Artificial Intelligence (AI) Code 901A for Class 6 introduces students to the exciting world of smart machines. In this subject, learners understand how computers can think, learn, and make decisions like humans. The notes help students explore basic AI concepts such as machine learning, computer vision, natural language processing, and real-life AI applications. These Class 6 AI notes are designed in easy language so that students can understand the topics quickly and score well in exams.
Artificial Intelligence Code 901 Class 6 Notes
Session 1: What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
What is intelligence?
The intelligent person has an ability to learn, understand, and solve problems. For example, when you solve a puzzle, it means that you are intelligent. If you are finding a new way to play a game, it is also intelligence too. Intelligence is the power of the mind to learn and solve problems.
Can you name any intelligent person?
Albert Einstein, a famous scientist He is remembered for his great ideas about energy and the universe. He is an intelligent person, but it is not like that; Albert Einstein is not the only intelligent person. The person who can think clearly, remember things, and make a decision is intelligent. For example, you teachers, parents, students, and friends who solve the problems are intelligent.
Fill in the blanks.
Can you find out the 3 words related to human intelligence?
___h___nk
L___a___n
S___lv___ P___ob___e___s
Human Intelligence and Artificial Intelligence
Human Intelligence: The natural ability of people to think, learn, and solve problems is human intelligence. For example, a child learns to ride a bicycle. A teacher explaining a story, a friend finding a new way to play a game, etc. Humans can also feel the emotions, be creative, and imagine new things.
Artificial Intelligence (AI): Artificial intelligence means a machine or computer that can think and learn like humans. Artificial intelligence is not natural like our brain; it is created by people using technology. AI helps machines to solve problems, remember things, and make decisions. For example, a phone that understands your voice and answers your questions. A robot that plays chess or An app that shows you the fastest way home.
What is artificial intelligence?
Artificial intelligence means when the machines or computers are made to act like humans by learning, thinking, and solving problems. It refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines. The AI can help to predict the weather, clean a room, and charge a car using smart systems. play chess, or recognize a face or voice.
How does AI do these tasks?
AI uses data (information) to make decisions. For example, if you want to clean a room, then the AI machine sensors see where dirt is there. To play chess, the AI uses rules and strategies stored in its memory.
Join Marie and Argo in cyberspace as they learn more about artificial intelligence: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HdIppwUJ0f8.
Session 2: Automation and Artificial Intelligence
What is automation?
The word “automation” comes from “automatic” and “operation.” Automation is a process where machines or computers can do the task without human involvement. For example, a washing machine that washes clothes after you press the “Start” button. Robot vacuum cleaner, traffic lights, factory machine, etc.
Understanding the Difference Between Automation and AI
Automation helps to perform the tasks automatically based on the preset of rules and instructions given by the humans. Automation does not require human involvement once it is started. Automation is best for repetitive tasks like traffic lights, automatic email replies, washing machines, etc.
Artificial Intelligence: When the machines are designed to simulate human intelligence, they can learn, adapt, and make decisions. AI can learn from data and experiences. AI can self-correct and improve over time and handle complex, changing tasks, etc. For example, voice assistants like Alexa or Siri and self-driving cars, which make decisions on the road.
Comparison Table
| Automation | Artificial Intelligence |
| Fixed rules | Learning + decision‑making |
| Flexibility Low | Flexibility High (adapts to new data) |
| Task type: Repetitive | Task type: Complex, changing |
| Think like a human. No | Think like a human. Yes |
| Traffic lights | Self‑driving car |
Session 3: What are the applications of AI? Where is it used in everyday life?
Artificial intelligence (AI) has become deeply integrated into various aspects of everyday life, impacting everything from the way we communicate to how we work and play. Here are some common examples of AI in everyday life!
- YouTube video suggestions: The AI is used in YouTube, which helps find videos easier and improve recommendations, help creators, and even add new interactive features.
- Google Maps Navigation: Google Maps Navigation is an AI application that helps to find the fastest route. Google Maps uses traffic data, road conditions, and time to guide drivers. For example, it can warn about traffic jams or suggest shortcuts.
- Digital Assistants—Alexa, Siri, Google Assistant, etc.: The Digital Assistants are voice-controlled helpers that use AI to understand speech and give answers. For example, setting alarms, playing songs, or answering questions, etc.
- Self-Driving Cars (Driverless Cars): Self-driving cars can run on the road without human help; they use cameras and sensors for finding optical. It makes a decision like when to stop, turn, or change lanes.
- AI-assisted fitness app: The fitness app can track exercise, posture, and health data. They can also give personalized tips for workouts. For example, smartwatches count steps and monitor heart rate, etc.
- AI in Music: Now AI can compose songs, remix tracks, or suggest playlists. AI can learn the music style and follow the patterns. For example, Spotify recommending songs you might like.
- AI in Art: AI also can create paintings, drawings, or digital designs. For example, AI can generate portraits or abstract art.
UNIT-II: AI and Other Technologies—Domains of AI
Session 1: Domains in AI
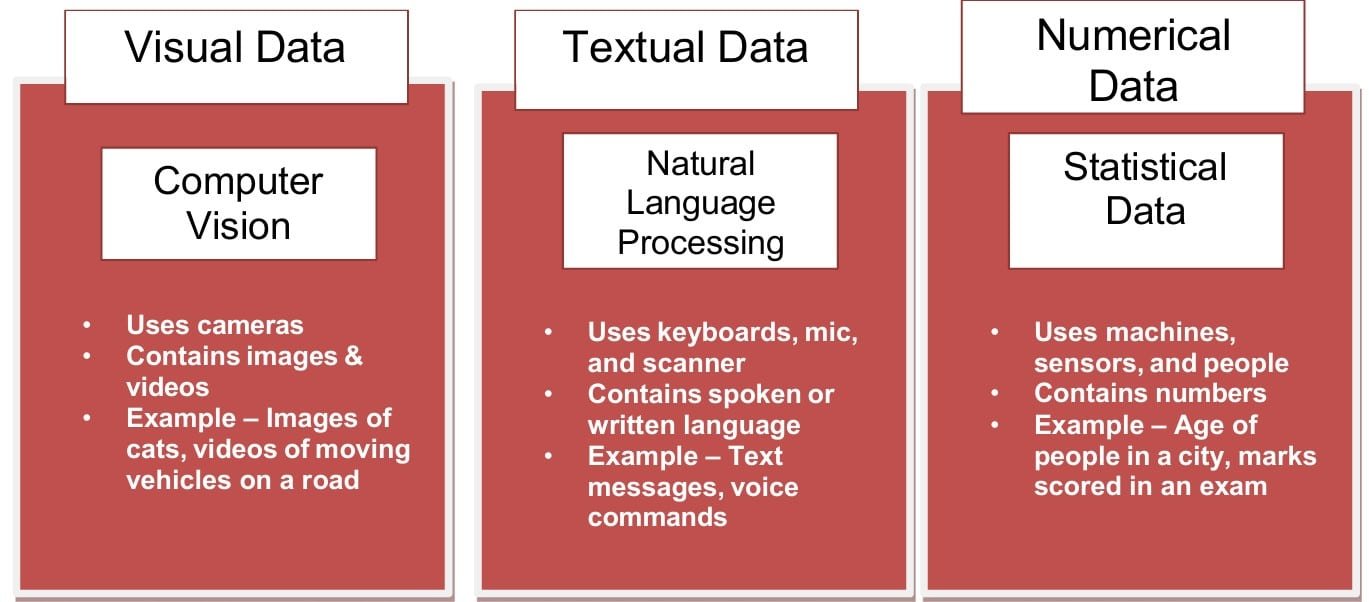
The domains of artificial intelligence (AI) refer to the various areas or fields where AI technologies and techniques are applied to solve specific problems or tasks. Nowadays, machines can see things, understand language, and make sense of numbers. Artificial intelligence operates in three main domains, each using specific data types:
- Computer Vision: Uses image and video data (pixels, matrices) to help machines “see” and interpret visual information like objects and faces.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Works with text data, converting it into numerical formats to enable machines to understand and process human language.
- Statistical Data: Utilizes structured numerical data and unstructured data to allow machines to learn from patterns and make predictions.
Think about your subject teachers; each teacher has a specific specialization. In a similar manner in AI, also, the domains are categorized into three types; each type has a specific type of feature.
Why are there different domains?
Depending on the type of data, we can divide AI into different domains.
How Does Computer Vision Work?
- Recognizing Objects and Patterns: Computer vision is trained on large sets of images. It can learn specific objects, shapes, or patterns like faces, traffic signs, or handwritten digits.
- Analyzing Visual Data: Computer vision can identify and analyze more correctly than humans. For example, an AI system can detect tiny details in medical scans that a doctor might miss.
- Speed and Accuracy: Computer vision has the capability to make decisions more accurately like humans. They do not get tired or distracted; that way, they can process thousands of images continuously.
Why is computer vision important?
- Computer vision can learn from thousands of images or from videos.
- They can identify the patterns in the images and videos, like if a dog image is there, then computer vision can understand how many eyes, ears, or noses there are.
- When the new image or video comes to computer vision, then it will compare the image and identified patterns to understand.
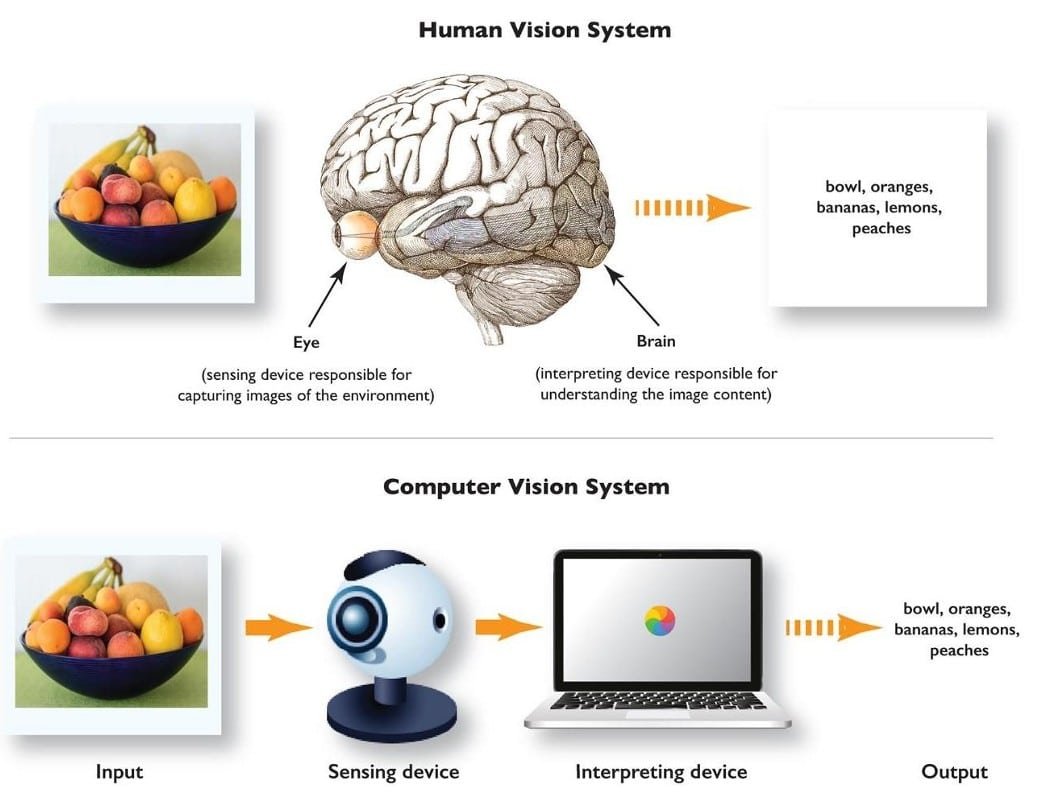
Human Vision v/s Computer Vision
What are the applications of computer vision in our daily lives?
- Facial Recognition: Facial recognition is used in many areas, like in mobile phones, smart cities, and smart homes for security. It helps to recognize the image.
- Face Filter: Face Filter uses a camera and algorithm to identify facial dynamics like eyes, nose, mouth, etc. It is a popular feature that is used in Instagram and Snapchat.
- Google’s Search by Image: The maximum amount of searching for data on Google’s search engine comes from textual data, but at the same time, it has an interesting feature of getting search results through an image. This uses computer vision as it compares different features of the input image to the database of images and gives us the search result while at the same time analyzing various features of the image.
Disclaimer: We have provide you with the accurate handout of “Artificial Intelligence Code 901 Class 6 Notes“. If you feel that there is any error or mistake, please contact me at anuraganand2017@gmail.com. The above CBSE study material present on our websites is for education purpose, not our copyrights.
All the above content and Screenshot are taken from Artificial Intelligence Code 901A Class 6 NCERT Textbook, CBSE Sample Paper, CBSE Old Sample Paper, CBSE Board Paper and CBSE Support Material which is present in CBSEACADEMIC website, NCERT website This Textbook and Support Material are legally copyright by Central Board of Secondary Education or NCERT. We are only providing a medium and helping the students to improve the performances in the examination.
Images and content shown above are the property of individual organisations and are used here for reference purposes only. To make it easy to understand, some of the content and images are generated by AI and cross-checked by the teachers. For more information, refer to the official CBSE textbooks available at cbseacademic.nic.in.
