Teachers and Examiners (CBSESkillEduction) collaborated to create the Computer Organization Class 11 Notes. All the important Information are taken from the NCERT Textbook Information Technology (802) class 11.
Computer Organization Class 11 Notes
Session 1: Fundamentals of Computer
What is Computer System?
The word “computer” is derived from “compute,” which means to calculate. A computer is an electronic machine that is used for computing. A computer is an electronic device that can accept data, store it, and process it according to the instruction. Computers come in various forms depending on the size, like laptops, desktops, tables, smartphones, mainframes, and supercomputers. Computers work on binary language 0 and 1 using electronic signals. Computers consist of hardware and software.
- Hardware: Physical components of a computer like a mouse, keyboard, and monitor, etc.
- Software: The intangible instruction in the computer-like operating system and applications.
Characteristics of a computer system
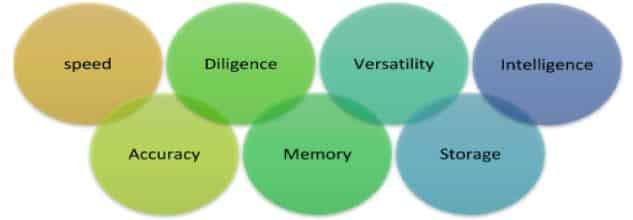
- Speed – The computer can process data and instructions at high speed. The speed of a computer can be measured in MIPS (million instructions per second). The number of signals transmitted in the transmission medium is known as baud.
- Versatility – Computers are capable of doing multiple tasks at once. For example, you can multitask while downloading movies, playing music, and creating word documents.
- Accuracy – The machine not only completes various tasks quickly, but also precisely and accurately. If any fault is found in the output, then the computer will generate an error instead of giving the wrong output. This process in computers is known as GIGO (Garbage In, Garbage Out).
- Diligence – A computer is free from tiredness. It can operate for several hours without making any mistakes. A computer will complete every calculation with the same accuracy even if millions of calculations need to be made.
- Memory – Computer memory is an important part of a computer. The main memory is volatile, meaning the data will be erased when the computer is turned off, like RAM. Second, secondary memory, which can store data permanently, like hard discs, pen drives, portable hard discs, etc.
- Storage – A computer is capable of holding a vast amount of data and information for later retrieval. A computer’s memory is unlimited and does not degrade over time like a human’s does.
- Intelligence – In early times, computers were programmed to carry out certain tasks. Now we have an intelligence-based computer that plays chess against the greatest players and drives a car without a human.
What are the components of a Computer?
Every computer follows an Input- Process- Output Cycle (IPO cycle). Computer can take input and based on the inputs computer can process and give output after processing.
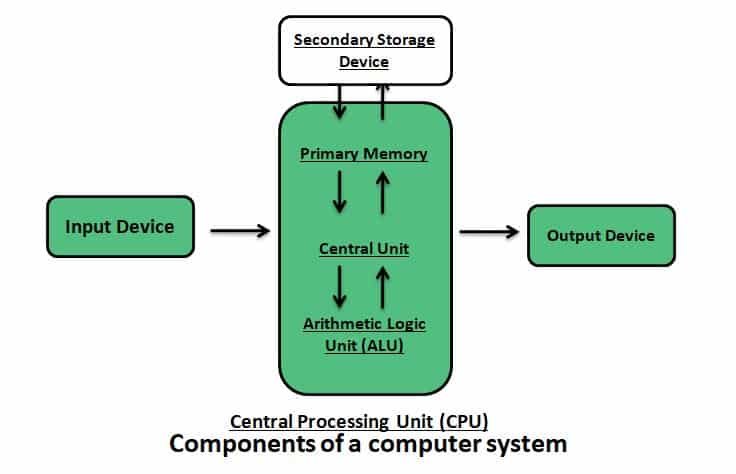
- Input Unit: The input unit takes the input from the input device like keyboard, mouse, microphone etc.,
- Process: The central processing unit does the processing of data
- Output Unit: The output unit produces the output.
- Memory Unit: The memory unit holds the data and instructions during the processing.
Block diagram of Computer System?
A block diagram of a computer helps to understand how the components of a computer are connected with each other.
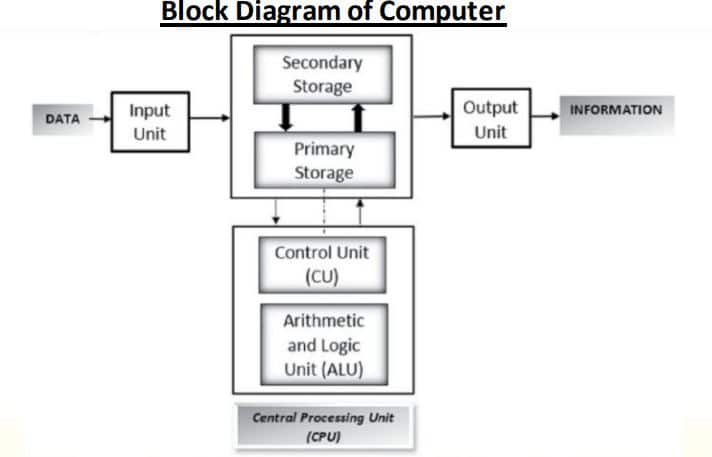
What is Control Unit?
The control unit is responsible for coordination between the different units of a computer. It controls the input, processing, and output operations. For example, it coordinates with the peripheral devices to accept the input or display the output. It is like a manager of all operations.
What is ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit)?
The actual processing of data is done by the arithmetic logic unit (ALU). The data is taken from the storage unit and subjected to arithmetic operations before being compared or otherwise processed. The processed data is then transferred back to the storage.
What is Storage device?
In computer system storage device is used to store informationa and instruction. There are basically two types of computer storage devices:
a. Primary Memory
Primary memory is known as main memory. Primary memory has internal storage, and the CPU can access it directly, meaning the CPU has direct access to information kept in primary memory. Primary memory is also known as volatile memory. The primary memory RAM has two types: DRAM and SRAM.
- DRAM – DRAM is used in main memory and is less expensive than SRAM. It is slower and consumes less power than SRAM, but it has a greater capacity for data storage.
- SRAM – SRAM is more expensive, consumes more power than DRAM, and is utilised in cache memory.
Difference between DRAM and SRAM
| DRAM | SRAM |
|---|---|
| Used in main memory | It is used in cache |
| Inexpensive | Expensive |
| Uses less power | Uses more power |
| Slower than SRAM | Faster than DRAM |
b. Secondary Storage
Secondary memory is also known as auxiliary or external memory, which can store the data for the long term. Secondary memory does not connect to the computer system internally. Some of the secondary memory are magnetic tapes, compact discs, and portable hard drives. These aren’t connected to the CPU directly.
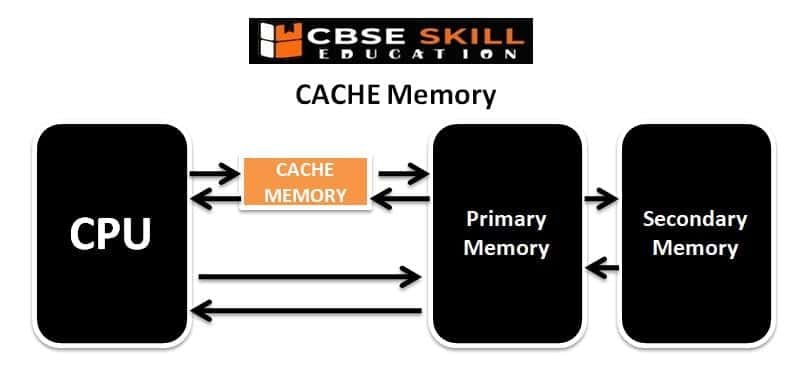
What is Cache Memory?
Cache memory works as a temporary storage space in a computer. Cache memory can hold data and instructions just like RAM and is located between the CPU and the main memory. The cache memory is fast memory and is used to improve the performance of the CPU. Cache memory is expensive but decreases the average time when every CPU accesses the information from main memory.
Session 2: Components of Computer
Inside the Computer
If we look at a personal computer, from outside, it looks like a box (sometimes called CPU) that contains CPU and hard disks, keyboard, mouse, monitor and speakers. The major functionality in a computer is done in the Processing Unit.
The computer has several components inside the CPU that are connected to each other to perform any task. Some of the components inside the CPU are the motherboard, processing unit, storage device, random access memory, hard disc, etc.
a. Motherboard: This is the main circuit board which holds together various components like CPU, memory, connectors for the hard drive and optical drives, expansion cards to control the video and audio, and connections in the form of various ports (such as USB ports). It provides a connection to every component of the computer.
b. Input Device: Input devices takes input from the user. The input may be in the form of text, image, sound, video
etc.
- Keyboard: this is a standard input device and takes data in the form of text.
- Mouse ; it is a pointing input device.
- Webcam: it takes data in the form of video/image
- Scanner : it generally stores data in the form of graphics
- Microphone : it is used for voice input/ audio input
- Handwriting input board: it is used for giving input from
c. Output Devices: devices that are used to give output to the user. Output may be in the form of visuals, text, audio, printout etc.
- Monitor/ VDU ( Visual Display Unit) : it is the standard output device and is similar to a television screen.
- Speaker : it is an output device that gives output in the form of an audio/ voice.
- Printer : it is also a very commonly known output device that gives output in the form of print out also called as hard copy.
- Plotter : it is a large printer like device that is used to take print of large maps, architectural designs.
- Projector : it is an output device that gives an enlarged view of the output on a large screen. It is generally used for giving a view of output to a large audience.
d. CPU: The CPU is a primary component of a computer; it is also known as the central and main processor of the computer. The CPU executes the user instructions and coordinates among all other units of the computer. Thus, it is primarily responsible for the performance of the machine. Central Processing Units can be classified on the basis of speed, technology, and their manufacturers, like dual-core, quad-core, octa-core, Intel, AMD, etc.
Note: Speed of processors is usually measured in megahertz (MHz) (millions of instructions per second) and gigahertz (GHz) (billions of instructions per second), which is indicative of its power.
e. Power Supply Unit: This component of the computer is the one which converts the alternate current power supply being received by homes or offices to the low voltage direct current required by the machine.
f. Random Access Memory (RAM): RAM plays an important role in computer systems. The operating system, instructions, and the software that manage the computer are loaded in the RAM. Nowadays, the computer has around 8 to 32 GB of RAM. More RAM can increase the performance of the computer.
g. Hard Disk(HD): A hard disc is a physical device that is used to store data. It is a non-volatile storage device, which means that the data can be stored for a long time. When you save the file on the computer, it is first stored on the hard disc, from where it is transferred to RAM. These days the capacity of a hard disc is expressed in terms of gigabytes and terabytes.
h. Pen drive/Flash drives: it is a small pen-like storage device of and can be accessed by directly inserting in the USB(Universal Serial Bus) Port. It is very popular these days because of its small size and easy accessibility.
Every bit of information in computer is stored in terms of Bits (Binary Digits) i.e. 0s and 1s
| 1 nibble = 4 bits |
| 1 byte = 8 bits |
| 1024 bytes = 1 Kilobyte (KB) 1024 KB = 1 Megabyte (MB) |
| 1024 MB = 1 Gigabyte (GB) |
| 1024 GB = 1 Terabyte (TB) |
| 1024 TB = 1 Petabyte (PB) |
| 1024 PB= 1 Exabyte(EB) |
| 1024 EB = 1 Zettabyte(ZB) |
| 1024 ZB = 1 Yottabyte (YB) |
i. Optical Storage devices: Digital video discs (DVD) and compact discs (CD) are two types of optical storage media. A DVD has a larger capacity than a CD. By placing the disc in a disc drive, you can access the data on a CD or DVD.
Session 3: Operating System
What is Operating System?
The operating system is a system software that helps to manage computer hardware and software resources. It acts as a channel between computer hardware and the users. Every computer required an operating system to communicate with computer hardware. for example, Windows, Linux, Unix, MS-DOS, Solaris, and Mac OS. The father of operating systems is regarded as Gary Arlen Kildall.
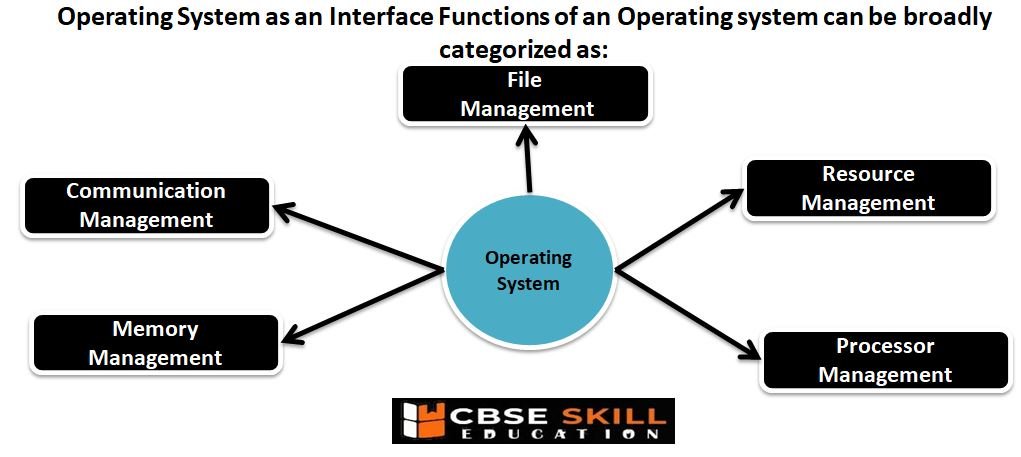
Operating System as an Interface Functions of an Operating system can be broadly categorized as:
− Communication Manager
− Resource Management
− Process Management
− File Management
− Memory Management
- Communication Manager – Manages the communication needs of the system, be it communicating with the peripheral devices or the internet, are addressed by the operating system.
- Resource Management – The working of a computer system is predominantly dependent on how its resources are being managed. The resources that we talk of here are -the memory of the computer, the CPU time, files, secondary storage, input/output devices etc.
- Process Management – A process is a program currently executing in the memory or waiting for the CPU. In a computer there are multiple processes in the system.
- Memory Management – For a process to be executed, it has to be loaded in the working memory that is the RAM (Random Access Memory).
- File Management – Operating system takes care of all the files and folders (directories) maintained on the computer disk. The basic tasks that a user needs to perform on files are creation, renaming, deletion, copying or moving of a file or folder.
Types of Operating system
Operating systems can be classified in different ways; depending on various parameters.
a. Single-tasking and Multi-tasking operating system
- Single Task Operating System – These operating systems only permit the execution of one programme at a time.
- Multi-tasking Operating System – An operating system that supports multiple tasks can run multiple programmes at once. Various processes share the processor time in this scenario.
b. Single user and Multi-user operating system
- Single user Operating System – Operating systems for one user only permit one user to use the system at a time. The desktop systems are within the category of standard single user systems.
- Multi-user Operating System – By keeping track of every user who has registered, multi-user operating systems enable several users to access the system simultaneously.
c. Real-Time Operating System
Real-time operating systems are defined as those that provide a constant response time. They are designed for applications that require speedy, minimal delays in the processing of data.
d. Batch Processing Systems
Similar jobs are grouped together and sent to the processor as a block for processing in a batch processing system. User involvement in such systems is low. One by one, the tasks are selected and carried out.
Session 4: Troubleshooting and utilities
Common Troubleshooting Steps
As soon as the system is turned on, the power supply recognises the CPU and peripherals. Most computers will beep when the system boots up if all peripheral devices have been correctly detected. Try the following if any connected device—such as a keyboard, mouse, printer, and monitor—fails to turn on:
- Check the Cables connection
- Use Operating System Help to identify the problem
- Check the Error Messages and act acodianly
Troubleshooting Hardware Problem
Monitor is not Showing any Display/ The Screen is Blank
- The System is in Sleep Mode
- The wire is connected properly
- Check the Laptop battery is charged or not
Keyboard Troubleshooting
- Check the cable connection
- Check for any damage
- Check the batteries if wireless keyboard
- Check weather key is not stuck
Mouse Troubleshooting
- Check the cable connection
- Check for any damage
- If coddles moue then check the battery
- Clean the mouse if dust is there
Troubleshooting Printer Problems
- Check weather Printer is Not Connected Properly or Not Switched On
- The Printer is Out Of Paper
- The Printer Paper Jam
- The Ink Cartridge of Printer is Empty
- Incorrect Printer Driver
Printer is Slow
By lowering the printing quality and using Fast Draft/Fast Printing, the printing speed can be increased. This is effective for routine printing. Make Fast Draft the default printer quality option instead of Normal.
Sound Troubleshooting
- Check Speaker Volume
- Check Audio Player Controls
- Check the Cables
- Check the Sound Using Headphones
An Application is Running Slow
Check for Available Updates
Check for updates if restarting the application does not increase performance. Look for the option to check for updates under the Help menu. If this choice is not available, You can look for application updates online.
An Application is Frozen
An application might freeze occasionally. You won’t be able to click any application buttons or close the window when this occurs. You might try the following troubleshooting techniques –
Utilities
Utilities are the special programs that help computer systems to work more smoothly, efficiently and effectively. Utility software programs help in :
– improving the performance of computer
– provide security from virus,
– manage disk space
– free disk space on hard Disk – provide backup etc.
Check Minimum Free Disk Space Required
On your system, there should be between 200 and 500 MB of free hard drive space. The lack of available free space inhibits the computer’s operation. Open the Windows Explorer application and select My Computer to see the available disc space. This will display the various hard disc partitions, including C and D.
Delete Unused Files and Programs
Delete unnecessary files and programmes on a regular basis. Your disk’s free space will rise as a result, improving computer performance. Images and movies occupy a large amount of storage. You can transfer these to an external drive.
Empty Your Recycle Bin
This can be done by right-clicking on the Recycle Bin icon (usually on the desktop), and then selecting Empty Recycle Bin.
Remove Temporary files
It is important to periodically remove the temporary files and the Internet browsing history. This too will increase the free space on your disk.
Disk Defragmentation
The data in our files is always changing. As a result, the memory file becomes incomplete or has gaps in it (hard disk). As a result, the file uses up more space on the computer, which could slow it down. To regain this space, you must use a disc defragmentation application. The next steps can help you do that.
- Open the Windows Explorer Application and click on My Computer.
- Highlight the C drive and right click to get a pop-up menu.
- Select the Properties option from this popup Menu.
- The dialog box showing the properties of the local disk (C:)
Troubleshooting Networking Problems
Points to Remember:
- Computer is an electronic device that takes input from the user, processes it and displays output.
- The on and off signals denote 1 and 0 respectively. The binary language, also called machine language,
- Commands given in high level languages need to be converted into binary language with the help of translators.
- Speed, accuracy, memory, diligence, versatility are some of the features of computer.
- Hardware are the physical components of a computer like motherboard, memory devices, monitor, keyboard etc.
- Software is the set of programs or instructions.
- It is sometimes difficult to judge if the problem is hardware-related or software related. Identify the part of the computer system that is not functioning properly.
- Before handing over your machine to an engineer, take a backup of important files to another source, like a pen drive or an external hard disk. This would ensure a copy of your data is available, in case something unforeseen happens while your computer is being repaired.
- Most systems produce a beep when a system boots successfully (i.e. all peripheral devices have been successfully detected). If any connected device does not switch on, try the common troubleshooting tips: close running programs that are not being currently used; check the cables; repeat to see if the problem recurs; use help; record error messages and restart the computer.
- If the monitor is not showing any display or the screen is blank: the system could be in sleep mode; check all the connections; the laptop’s battery may be low. If the keyboard is not responding: check connections; check for any damage; try changing batteries in a wireless keyboard; the keys may be stuck, replacing the keyboard.
- In case the mouse is not working: check connections; check for any damage and replace the mouse if required; restart the cordless mouse; clean the mouse.
- The printer may not be responding because: it may not be connected properly or not switched on; the printer could be out of paper; there could be a paper caught in the printer; printer’s ink cartridge could be empty; an incorrect printer driver may be configured.
- The printer and computer may not be communicating properly when a wireless connection is being used to connect a PC/ laptop to a printer. The IP address configured on your computer should match the Dynamic IP address allocated to the printer.
- When the print jobs are being sent to the wrong printer: change the default printer or choose an alternate printer for the current print job.
- To improve the printing speed, reduce the printing quality by using Fast Draft/ Fast Pri nting.
- When there is no sound from the speakers: check speaker volume; check audio player controls; check the cables; check the sound using headphones.
- When an application is running slow, check for available updates.
- Sometimes an application may freeze. Forcefully end the application or restart the computer.
- When all programs on the computer run slowly, check for viruses or try freeing space on the hard disk.
Employability Skills Class 11 Notes
- Unit 1 : Communication Skills Class 11 Notes
- Unit 2 : Self-Management Skills Class 11 Notes
- Unit 3 : Information and Communication Technology Skills Class 11 Notes
- Unit 4 : Entrepreneurial Skills Class 11 Notes
- Unit 5 : Green Skills Class 11 Notes
Employability Skills Class 11 MCQ
- Unit 1 : Communication Skills Class 11 MCQ
- Unit 2 : Self-Management Skills Class 11 MCQ
- Unit 3 : Information and Communication Technology Skills Class 11 MCQ
- Unit 4 : Entrepreneurial Skills Class 11 MCQ
- Unit 5 : Green Skills Class 11 MCQ
Employability Skills Class 11 Questions and Answers
- Unit 1 : Communication Skills Class 11 Questions and Answers
- Unit 2 : Self-Management Skills – III
- Unit 3 : Information and Communication Technology Skills Class 11 Questions and Answers
- Unit 4 : Entrepreneurial Skills Class 11 Questions and Answers
- Unit 5 : Green Skills Class 11 Questions and Answers
Information Technology Class 11 Notes
- Unit -1 : Computer Organization Class 11 Notes
- Unit -2 : Networking And Internet Class 11 Notes
- Unit-3 : Office Automation Tools Class 11 Notes
- Unit-4: RDBMS Class 11 Notes
- Unit-5: Fundamentals of Java Class 11 Notes
Information Technology Class 11 MCQ
- Unit -1 : Computer Organization Class 11 MCQ
- Unit -2 : Networking And Internet Class 11 MCQ
- Unit-3 : Office Automation Tools Class 11 MCQ
- Unit-4: RDBMS Class 11 MCQ
- Unit-5: Fundamentals of Java Class 11 MCQ
