The Introduction to DBMS (Database Management System) is an important topic in the Class 11 Information Technology (IT) HSC syllabus. It introduces students to the concept of databases and explains how data is stored, managed, and retrieved efficiently using computer systems. These notes are prepared according to the Maharashtra State Board (HSC) curriculum, keeping exam requirements in mind.
Introduction to DBMS Class 11 HSC Notes
Definition of a Database
A database is an organised collection of data that allows you to store, retrieve and manage the data efficiently. It is just like a centralised system where multiple users or applications can access and update data securely.
| Data | Information |
|---|---|
| Data is raw facts | Information is processed data |
| Data does not help in decision making | Information helps in decision making |
| Data could be relevant or irrelevant | Without data information cannot be processed |
| Each student’s exam score is one piece of data. | The average score of a class or of the entire school is information that can be derived from the given data. |
Introduction to Database Management System (DBMS)
A Database Management System (DBMS) is software for creating and managing databases. The DBMS provides users and programmers with a systematic way to create, retrieve, update and manage data. It stores data in such a way that it becomes easier to retrieve, manipulate, and update information. Examples of popular DBMS are MySQL, PostgreSQL, Access, Oracle, SQL Server, IBM, DB2 and Sybase.
Some Applications of DBMS
- Railway Reservation System
- Library Management System
- Banking Application System
- Application in universities and colleges
- Application for Credit Card Transactions
- Social Media Sites
Advantages of DBMS
- Reducing Data Redundancy: Sometimes in a database, multiple copies of the same data can be stored; databases help to reduce the data duplication.
- Sharing of Data: The user can share the database with multiple users or applications based on the privilege given to them.
- Data Integrity: Data integrity means that the data is accurate and consistent in the database.
- Data Security: Only authorised users should be allowed to access the database, and their identity should be authenticated using a username and password.
- Privacy: The privacy rule in a database means only the authorised users can access a database according to its privacy constraints.
- Backup and Recovery: The database management system automatically takes care of backup and recovery.
- Development and Maintenance Time: DBMS reduces application development and maintenance time.
Data types in the DBMS
When you create a table or add a field to a table in the database, fields are created with specific data types. Data types are classifications that identify possible values for and operations that can be done on the data, as well as the way the data in that field is stored in the database.
| Class | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Text | CHAR | Holds a fixed length string (can contain letters, numbers, and special characters). The fixed size is specified in parenthesis. |
| Text | VARCHAR | Holds a variable length string (can contain letters, numbers, and special characters). The maximum size is specified in parenthesis. |
| Numeric | DECIMAL | It can represent numbers with or without the fractional part |
| Numeric | INT | It is used for storing integer values. |
| Date | DATE | It holds the date including day,month and year |
| Time | TIME() | It holds time. Format: HH:MM:SS |
Data model
The database is designed according to certain rules. This logical structure of a database is known as a data model. Data models define how the data are connected to each other and how they are processed and stored inside the system. There are different types of data models, like the network model, the hierarchical model and the relational model.
Relational Model
The relational model organises data into tables (relations) made up of rows (tuples) and columns (attributes).
Transactions in Databases
A logical unit of work performed on a database is known as a transaction in the database. For example, inserting a new record, updating a record or deleting a record in the database. Transactions helps to ensure data integrity and handlehelp the error efficiently.
Properties of Transactions
Transactions have the following four standard properties, usually referred to by the acronym ACID.
- Atomicity: It ensures that all operations within the work unit are completed successfully. For example, if you transfer ₹500 from Account A to B, either both debit and credit happen, or neither does.
- Consistency : It ensures that the database properly changes states upon a successfully committed transaction.
- Isolation:: It enables transactions to operate independently of and transparently to each other.
- Durability: It ensures that the result or effect of a committed transaction persists in case of a system failure.
Introduction of RDBMS
RDBMS stands for Relational Database Management System. In RDBMS a database is considered as a collection of interrelated data.
Basic Database Concept
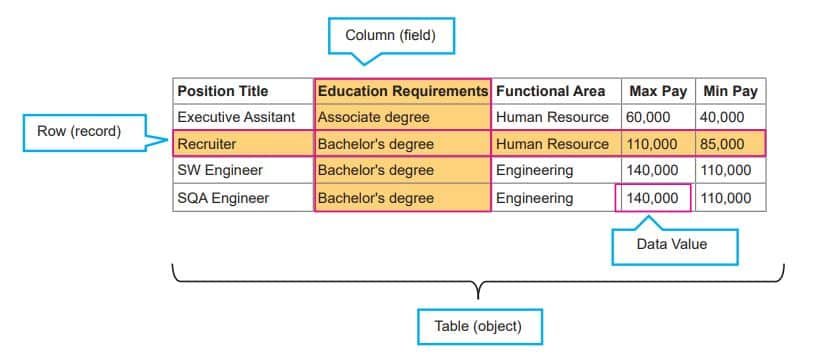
- Table: A table consists of columns and rows. A database consists of one or more tables according to which data is stored in a table.
- Field: A table consists of information which is stored under different headings, called ‘fields’ or ‘columns’.
- Record: All the columns in a table make a row. Each row contains information on individual topics, which is known as a record.
- Key: A column or a combination of columns which can be used to identify one or more rows (tuples) in a table is called a key of the table.
- Primary Key: The group of one or more columns used to uniquely identify each row of a relation is called its primary key.
- Foreign Key: It is a field (or collection of fields) in one table that refers to the primary key in another table.
Relationships in database
In databases, relationships describe how data in one table is connected to data in another. Since the relational model organises data into tables, relationships are the glue that links those tables together. There are 3 types of relationships in relational database design. They are:
- One-to-One
- One-to-Many (or Many-to-One)
- Many-to-Many
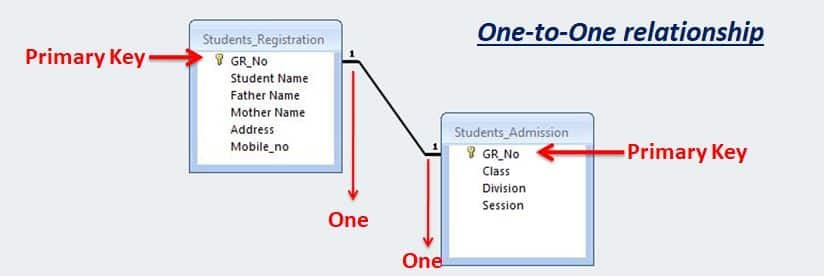
One-to-One relationship
In a One-to-One relationship, the master table and transaction table both have one record.
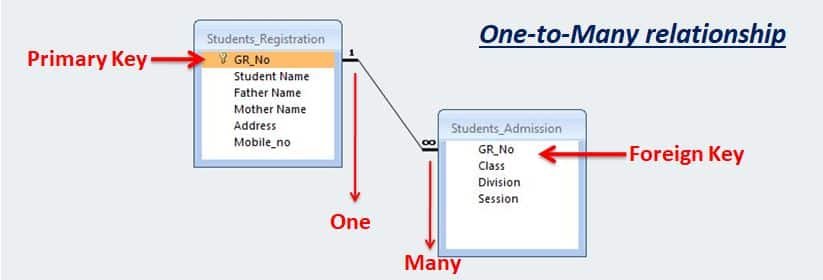
One-to-Many relationship
In a One-to-Many relationship, the master table having one record and transaction table having multiple records. This is a very common type of relationship between the tables in the database.
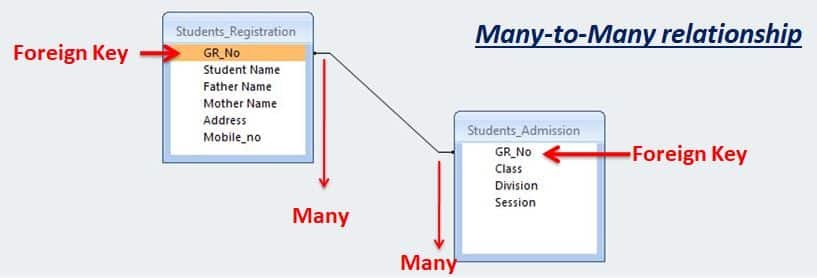
Many-to-Many relationship
In a One-to-Many relationship, the master table has multiple records and the transaction table has multiple records.
Introduction to SQL
SQL is Structured Query Language, which is a computer language for storing, manipulating and retrieving data stored in a relational database. SQL helps to –
- Create new databases.
- Create new tables in a database.
- Insert records in a database.
- Retrieve data from a database.
- Update records in a database.
- Delete records from a database.
- Execute queries against a database.
- Create stored procedures in a database.
- Create views in a database.
Categories of SQL Commands
Data Definition Language (DDL): DDL statements or commands are used to define and modify the database structure of your tables or schema.
| COMMAND | USED FOR |
|---|---|
| CREATE DATABASE | Creates database |
| CREATE TABLE | Creates a new table |
| ALTER TABLE | Modifies a table |
| DROP TABLE DROP DATABASE | Deletes a table or Database |
Data Manipulation Language (DML): Data Manipulation Language (DML) statements or commands are used for managing data within tables.
| COMMAND | USED FOR |
|---|---|
| SELECT | Extracts data from a table |
| UPDATE | Updates data in a table |
| DELETE | Deletes data from a table |
| INSERT INTO | Insert data into a table |
Data Control Language (DCL): DCL is used to control user access in a database. It is related to a security issue. It also deals with the rights and permissions of the database access.
| COMMAND | USED FOR |
|---|---|
| GRANT | To provide access or privileges on the database objects. |
| REVOKE | To remove access rights or privileges on the database object |
Disclaimer: We have provide you with the accurate handout of “Introduction to DBMS Class 11 HSC Notes“. If you feel that there is any error or mistake, please contact me at anuraganand2017@gmail.com. The above study material present on our websites is for education purpose, not our copyrights.
All the above content and Screenshot are taken from Information Technology Class 11 Textbook and MSBSHSE (HSC) Support Material which is present in MSBSHSE (HSC) website, This Textbook and Support Material are legally copyright by Maharashtra State Bureau of Textbook Production and Curriculum Research, Pune. We are only providing a medium and helping the students to improve the performances in the examination.
Images and content shown above are the property of individual organisations and are used here for reference purposes only. To make it easy to understand, some of the content and images are generated by AI and cross-checked by the teachers. For more information, refer to the official website.
