Emerging Technologies is an important chapter of Information Technology Class 12 (HSC Maharashtra Board). It introduces students to modern technologies like Artificial Intelligence, IoT, Cloud Computing, Big Data, Blockchain, and Cyber Security. These notes are prepared in simple language and are useful for board exam preparation, revision, and practical exams.
Emerging Technologies Class 12 Notes
IoT (Internet of Things)
IoT stands for Internet of Things. IoT helps to connect the devices to the internet; this device helps to communicate, monitor and even make decisions without human involvement. For example, fitness trackers, industrial robots, vehicles, home appliances, etc.
Advantages of IoT
- Efficient resource utilisation: IoT can monitor and manage natural resources more effectively, like measuring soil moisture, detecting someone entering a room, etc.
- Minimise human effort: IoT devices communicate and perform tasks automatically, reducing the need for manual work.
- Time Saving: IoT does the process automatically; due to this, it saves time in daily life and industries.
- Enhanced Data Collection: Sensors collect the data from weather, pollution, sound, etc., and analyse it for better decision-making.
- Improve Security: Smart surveillance and IoT-based security systems make homes, offices and cities safe.
Disadvantages of IoT
- Privacy Concerns: IoT devices collect huge amounts of personal data like location, habits, health, etc. Even without user permission, this data can be misused or shared with others without permission.
- System Complexity: Designing, developing and maintaining IoT systems can be complicated. It required advanced technology, skilled professionals and constant updates to keep the device working together.
Applications of IoT
- Smart lighting – Illumination of light is controlled on the basis of day light.
- Smart thermostats – Allows users to schedule, monitor and remotely control home temperatures.
- Smart locks and garage-door openers – Password based or facial recognition based doors and locks.
- Smart security cameras – Security cameras that can identify known and unknown person and raise alarm, in case of security threat.
- Smart traffic signals – Signal that can adjust their timing to accommodate commutes and holiday traffic and keep cars moving.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is an online computing service like storage, servers, databases, networking and software without purchasing physical infrastructure. For example, Google Drive, Dropbox, Gmail, Netflix, YouTube, etc.
Models of Cloud computing
There are three primary service models of cloud computing that are Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS).
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS)
IaaS is a cloud service model that gives users access to basic computing resources (like servers, storage, and networking) over the internet.
Examples : Amazon web services (AWS) ec2, Microsoft Azure VM, Google Compute Engine (GCE)
Key features
- Instead of purchasing hardware outright, users pay for IaaS on demand.
- Infrastructure is scalable depending on processing and storage needs.
- Enterprises saves the costs of buying and maintaining their own hardware.
Platform as a service (PaaS)
PaaS is a cloud service model where the provider gives users a ready‑made environment to develop, test, and deliver applications.
Key features
- PaaS provides a platform with tools to test, develop and host applications in the same environment.
- Enables organizations to focus on development without having a worry about underlying infrastructure.
- Providers manage security, operating systems, server software and backups.
- Facilitates collaborative work even if teams work remotely
Software as a service (SaaS)
A service provider delivers software and applications through the internet. Users do not install applications on their local devices. Instead, the applications reside on a remote cloud network accessed through the web or an API.
Examples : Google’s G suite, GitHub, SAP, Slack, Dropbox.
Key features
- SaaS vendors provide users with software and applications via a subscription model.
- Users do not have to manage, install or upgrade software; SaaS providers manage this.
- Data is secure in the cloud; equipment failure does not result in loss of data.
- Use of resources can be scaled depending on service needs.
- Applications are accessible from almost any internet-connected device, from virtually anywhere in the world.
Types of Cloud Computing
There are three basic types of deployment of cloud computing that are Public, Private and Hybrid.
- Public Cloud: In a public cloud, service and infrastructure are managed by the provider, and the service is shared with the multiple users using the internet. Public clouds are more efficient and cost-effective than private and hybrid cloud solutions. Examples: Amazon AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform.
- Private cloud: A private cloud provides IT services through the internet or a private network to selected users rather than to the general public. All the data is protected behind the firewall. Private cloud solutions are preferred for enhanced security and privacy by the users.
- Hybrid Cloud: Hybrid cloud environments combine both public and private cloud elements. The clouds in a hybrid environment communicate over an encrypted connection and allow for the portability of data and applications.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
- Cost saving : Cloud computing solutions are inexpensive than the actual overall Infrastructure set up for the I.T services.
- Reliable : Cloud computing solutions are more reliable than In-house I.T infrastructure.
- Mobility : Cloud computing solutions are more portable because user can access data anytime, anywhere as required.
AI (Artificial Intelligence)
AI is a branch of computer science focused on creating machines that can think, learn, and react like humans. AI is different from robotics, but related to some extent, in which machines sense their environment, perform calculations and do physical tasks either by themselves or under the direction of people.
AI has some sub fields like
- Machine Learning (ML): A computer can learn from data and improve automatically without being explicitly programmed.
- Neural Networks: Neural networks work like human brains; they use interconnected nodes (“neurones”) to process information.
- Deep Learning: Deep learning uses very large neural networks and high computing power to find complex patterns.
- Cognitive Computing: It creates human-like interactions by interpreting speech, text and context.
- Computer Vision: Computer vision employs pattern recognition and deep learning to understand the content of pictures and videos and to enable machines to use real-time images to make sense of what’s around them.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Natural language processing involves analysing and understanding human language and responding to it.
Advantages of Artificial Intelligence
- Reduction in Human Error: AI can do 100% accuracy tasks as compared to humans.
- Digital Assistance: AI-powered assistants like chatbots interact with users, reducing the need for human staff.
- Faster Decisions: AI can analyse the data and make the decision faster than humans.
- Daily Applications: Nowadays, AI is part of everyday life, like Siri, Cortana, and Google Assistant.
Disadvantages of AI
- High Costs of Creation: AI machines are complex and expensive to build and maintain.
- Unemployment: AI can replace humans with robots and reduce human involvement, which will cause unemployment.
5G
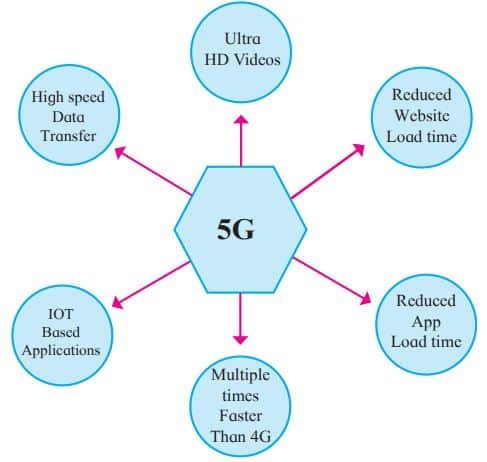
5G is the fifth generation of cellular network technology. 5G is the next generation of wireless communications. It is expected to provide Internet connections that are multiple times faster than 4G LTE (Long Term Evolution). 5G technology may use a variety of spectrum bands, including millimeter wave (mmWave) radio spectrum, which can carry very large amounts of data at a short distance. The drawback of the higher frequencies is that they are more easily obstructed by the walls of buildings, trees and other foliage, and even changes in the weather.
5G can support upto a million devices per square kilometer, compared to 4G. Features of 5G are shown in fig. 4.2
Applications :
- Online 5G Games.
- Automated Vehicles.
- Virtual Classrooms.
Disclaimer: We have provide you with the accurate handout of “Emerging Technologies Class 12 Notes“. If you feel that there is any error or mistake, please contact me at anuraganand2017@gmail.com. The above study material present on our websites is for education purpose, not our copyrights.
All the above content and Screenshot are taken from Information Technology Class 12 Textbook and MSBSHSE (HSC) Support Material which is present in MSBSHSE (HSC) website, This Textbook and Support Material are legally copyright by Maharashtra State Bureau of Textbook Production and Curriculum Research, Pune. We are only providing a medium and helping the students to improve the performances in the examination.
Images and content shown above are the property of individual organisations and are used here for reference purposes only. To make it easy to understand, some of the content and images are generated by AI and cross-checked by the teachers. For more information, refer to the official website.
