Impressive Web Designing is an important chapter in the Class 11 Information Technology (IT) HSC syllabus that introduces students to the basics of creating attractive and user-friendly websites. These notes are prepared according to the Maharashtra State Board (HSC) curriculum, focusing on both theoretical concepts and practical understanding.
Impressive Web Designing Class 11 HSC Notes
Introduction
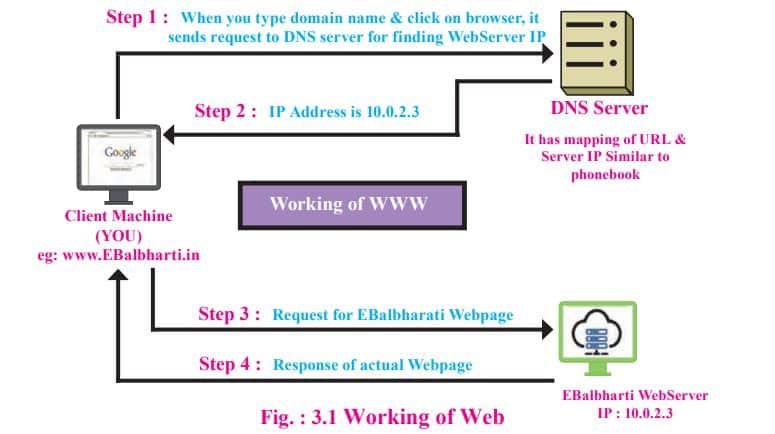
The internet is a powerful medium to transmit information. The pages of information displayed on the internet is referred to as web pages.
How does the web work?
WWW stands for ‘world wide web’ normally referred to as the web.
Components of web
Web uses the following terms:
- Webpage: A simple text file created using HTML.
- Website: A collection of interlinked web pages containing text, images, audio and videos. For example, www.cbseskilleducation.com
- Web Browser: A web browser is software used to view web pages or websites available on the internet. For example, Internet Explorer, Google Chrome, and Mozilla Firefox.
- Web Server: A web server is an application or a computer that sends webpages over the internet using the HTTP protocol.
- URL (Uniform Resource Locator): It is an address of a web page on the internet. For example, https://cbseskilleducation.com/aboutus
- HTML: Hyper Text Markup Language, enables you to write code for a webpage. All the webpages in a website are linked with one another with the help of hypertext links.
Introduction to HTML5
HTML is used for creating interactive websites, introduced by Tim Berners Lee. HTML documents can be created in any text editor, and they can run (execute) on any computer or mobile device web browser. HTML is compatible with most of the web browsers.
Basic structure
HTML tags are keywords enclosed within angular brackets. Tags are not case sensitive. Most of these tags are enclosed within two tags: an open tag and a close tag, like <html> and </html>. HTML tags are divided into two sections: head section and body section. The head section contains the title tag, and the body section contains all the tags related to the actual text.
An attribute
An attribute defines a property for an element, consists of an attribute/value, and appears within the element’s start tag.
<html>
<head>
<title> First Page </title>
</head>
<body bgcolor = green >
attribute value of attribute
This is my first web page
</body>
</html>Classification of HTML Tags
HTML tags are categorised as:
- Container Tags: Container tags are also called paired tags. Container tags have a beginning tag and an end tag. For example,</head>, <body> </body>
- Empty Tags: Empty tags are standalone tags and do not have an end tag. <Br> is an example of a singular tag/empty tag.
Basic structure of HTML
- <html> and </html>: This tag indicates that the document is an HTML file.
- <head> and </head>: It includes <Title> within it the text within, which<head> is not displayed on the webpage. This is used for search engine optimisation.
- <title> and </title>: The content within this tag is displayed on the title bar.
- <body> and </body>: This tag includes all content which is to be developed in the web browser. Most of the tags are included in this tag.
Structure of a web page using HTML5
- <!DOCTYPE html> – The first line on the page, it declares that the code is HTML 5.
- <header> – Defines a header for a document or a section.
- <nav> – Defines a container for navigation links.
- <section> – Defines a section in a document.
- <article> – Defines an independent self-contained article.
- <aside> – Defines content apart from the content (like a sidebar).
- <footer> – Defines a footer for a document or a section.
- <details> – Defines additional details.
Text formatting element
Text formatting is used to make a document look attractive, thereby enhancing its appearance.
Heading levels
HTML provides six levels of heading tags. The range is from <H1> to <H6>.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Heading levels</title>
</head>
<body bgcolor=skyblue>
<H1>Heading level 1 Text is largest in size</H1>
<H2>Heading level 2 </H2>
<H3>Heading level 3</H3>
<H4>Heading level 4</H4>
<H5>Heading level 5</H5>
<H6>Heading level 6 Text is smallest in size</H6>
</body>
</html>Inserting an image
The <img> tag is an empty tag, and it is used to insert an image within a webpage. It uses the following attributes:
<IMG> tag is used to insert an image within a webpage. It uses the following attributes:
- src: It is used to give the path of the image.
- height: height of the image in pixels.
- width: width of the image in pixels.
- alt: It is defined as alternate text.
<IMG src=”Desert.jpg” height=”400″ width=”400″ alt=”Desert image”>
Horizontal ruler
<Hr> tag is used to display a horizontal ruled line.
- colour: Sets colour for the horizontal ruled line.
- width: It specifies the length of the ruled line in % or pixels.
- Size: It sets the thickness of a ruled line.
Paragraph
<P> tag: It is used to define paragraphs. It is a container tag.
Creating a table
A table is made up of rows and columns. A table in a webpage is created by using the <table> <table> tag, which is a container tag.
- <table> : It is used to indicate the creation of a table.
- <caption> : It is used to specify a table heading.
- <tr> : This tag is used to create each row of the table.
- <th> : It indicates table heading.
- <td> : It specifies data within the table (cell content).
The attributes of the table are
- border: This attribute is required to display a border for the entire table.
- bordercolor: It displays a border in a specific colour.
- Align: It aligns the table either to the left, right or centre.
- bgcolor: Sets the background colour for the table.
The attributes of the <td>
- Align: It aligns the text horizontally. The values are aligned to the left, right or centre.
- colspan: This attribute is used within <td> or <th>. It creates a single column spanning across the table.
- rowspan: This attribute is used within <td> or <th>. It creates a single row spanning across the table.
Creating hyperlinks in a webpage
Hyperlinks are used to connect one document with another document. In HTML, links are created by using <a> tags.
Syntax:
<a href = ”Mypage. htm”> Click here for my page. </a>
HTML link colours
A hyperlink by default appears blue in colour with an underline.
- It is not visited by any user.
- A visited link is underlined and purple.
- An active link is underlined and blue.
Image hyperlink
Many websites have images as hyperlinks. For example, the previous arrow is an image which, on clicking, displays a previous webpage. The arrow is actually an image hyperlink.
Syntax:
<a href = “Mypage2.htm”><Img src = “arrow. gif” alt = “Click on arrow”></a>
Forms in HTML
Forms in HTML are used to accept user input. The form in HTML is created by using <form> the element ‘as’.
Form controls
A form has multiple elements, like a textbox, radio button, checkbox, submit button, etc. These elements are known as form controls.
Attributes used with the form element and Input element.
<Form> tag can have the followinginput attributes
- Name: It specifies a name for a form.
- Action: The action attribute specifies the path where the form is to be submitted.
- Method: The method attribute specifies the GET or POST method to be used when submitting the form data.
- GET method: The default method of submitting form data is GET.
- POST Method: The POST method of sending data does not display the form data in the address bar.
The <Input> tag
The <Input> tag is used to specify the different types of controls by using the type attribute.
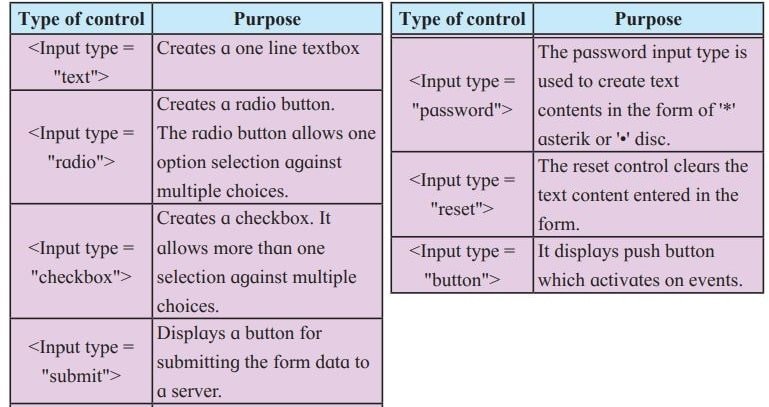
Attributes of <Input>
There are attributes which are specific to a particular type of control. The following table specifies the description.
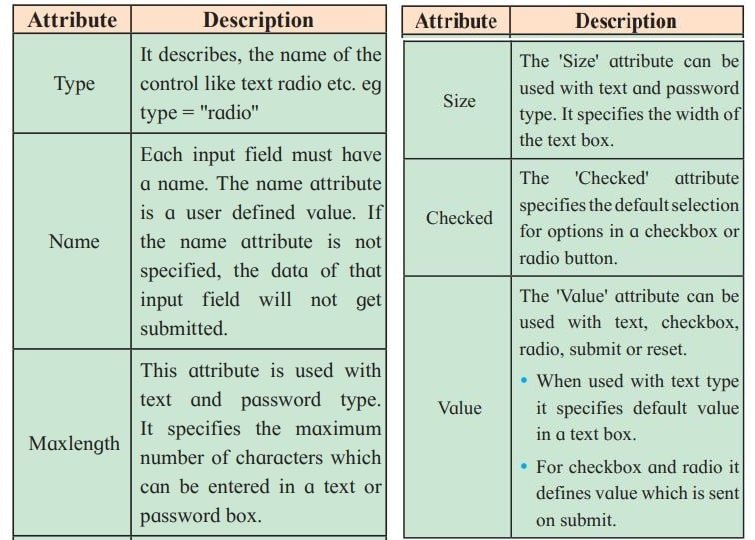
<Textarea> tag
This <textarea> is used to create a textbox with multiple lines. They <textarea> can have the following attributes.
- name: Gives the textarea a name (e.g., name=”ta1″).
- rows: Number of visible text lines (e.g., rows=”5″).
- cols: Width of the textarea in characters.
- maxlength: Maximum characters allowed.
- placeholder: Hint text inside the box (e.g., “your address”).
- Required: Makes the field mandatory (cannot be left blank).
<Select> tag
<select> The <tag> tag is used to create drop-down lists. The attributes of <select> a tag are:
<select> attributes
- name: Assigns a name to the dropdown control.
- multiple: Allows selecting more than one option.
- Size: Defines how many options are visible at once.
<option> attributes
- selected: Marks an option as preselected.
- value: Assigns a value to the option in the list.
Client-Side Scripting
What is a scripting language?
Scripts are used to generate dynamic web pages on the Web. Scripts can be opened and edited by using a text editor.
Insertion of JavaScript in HTML
JavaScript can be used for client-side or server-side scripting language. JavaScript code can be inserted in an HTML program between the <script> <script> and </script> </script> tags. There are two methods to insert JavaScript in the HTML. Scripts can be placed in <body> or in <head> a section of an HTML or in both.
Script placed inside body section
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head><title>First</title>
</head>
<body>
<script language="javascript">
// javascript statements
</script>
</body>
</html>Script placed inside head section
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head><title> Second </title>
<script language="javascript">
// javascript statements
</script>
</head>
<body></body>
</html>Variables
The variable is a basic unit of storage in a JavaScript program.
Rules to declare variables
Variable names may consist of alphabets, digits, underscores and dollar characters with the following rules:
- They must start with an alphabet.
- Uppercase and lowercase are distinct. This means that the variable ‘sum’ is not the same as ‘SUM’.
- It should not contain blank space or special symbols except underscores.
- Standard keywords are not allowed as variable names. For example, document while.
- Variable names can be limited to up to 255 characters.
Syntax:
var variablename;
var variablename, variablename;Data Types
Data types are the categories of values that a programming language can handle. They define what kind of data can be stored and what operations can be performed on it.
1. Number type
The number data type stores (holds) both whole numbers (integers) and decimal point numbers, which store the fractional part of a number (also called floating point numbers).
Example:
var y=100000
var z = -67.992. String Type
Strings are used for storing text. Strings must be inside of either double or single quotes.
Example:
var x=“Hello”
var str= ‘Information Technology’3. Boolean Type
It represents only two values, ‘true’ and ‘false’.
4. Infinity
Division by 0 gives you another special value.
Example:
a=3/0
Result: Infinity5. null
In JavaScript, null is just a value which means “nothing”, ”empty”, or ”unknown”.
6. undefined
JavaScript returns ‘undefined’ when a variable is declared but not assigned.
Operators
Operators are used to do arithmetic and logical operations.
Arithmetic operators
Arithmetic operators are used in mathematical expressions in the same way that they are used in algebra. For the following example, consider:
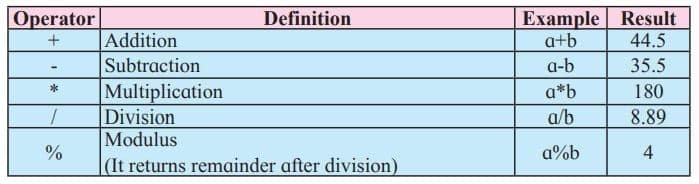
‘+’ operator in JavaScript
In JavaScript the ‘+’ operator has two meanings: arithmetic addition and string concatenation.
Example:
var a=15+”Hello”
Result: 15 Hello
Example: var a=15+7+ ”Hello”
Result: 22HelloAssignment Operators (=)
The assignment operator is used to assign the value of an expression to a variable. This means that the value of an expression on the right-hand side is assigned to the single variable on the left-hand side.
Expression
There is a difference between algebraic mathematical equations and computer programming statements.
10=x; //error
X=10; //validRelational Operators
Relational operators are used to check conditions or comparisons of operands. The result of relational operators is the Boolean value ‘true’ or ‘false’. The following table shows JavaScript relational operators. For the result, consider the values as a=10 and b=30…
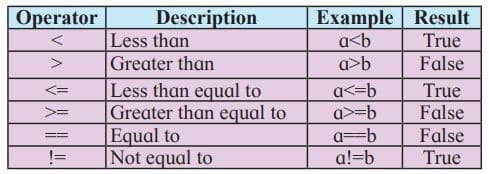
Logical Operators
Logical operators are used to verify more than one condition at a time or to negate the condition. JavaScript has three logical operators.
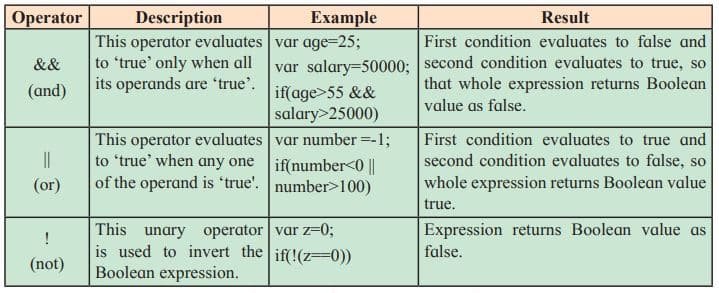
Increment (++) and Decrement (–) Operators
The increment (++) operator in JavaScript is used to increment the value of a variable by one, and the decrement (–) operator in JavaScript is used to decrement the value of a variable by one. They can be used in two ways:
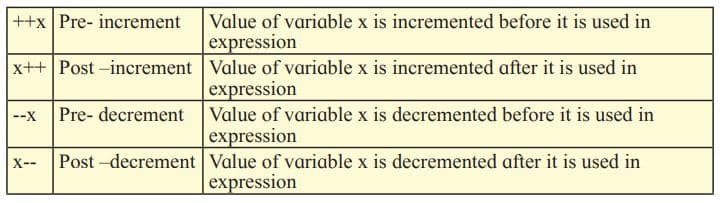
Comments in JavaScript
Comments are non-executable statements in a program. It supports two types of comments.
- Single-line comment (//…………..): A single-line comment begins with //. The JavaScript ignores everything from // to the end of the line.
- Multiline comment: Multiline comments are used to comment on more than one line. It starts with /* and ends with */.
Commonly Used Built-In Functions in JavaScript
A function is used to perform repetitive tasks whenever required. It is a reusable code block that will be executed when it is called.
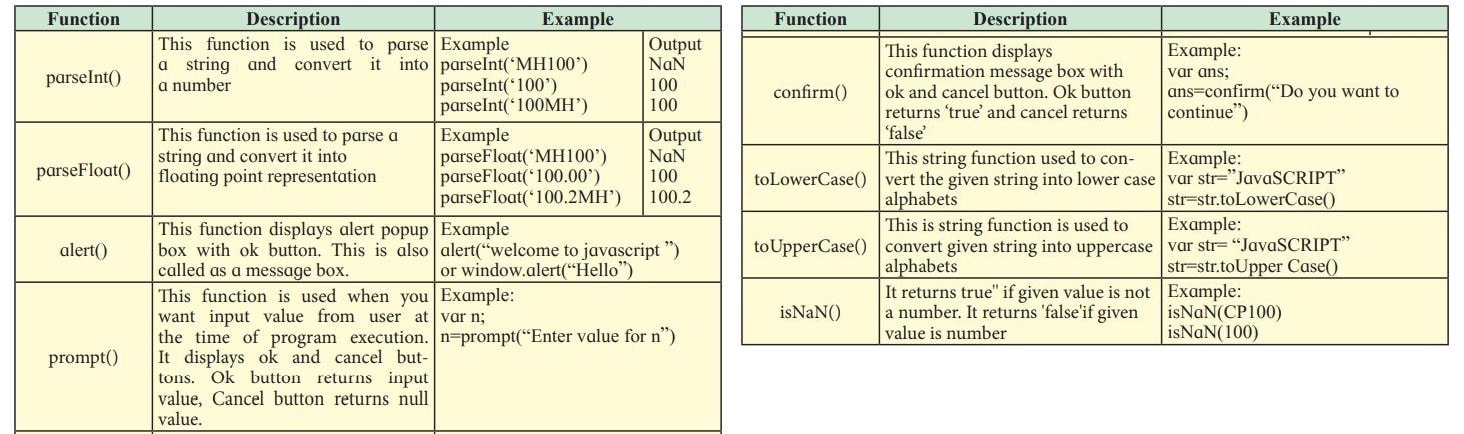
Decision-Making Statements
1) if statement:
The if statement in JavaScript is used to make decisions in code. It checks a condition, and if the condition is true, the block of code inside runs.
Syntax:
if(condition)
{
statement block;
}2) if-else statement:
The if…else statement in JavaScript is used when you want to run one block of code if a condition is true and another block if the condition is false.
Syntax:
if(condition)
{
statement block;
}
else
{
statement block;
}3. User-Defined Functions
A User Defined Function (UDF) in JavaScript is a block of code written by the programmer to perform a specific task. Instead of repeating code, you can define a function once and reuse it whenever needed.
Syntax:
function functionname(argument1, argument2…)
{
statement block;
}4. Event Handling
JavaScript is an event-driven language. An event is an action done by the user or an application. JavaScript’s interaction with HTML is handled through events that occur when a user or browser manipulates a page. When the page loads, it is called an event.
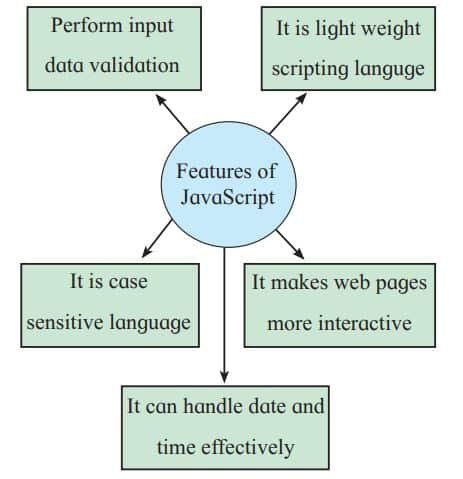
Features of JavaScript
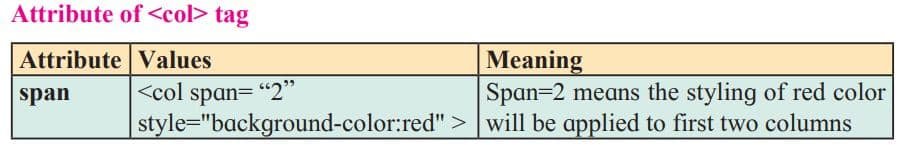
Use of the colspan attribute in a table
<colgroup> and <col> Tags
<colgroup>
The <colgroup> <colgroup> (short for column group) tag specifies a group of one or more columns in a table for formatting.
<Col>
<Col> tag is used within <colgroup> tag. The <col> tag has no end tag.
HTML <tbody> Tag
In HTML, tables can be divided into sections using <thead>, <tbody> and <tfoot>. It <thead> holds the header rows, <tbody> contains the main data, and <tfoot> defines the footer. These tags help keep headers and footers fixed while scrolling, repeat them when printing large tables, and improve SEO by giving structure to tabular data. Inside each section, rows are created with <tr> and cells with <td>.
Disclaimer: We have provide you with the accurate handout of “Impressive Web Designing Class 11 HSC Notes“. If you feel that there is any error or mistake, please contact me at anuraganand2017@gmail.com. The above study material present on our websites is for education purpose, not our copyrights.
All the above content and Screenshot are taken from Information Technology Class 11 Textbook and MSBSHSE (HSC) Support Material which is present in MSBSHSE (HSC) website, This Textbook and Support Material are legally copyright by Maharashtra State Bureau of Textbook Production and Curriculum Research, Pune. We are only providing a medium and helping the students to improve the performances in the examination.
Images and content shown above are the property of individual organisations and are used here for reference purposes only. To make it easy to understand, some of the content and images are generated by AI and cross-checked by the teachers. For more information, refer to the official website.
