Database Concepts using LibreOffice Base Class 12 Notes is an important topic for Class 12 HSC students that explains how data is stored, managed, and retrieved efficiently using database software. In this chapter, students learn basic database terminology, components of LibreOffice Base, tables, queries, forms, and reports.
Database Concepts using LibreOffice Base Class 12 Notes
DBMS concepts
What is data?
Data are raw facts, figures, and details about people, places, things, or events. Data may be in any form. It may be written, oral, computerised or non-computerised.
What is infromation?
Information is the required result obtained from processing of the data. Information is the output generated through processing of raw data. Information is important because it forms the foundation for decision-making.
What is database?
A database is a collection of related data items stored in an organised manner. A database consists of different objects like tables, queries, forms and reports.
- A table is a collection of related data.
- A query is used to retrieve information from a database.
- The form is used to collect the information from the user.
- The report is used to represent the data in printed form.
Database Management System Software (DBMS)
A database management system is a software which helps to manage data in a database. It acts as a bridge between raw data and meaningful information, allowing users and applications to access, update, and secure data in a structured way
Introduction to Base
Base is a Relational Database Management Software(RDBMS). A DBMS that is based on relational data model is called as RDBMS. Relational data model is one of the most popular data model because it is very simple to understand and to manipulate. Base is collection of related data objects known as Tables, Forms, Queries and Reports.
Start -> All programs -> Libreoffice -> Libreoffice Base.

Screen of Base consist of following parts
- A) Title Bar: It is the topmost bar present on the screen of Base. It displays icon of the application, name of the file and name of the application.
- B) Menu Bar: It is present below Title bar. It displays names of different menus as File, Edit, View, Insert, Tools, Windows, Help etc.
- C) Standard Tool Bar: Standard tool bar consist of different icons which are used for standard operations.
- D) Working Area: Rest of the part below standard tool bar is called as working area. It is divided into two panes- Left pane and right pane. Left pane displays name of database objects like tables, queries, forms and reports. Right pane displays activities related to that particular object.
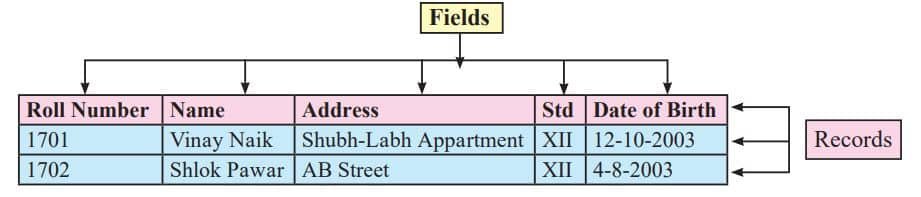
Table
Table is a basic unit for storing data in database.Tables are organised in the form of columns and rows. Before creating a table user should first decide the entity. Entity is any real world object about which data is to be stored. Each entity has collection of attributes associated with it.
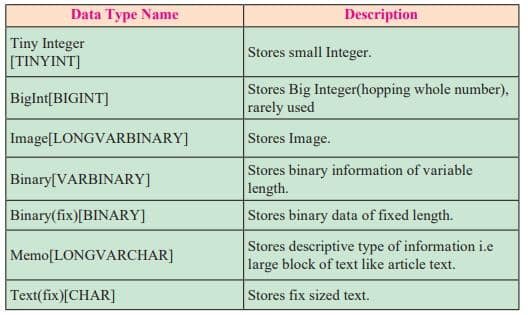
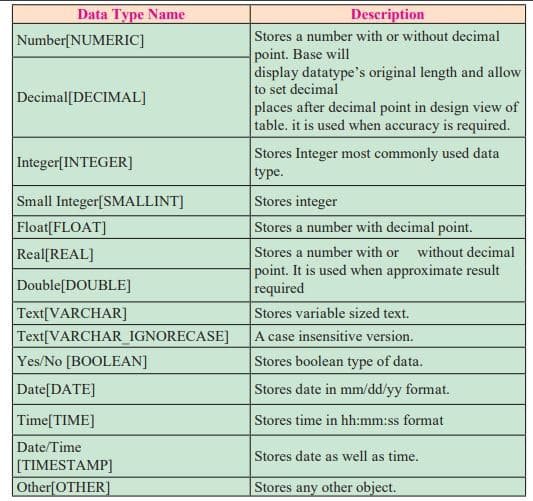
Data types in Base
Data types available in Base can be divided into three categories as alphanumeric, numeric, calender (date and time) and binary type.
Creating a table
- Step 1: Open database → click Tables icon (left pane).
- Step 2: Click Create Table in Design View (right pane).
- Step 3: Type Field Name.
- Step 4: Select Field Type (e.g., Text, Number).
- Step 5: Type Description of the field.
- Step 6: In Field Properties, set Entry Required = Yes.
- Step 7: Set Default Value / Decimal Places (for numeric fields).
- Step 8: Right‑click field → choose Primary Key.
- Step 9: Click Save icon → give table name → click OK.
Inserting records in the table
- Step 1: Open the database → click Tables icon (left pane).
- Step 2: In the right pane, double‑click the table name where data is to be inserted.
- Step 3: A window appears → type data under each field → complete one record → add more records as needed.
- Step 4: Click Edit Data icon to turn off edit mode → a window appears.
- Step 5: Click Yes → then click Close button.
Editing a record in the table
- Step 1: Double‑click on the required table.
- Step 2: Click on the record you want to edit.
- Step 3: Make the necessary changes.
- Step 4: Click on Edit Data icon to turn off edit mode → click Yes → then click Close.
Deleting a record from the table
- Step 1: Double‑click on the table → click on the record to be deleted.
- Step 2: Go to Edit menu → select Delete Record option.
- Step 3: Click on Yes button → record is deleted permanently.
Query Creation
A Query is a question asked within the database environment. Query displays subset of data contained in various tables of database Query is used to retrieve records from the table.
Steps to create query by using wizaid
- Step 1: Open database → click Queries (left pane).
- Step 2: Click Use Wizard to Create Query (right pane).
- Step 3: Select Table name → move fields from Available Fields to Fields in Query → click Next.
- Step 4: Choose a field for sorting → select Ascending/Descending → click Next.
- Step 5: Set search conditions → select field, condition, value → click Next.
- Step 6: (Optional) Type aliases to replace field names → click Next.
- Step 7: Type a name for the query → click Finish.
Steps to create query in design view
- Step 1: Open the database → click on Queries (left pane).
- Step 2: From the right pane, click Create Query in Design View.
- Step 3: A window appears → select the Table(s) you want to use → click Add → then Close.
- Step 4: In the design grid, select the fields you want to include in the query.
- Step 5: To sort records, choose Ascending/Descending under the Sort row.
- Step 6: To filter, type the criteria (e.g., Marks > 80) under the Criteria row.
- Step 7: Save the query → type a name → click OK.
- Step 8: Run the query to view the results.
Form Creation
Form is an object which allows entering the data and editing or deleting existing data in the table. It consists of format, style and widgets like radio button, list boxes. Steps to create a form are as follows :
- Step 1: Open database → click Forms (left pane).
- Step 2: Click Use Wizard to Create Form (right pane).
- Step 3: Select Table name → move fields from Available Fields to Fields in Form → click Next.
- Step 4: Click Next again.
- Step 5: Choose an arrangement for the form (e.g., Columnar, Labels Left) → click Next.
- Step 6: Click Next again.
- Step 7: Select a style for the form → click Next.
- Step 8: Type a name for the form → click Finish.
- Step 9: To add a record → click New Record icon (bottom toolbar) → fill details → click Save Record → click Close to exit.
Report Generation
The presentation of information in an organised and readable format as per the user’s requirement is known as report.
- Open a database, from left pane click on ‘Reports’ objects
- From right pane click on ‘Use Wizard to Create Report’
- Select name of ‘Table’ and shift fields from ‘Available fields’ list to ‘Fields in Report’ list by clicking on arrow button, click on ‘Next’ button
- Labels for the fields can be changed with new labels to display in report and click on ‘Next’ button
- If you want to see the records group-wise, (Ex-citywise) add a grouping level click on a field, click on arrow button and click on ‘Next’ button
- Select a field to sort the data, click on ‘Next’ button
- Choose Layout and Orientation, click on ‘Next’ button
- Type ‘Title for the Report’, click on ‘Finish’ button
- Report will be displayed in read-only mode in the form of ‘LibreOffice Writer’ file. Click on ‘Close’ button to
close the report window.
Introduction to Data Model
Data model defines how data is connected to each other and how they are processed and stored inside the system. There are many types of data models such as relational data model, network data model, hierarchical data model, object-oriented data model, entity-relationship data model etc.
Relational Data Model
The most commonly used data model is Relational Data Model. A relational database refers to a database that stores data in a structured format, using rows and columns. It is “relational” because the values within each table are related to each other. Tables may also be related to other tables. In relational model, tables are called relations that store data for different columns.
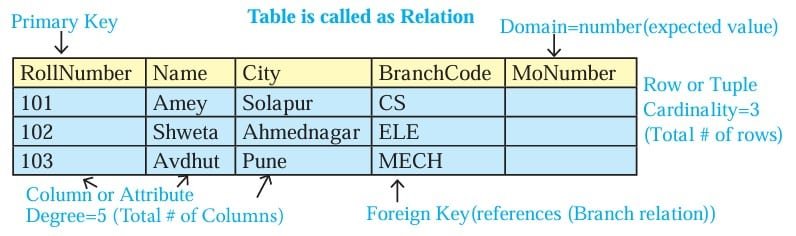
- Attribute: Characteristic or parameters for which data are to be stored in a relation.
- Tuple: Each row of data in a relation (table) is called a tuple.
- Domain: A data type is used to specify domain for an attribute.
- Degree: The number of attributes in a relation is called the Degree of the relation.
- Cardinality: The number of tuples in a relation is called the Cardinality of the relation.
| Term | Meaning (Simple) | Explanation | Example of Student Table |
|---|---|---|---|
| Attribute | Column in a table | A heading/ Field | Roll_Number, Name, Age |
| Tuple | Row in a table | A single record | (101, “Anita”, 15) |
| Domain | Allowed values for an attribute | Value range/ data type | Roll_Number → integers, Name → text |
| Degree | Number of columns | Count of attributes | If table has 3 columns → Degree = 3 |
| Cardinality | Number of rows | Count of records | If table has 50 students → Cardinality = 50 |
Keys in a Relational Database
- Candidate Key : A relation can have one or more attributes that takes unique values. Any of these attributes can be used to uniquely identify the tuples in the relation. Such attributes are called candidate keys as each of them are candidates for the primary key.
- Primary Key : Out of one or more candidate keys, the attribute used to uniquely identify the tuples in a
relation is called the primary key of that relation. - Composite Primary Key : If no single attribute in a relation is able to uniquely distinguish the tuples,
then more than one attribute are taken together as primary key. Such primary key consisting of more than one attribute is called Composite Primary key. - Foreign Key : A foreign key is used to represent the relationship between two relations. A foreign key is an attribute whose value is derived from the primary key of another relation.
There are 3 types of relationships in relational database design. They are as follows
- One-to-One
- One-to-many
- Many-to-Many
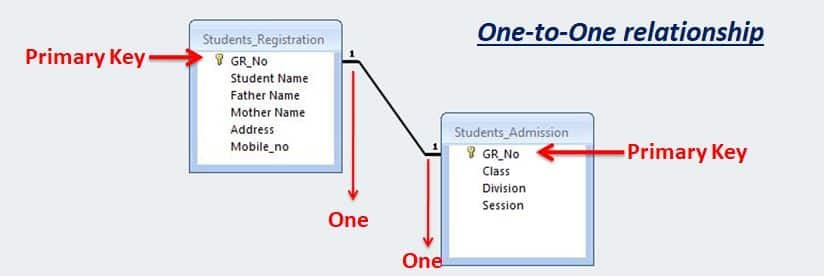
One-to-One relationship
In a One-to-One relationship, the master table and transaction table both have one record.
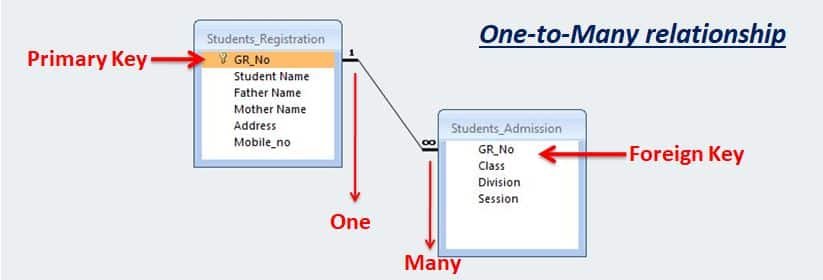
One-to-Many relationship
In a One-to-Many relationship, the master table having one record and transaction table having multiple records. This is a very common type of relationship between the tables in the database.
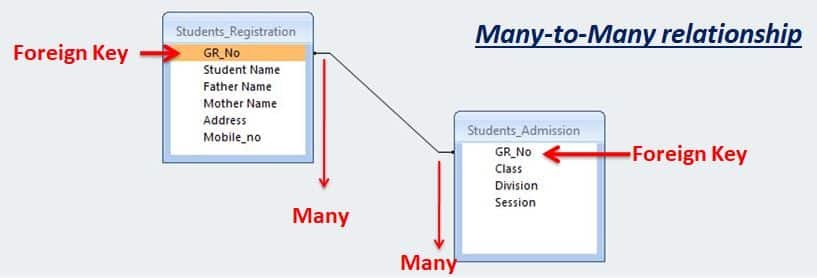
Many-to-Many relationship
In a One-to-Many relationship, the master table has multiple records and the transaction table has multiple records.
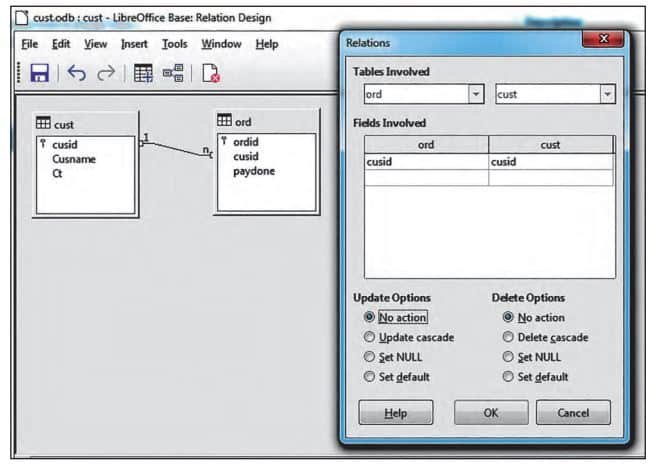
Steps to develop relationship between relations in LibreOffice Base
- Create relations (tables) with one field common which must be a primary key of first table and the same key is referenced in another relation and called as foreign key in that table.
- Click on ‘Tools’ menu and select ‘Relationships’ option.
- A small window will appear, select table name and click on ‘Add’ button.
Disclaimer: We have provide you with the accurate handout of “Database Concepts using LibreOffice Base Class 12 Notes“. If you feel that there is any error or mistake, please contact me at anuraganand2017@gmail.com. The above study material present on our websites is for education purpose, not our copyrights.
All the above content and Screenshot are taken from Information Technology Class 12 Textbook and MSBSHSE (HSC) Support Material which is present in MSBSHSE (HSC) website, This Textbook and Support Material are legally copyright by Maharashtra State Bureau of Textbook Production and Curriculum Research, Pune. We are only providing a medium and helping the students to improve the performances in the examination.
Images and content shown above are the property of individual organisations and are used here for reference purposes only. To make it easy to understand, some of the content and images are generated by AI and cross-checked by the teachers. For more information, refer to the official website.
