This value is very similar to an inline element, but the difference is that you are able to set the width and height.
- None: The element is completely removed.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
p {
display: inline;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>welcome to balbharti</p>
<p>Javascript</p>
<p>HTML5</p>
<p>CSS</p>
</body>
</html>Output

Ordered list or numbered list
The <ol> tag defines an ordered list. An ordered list can be numerical or alphabetical.
Attributes of <ol> tag
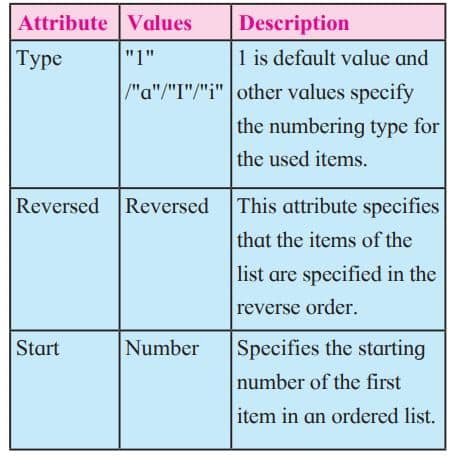
Unordered list or bulleted list
An unordered list created using the <ul> tag, and each list item starts with the <li> tag. The list items in unordered lists are marked with bullets (small black circles), by default.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Example of HTML Unordered List</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>HTML Unordered List</h3>
<ul>
<li>Basics of IT</li>
<li>HTML 5</li>
<li>PostgreSQL</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>Output

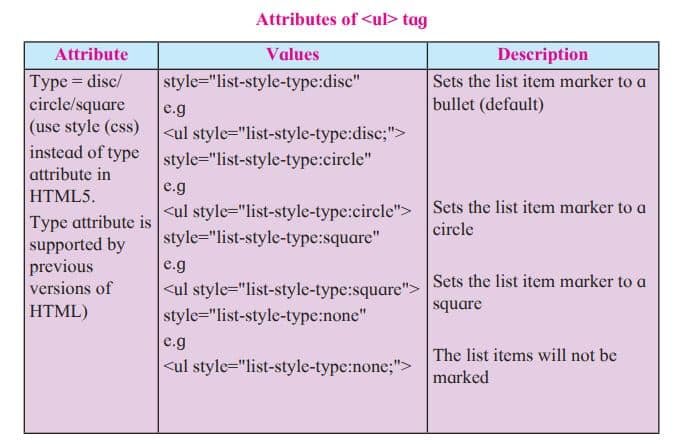
Note : HTML5 does not support bullets, circle and square value of type attribute instead you use CSS style.
Definition list
A definition list is used to group terms and their descriptions. It’s perfect for glossaries, FAQs, or any situation where you want to explain terms clearly.
A definition list uses three tags:
- <dl> → Definition List container
- <dt> → Definition Term (the word or phrase being defined)
- <dd> → Definition Description (the explanation of the term)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>definition List</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>Example of HTML definition List</h3>
<dl>
<dt><b>Web</b></dt>
<dd>The part of the Internet that contains websites and web pages</dd>
<dt><b>HTML</b></dt>
<dd>A markup language for creating web pages</dd>
<dt><b>CSS</b></dt>
<dd>A technology to make HTML look better</dd>
</dl>
</body>
</html>Output

Nested list
List within another list either order list or unordered list is called nested list.
Examples : Single level nested list
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html >
<head>
<title>Example of HTML nested list</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>HTML Nested List</h3>
<ol>
<li>Introduction to IT</li>
<li>Introduction to DBMS</li>
<ul style="list-style-type:circle">
<li>Definition of DBMS</li>
<li>applications of DBMS</li>
<li>Advantages of DBMS</li>
</ul>
<li>Postgresql</li>
</ol>
</body>
</html>Output

Inserting audio and video in HTML 5
HTML5 introduced the <audio> and <video> tags; these tags allow embedding audio and video directly without plugins like Flash.
Common Audio Formats:
- MP3: An audio format from MPEG (Moving/Motion Pictures Experts Group).
- AAC: Advanced Audio Coding, a standard format on iPhone, YouTube, etc.
- ogg: An open container and free audio format.
<Audio> Tag
The <audio> element enables you to embed(or add) audio files on Webpages. Declare the audio tag, and specify the source attribute with the Audio file location.
Syntax :
<audio src="sample.mp3" type="audio/mpeg" controls>
</audio>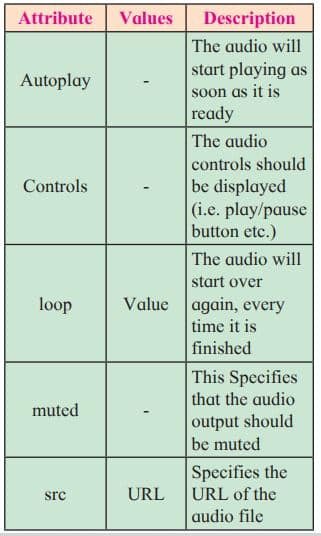
<Video> Tag
The HTML <video> tag is used to embed video into your web page, it has several video sources. There are three different formats that are commonly supported by web browsers – .mp4, .Ogg and .WebM.
Syntax :
<video src="URL" controls></video>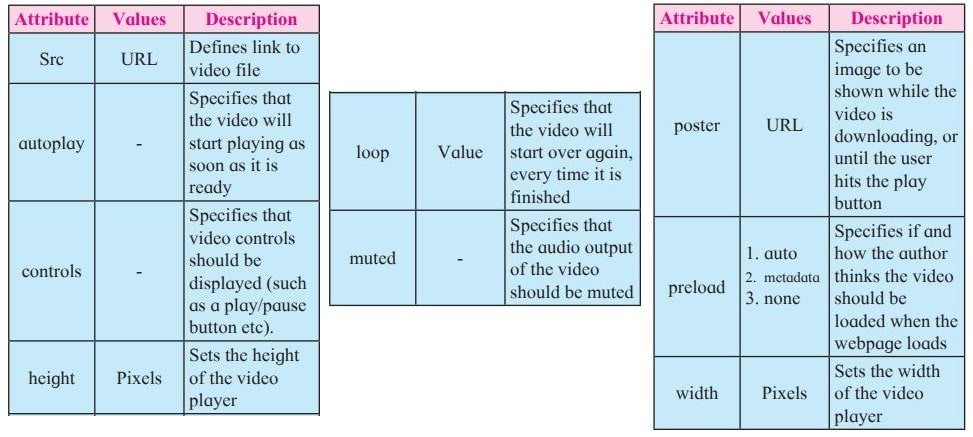
Image map in HTML 5
An image with multiple hyperlinks is called an image map. Image map is used to connect links to different regions on the webpage. An Image map is created by marking certain regions on an image clickable. These clickable regions are called as hotspots.
Image Maps are of two types; Client Side and Server Side. We will confine only to Client Side image map. The tags used to define client side image map are
- <Img> : It is used to insert an image on a web page. To create a client side image map usemap attribute of <img> is used with value which is preceded with a # symbol. The usemap attribute acts as a pointer which indicates that the image is a client side image map.
- <map> : It has only one attribute name. It specifies name of the image used for client side image map. The value of the name attribute is the value specified in usemap attribute of <img>.
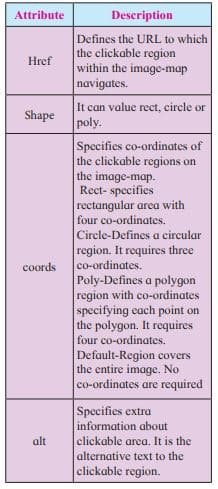
- <area> : It defines specific clickable regions. A given <map> element can contain multiple <area> element within it.<area> is singular tag and <map> is paired.
Attributes of <area>
Inline Frame in HTML 5
The <iframe> element creates an inline frame. Inline frames are often used in online advertising, where the contents of the <iframe> is an advertisement from an external party. HTML5 allows the incorporation to be seamless (no scrollbars, borders, margins etc).
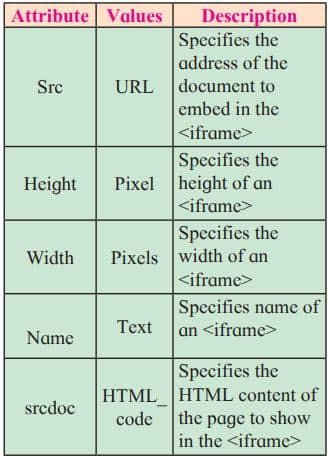
Attributes of <iframe>
What is web hosting?
Web hosting is the service of providing storage space. The website is made available on the Internet with the help of web hosting.
What is Web Host?
The companies that provides web hosting services are called web hosts. Web hosts own and manage web servers. These web servers offer uninterrupted Internet connectivity.
Types of Web hosting :
Types of web hosting are
- Shared hosting : It is cost effective. It gives domain name to your website.
- Free hosting : There are some hosting websites which provide you free hosting of the website for limited
period of time. - Dedicated hosting : These are paid hosting servers for large websites.
About Website
A website is a collection of interlinked web pages, and each page can show text, pictures, videos or forms.
Disclaimer: We have provide you with the accurate handout of “Advanced Web Designing Class 12 Notes“. If you feel that there is any error or mistake, please contact me at anuraganand2017@gmail.com. The above study material present on our websites is for education purpose, not our copyrights.
All the above content and Screenshot are taken from Information Technology Class 12 Textbook and MSBSHSE (HSC) Support Material which is present in MSBSHSE (HSC) website, This Textbook and Support Material are legally copyright by Maharashtra State Bureau of Textbook Production and Curriculum Research, Pune. We are only providing a medium and helping the students to improve the performances in the examination.
Images and content shown above are the property of individual organisations and are used here for reference purposes only. To make it easy to understand, some of the content and images are generated by AI and cross-checked by the teachers. For more information, refer to the official website.
