Atoms and Molecules Class 9 Notes, Ancient Indian and Greek philosophers have always wondered about the unknown and unseen form of matter. The idea of divisibility of matter was considered long back in India, around 500 BC. An Indian philosopher Maharishi Kanad, postulated that if we go on dividing matter (padarth), we shall get smaller and smaller particles.
Atoms and Molecules Class 9 Notes
Laws of Chemical Combination
- Law of Conservation of Mass: Law of conservation of mass states that mass can neither be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. When the two solutions are mixed, the total mass before and after the reaction stays the same. That’s why we use a cork—to prevent any loss of gas or liquid.
- Law of Constant Proportions: This law state that a compound always contains the same elemtnes in the same fixed ration by mass. For example, water always has hydrogen and oxygen in a 1:8 ratio, no matter how or where it is made.
Dalton’s Atomic Theory
According to Dalton’s atomic theory, all matter, whether an element, a compound or a mixture is composed of small particles called atoms. The postulates of this theory may be stated as follows:
- All matter is made of very tiny particles called atoms, which participate in chemical reactions.
- Atoms are indivisible particles, which cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction.
- Atoms of a given element are identical in mass and chemical properties.
- Atoms of different elements have different masses and chemical properties.
- Atoms combine in the ratio of small whole numbers to form compounds.
- The relative number and kinds of atoms are constant in a given compound.
What is an Atom?
Atoms are very small, they are smaller than anything that we can imagine or compare with. More than millions of atoms when stacked would make a layer barely as thick as this sheet of paper.
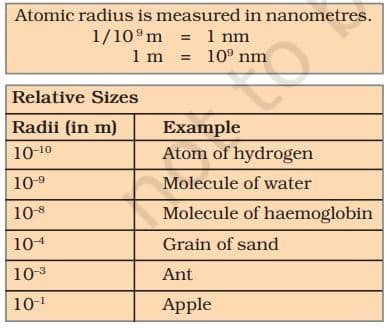
WHAT ARE THE MODERN DAY SYMBOLS OF ATOMS OF DIFFERENT ELEMENTS?
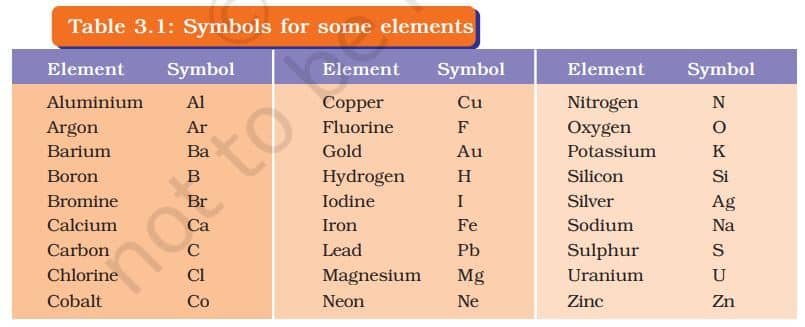
Dalton was the first scientist to use the symbols for elements in a very specific sense. Berzilius suggested that the symbols of elements be made from one or two letters of the name of the element.
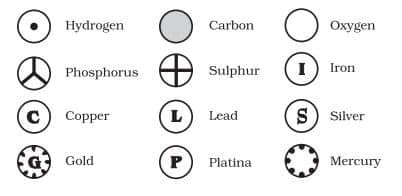
IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) is an international scientific organisation which approves names of elements, symbols and units. Many of the symbols are the first one or two letters of the element’s name in English. The first letter of a symbol is always written as a capital letter (uppercase) and the second letter as a small letter (lowercase).
For example
- hydrogen, H
- aluminium, Al and not AL
- cobalt, Co and not CO.
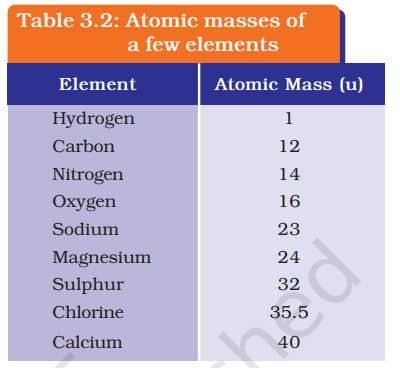
ATOMIC MASS
Dalton’s atomic theory introduced the idea of atomic mass, saying each element has a fixed mass. Since measuring a single atom is hard, scientists used relative atomic masses. Today, we use carbon-12 as the standard: one atomic mass unit (u) is 1/12th the mass of a carbon-12 atom. This helps compare the masses of all elements easily, just like using a watermelon slice to weigh other fruits.
HOW DO ATOMS EXIST?
Atoms of most elements are not able to exist independently. Atoms form molecules and ions. These molecules or ions aggregate in large numbers to form the matter that we can see, feel or touch.
What is a Molecule?
A molecule is in general a group of two or more atoms that are chemically bonded together, that is, tightly held together by attractive forces. A molecule can be defined as the smallest particle of an element or a compound that is capable of an independent existence and shows all the properties of that substance. Atoms of the same element or of different elements can join together to form molecules.
MOLECULES OF ELEMENTS
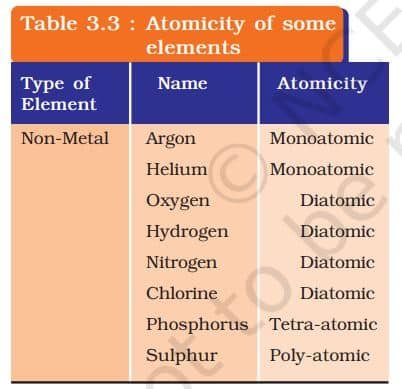
The molecules of an element are constituted by the same type of atoms. Molecules of many elements, such as argon (Ar), helium (He) etc. are made up of only one atom of that element. But this is not the case with most of the nonmetals. For example, a molecule of oxygen consists of two atoms of oxygen and hence it is known as a diatomic molecule, O₂. If 3 atoms of oxygen unite into a molecule, instead of the usual 2, we get ozone, O₃ . The number of atoms constituting a molecule is known as its atomicity

WHAT IS AN ION?
An ion is a charged particle formed when an atom or group of atoms gains or loses electrons. If it loses electrons, it becomes a positively charged ion called a cation (like Na⁺). If it gains electrons, it becomes a negatively charged ion called an anion (like Cl⁻). Compounds like sodium chloride (NaCl) are made of these ions. When a group of atoms carries a charge together, it’s called a polyatomic ion.
Writing Chemical Formulae
A chemical formula shows which elements are in a compound and how many atoms of each are present. To write a formula, we need to know the symbols and valency (combining power) of the elements.
Think of valency like arms: if an octopus (O) has 8 arms and each human (H) has 2, the octopus can hold 4 humans. So, the formula becomes OH₄.
The rules that you have to follow while writing a chemical formula are as follows:
- the valencies or charges on the ion must balance.
- when a compound consists of a metal and a non-metal, the name or symbol of the metal is written first. For example: calcium oxide (CaO), sodium chloride (NaCl), iron sulphide (FeS), copper oxide (CuO), etc., where oxygen, chlorine, sulphur are nonmetals and are written on the right, whereas calcium, sodium, iron and copper are metals, and are written on the left.
- in compounds formed with polyatomic ions, the number of ions present in the compound is indicated by enclosing the formula of ion in a bracket and writing the number of ions outside the bracket. For example, Mg (OH)₂ . In case the number of polyatomic ion is one, the bracket is not required. For example, NaOH.
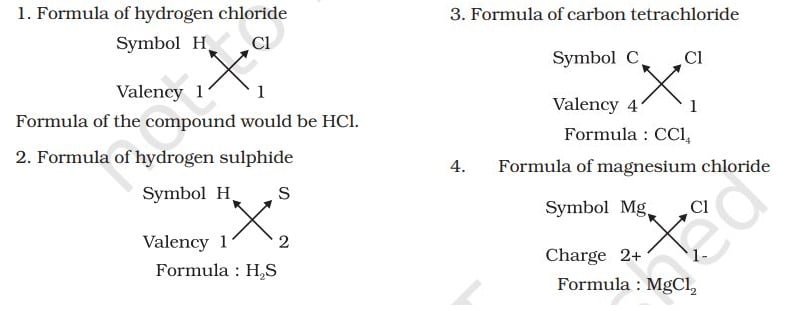
FORMULAE OF SIMPLE COMPOUNDS
The simplest compounds, which are made up of two different elements are called binary compounds. While writing the chemical formulae for compounds, we write the constituent elements and their valencies as shown below. Then we must crossover the valencies of the combining atoms.
Example,
Molecular Mass
Molecular mass is the total of atomic masses of all atoms in a molecule. It is measured in atomic mass units (u).

FORMULA UNIT MASS
The formula unit mass of a substance is a sum of the atomic masses of all atoms in a formula unit of a compound. Formula unit mass is calculated in the same manner as we calculate the molecular mass. The only difference is that we use the word formula unit for those substances whose constituent particles are ions. For example, sodium chloride as discussed above, has a formula unit NaCl. Its formula unit mass can be calculated as – 1 × 23 + 1 × 35.5 = 58.5 u
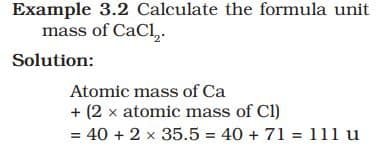
Disclaimer: We have taken an effort to provide you with the accurate handout of “Atoms and Molecules Class 9 Notes“. If you feel that there is any error or mistake, please contact me at anuraganand2017@gmail.com.
The above CBSE study material present on our websites is for education purpose, not our copyrights. All the above content and Screenshot are taken from Science Class 9 NCERT Textbook, CBSE Sample Paper, CBSE Old Sample Paper, CBSE Board Paper and CBSE Support Material which is present in CBSEACADEMIC website, NCERT websiteThis Textbook and Support Material are legally copyright by Central Board of Secondary Education. We are only providing a medium and helping the students to improve the performances in the examination.
Images and content shown above are the property of individual organizations and are used here for reference purposes only.
For more information, refer to the official CBSE textbooks available at cbseacademic.nic.in
