This unit has introduced Tourism industry to you. You have learned to define tourism as well as tourist and excursionist. This unit helps you to differentiate between a traveller and a tourist as well as other travellers.
Introduction to Tourism Unit 1 Class 9 Notes
Introduction
Tourism is a widely experienced activity that includes everything like school trips, family vacations, and business travel. Tourism is not only joy for travelers but also a major global industry that generates employment and economic growth.

Defining Tourism
The word tourism comes from the Latin word tornare and the Greek word tornos, meaning “one’s turn.” Humans always traveled for exploration, survival, and trade. UNWTO (United Nations World Tourism Organization) states that tourism involves traveling and staying outside the usual environment for up to one year without earning income at the visited place.
The three criteria, as per UNWTO, are that the displacement must be such that:
- It involves a displacement outside the usual environment: This term is of utmost importance and will be discussed later on;
- Type of purpose: The travel must occur for any purpose different from being remunerated from within the place visited: the previous limits, where tourism was restricted to recreation and visiting family and friends, are now expanded to include a vast array of purposes;
- Duration: Only a maximal duration is mentioned, not a minimal. Tourism displacement can be with or without an overnight stay.
Tourist Typology
Tourism, as stated earlier in the chapter, is a socio-economic phenomenon, meaning tourism activity affects both the social fabric and the economy of a tourist destination. To measure its impact, it’s important to distinguish between different types of travelers. All tourists are travelers, but not all travelers are tourists. The tourism classification depends on the length of stay and purpose of the visit.
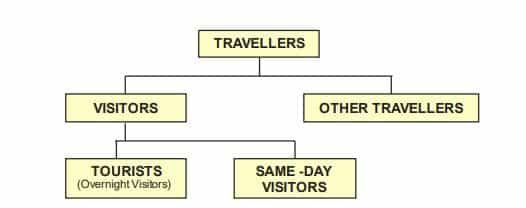
- Tourists: Stay at least 24 hours but less than one year. The journey can be classified under one of the following headings:
- Leisure (recreation, holiday, health, study, religion, and sport);
- Business, family, mission, meeting
- Same-day Visitor: Same—A same-day visitor is also called an excursionist, a temporary visitor staying less than twenty-four hours in the country visited (including travelers on cruises).
Purpose of Tourism
History tells us that humans have been travelling since ancient times in search of food, shelter, safety, and then for trade. In modern times, the purpose of travel can be classified under one of the following headings:
- Leisure: recreation, holiday, health, study, religion, sport, and so on;
- Business, family, meeting.
Let us explore these purposes of travel and understand their role as purposes of tourism.
Leisure Tourism
Travel for enjoyment, relaxation, or personal enrichment.
- Recreation: The annual vacation or the weekend getaway for some relaxation and fun activity is one of the primary purposes for tourism.
- Holiday: A special destination or site attracts us to visit that destination for a holiday.
- Health Travel: A change of climate often recommended by doctors for the recuperation of health, leads to a trip outside the usual place of residence.
- Education: : Education, especially higher education is reason for travelling out of the city of residence to another.
- Religion: Tourism for the purpose of religious belief is the one of the oldest known purposes of tourism.
- Sports: Sporting events attract fans and spectators from across the globe, especially international sporting events that occur after regular interval like Cricket World Cup or the Olympic Games and so on.
Business & Other Necessity-Based Tourism
Travel driven by professional or personal obligations:
- Business: A business will have to go on a tour out of necessity, whether to buy or sell the product.
- Meeting: An out – station meeting with clients will necessitate one to travel to another city or country.
- Family (VFR): A birth, wedding or even a funeral in the family and extended family means going on trip.
Components of Tourism
Components in laymen‟s term refer to the mechanism with the help of which the machinery of tourism works. These components of Tourism are commonly referred to as the A‟s of tourism, at times 4 A‟s of tourism.
- Attraction: It refers to the features of a destination that pulls or attracts tourists to a destination and is commonly known as Tourist Attractions.
- Accessibility: A destination can be a hill station pleasant climate with ancient monuments and ruins.
- Accommodation: This refers to the place of stay and rest for the tourists.
- Amenities: These are basic facilities provided to the tourists such as medical aid, foreign currency exchange, safety and security, communication facilities and so on.
Forms of Tourism
In the International Recommendations for Tourism Statistics 2008 (IRTS 2008) drafted by UNWTO, three basic forms of tourism were revised from earlier and updated as:
- Domestic Tourism: comprises the activities of a resident visitor within the country of reference.
- Inbound Tourism: comprises the activities of a non – resident visitor within the country of reference.
- Outbound Tourism: comprises the activities of a resident visitor outside the country of reference.
Disclaimer: We have taken an effort to provide you with the accurate handout of “Introduction to Tourism Unit 1 class 9 notes“. If you feel that there is any error or mistake, please contact me at anuraganand2017@gmail.com.
The above CBSE study material present on our websites is for education purpose, not our copyrights. All the above content and Screenshot are taken from Introduction to Tourism NCERT Textbook, CBSE Sample Paper, CBSE Old Sample Paper, CBSE Board Paper and CBSE Support Material which is present in CBSEACADEMIC website, NCERT websiteThis Textbook and Support Material are legally copyright by Central Board of Secondary Education. We are only providing a medium and helping the students to improve the performances in the examination.
Images and content shown above are the property of individual organizations and are used here for reference purposes only.
For more information, refer to the official CBSE textbooks available at cbseacademic.nic.in
