Science Class 10 Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations NCERT Solutions provide clear, step-by-step answers to all NCERT textbook questions. These solutions help students understand the concepts of chemical reactions, balancing chemical equations, types of reactions, and practical applications.
Science Class 10 Chapter 1 NCERT Solutions
1. Why should a magnesium ribbon be cleaned before burning in air?
Answer: Cleaning helps the magnesium to burn properly and give a strong, bright flame. Magnesium metal reacts with atmospheric oxygen and forms a white layer on it, which is known as magnesium oxide (MgO). Before burning, we have to clean the magnesium ribbon with sandpaper, which will help to remove the white layer which basically does not burn properly.
2. Write the balanced equation for the following chemical reactions.
(i) Hydrogen + Chlorine → Hydrogen chloride
(ii) Barium chloride + Aluminium sulphate → Barium sulphate + Aluminium chloride
(iii) Sodium + Water → Sodium hydroxide + Hydrogen
Answer:
(i) H2 + Cl2 → 2HCl
(ii) 3BaCl2 + Al2(SO4)3 →3BaSO4 + 2AlCl3
(iii) 2Na + 2H2O → 2NaOH + H2
3. Write a balanced chemical equation with state symbols for the following reactions.
(i) Solutions of barium chloride and sodium sulphate in water react to give insoluble barium sulphate and the solution of sodium chloride.
(ii) Sodium hydroxide solution (in water) reacts with hydrochloric acid solution (in water) to produce sodium chloride solution and water.
Answer:
(i) BaCl2 + Na2SO4 → BaSO4 + 2NaCl
(ii) NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H2O
4. A solution of a substance ‘X’ is used for whitewashing.
(i) Name the substance ‘X’ and write its formula.
(ii) Write the reaction of the substance ‘X’ named in (i) above with water.
Answer:
(i) The substance used in whitewashing is known as quicklime; it is the chemical name of calcium oxide. The formula of calcium oxide is CaO.
(ii) When this quicklime (CaO) is mixed with water, then it becomes slaked lime. This slaked lime is used when we want to paint walls, and it is called whitewashing. The formula is CaO + H2O → Ca(OH)2
5. Why is the amount of gas collected in one of the test tubes in Activity 1.7 double of the amount collected in the other? Name this gas.
Answer: In activity 1.7, the water is broken down using electricity; this process is known as electrolysis. We know that the water (H2O) contains 2 hydrogen atoms and 1 oxygen atom. So when we split (H2O) it gives 2 parts of hydrogen gas (H2) and 1 part of oxygen gas (O2) Because of this, the amount of gas collected in one test tube is double due to hydrogen gas.
6. Why does the colour of copper sulphate solution change when an iron nail is dipped in it?
Answer: The copper sulphate solution is blue in colour. When an iron nail is dipped into the solution, then iron displaces copper from the solution, and copper gets deposited on the nail as a reddish-brown layer because the iron is more reactive than copper.
7. Give an example of a double displacement reaction other than the one given in Activity 1.10.
Answer: In chemistry when the two compounds mix, they can form new compounds. When silver nitrate (AgNO₃) and sodium chloride (NaCl) are mixed (both dissolved in water), then silver (Ag⁺) leaves nitrate (NO₃⁻) and joins chloride (Cl⁻), forming silver chloride (AgCl), a white solid that settles down. Sodium (Na⁺) stays with nitrate (NO₃⁻), forming sodium nitrate (NaNO₃), which remains dissolved in water.
The final reaction will be AgNO₃ + NaCl → AgCl↓ + NaNO₃.
8. Identify the substances that are oxidised and the substances that are reduced in the following reactions.
(i) 4Na(s) + O2(g) → 2Na2O(s)
(ii) CuO(s) + H2(g) → Cu(s) + H2O(l)
Answer:
(i) Sodium (Na) losing electrons means it is oxidised, and oxygen (O2) gaining the electrons means it is reduced.
Oxidised: Sodium (Na)
Reduced: Oxygen (O2)
(ii) Hydrogen (H2) losing electrons means it is oxidised, and copper (Cu in CuO) gains electrons, which means it is reduced.
Oxidised: Hydrogen (H2)
Reduced: Copper (Cu)
9. Which of the statements about the reaction below are incorrect?
2PbO(s) + C(s) → 2Pb(s) + CO2(g)
(a) Lead is getting reduced.
(b) Carbon dioxide is getting oxidised.
(c) Carbon is getting oxidised.
(d) Lead oxide is getting reduced.
(i) (a) and (b)
(ii) (a) and (c)
(iii) (a), (b) and (c)
(iv) all
Answer: (iii) (a), (b) and (c)
10. Fe2O3 + 2Al → Al2O3 + 2Fe
The above reaction is an example of a
(a) combination reaction.
(b) double displacement reaction.
(c) decomposition reaction.
(d) displacement reaction.
Answer: (d) displacement reaction.
11. What happens when dilute hydrochloric acid is added to iron fillings? Tick the correct answer.
(a) Hydrogen gas and iron chloride are produced.
(b) Chlorine gas and iron hydroxide are produced.
(c) No reaction takes place.
(d) Iron salt and water are produced.
Answer: (a) Hydrogen gas and iron chloride are produced.
12. What is a balanced chemical equation? Why should chemical equations be balanced?
Answer: When the same number of atoms of each element are present before and after the reaction, it is known as a balanced chemical equation. As per the rules of the Law of Conservation of Mass, matter cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction, so in the balanced equation nothing is lost or gained, only rearranged.
13. Translate the following statements into chemical equations and then balance them.
(a) Hydrogen gas combines with nitrogen to form ammonia.
(b) Hydrogen sulphide gas burns in air to give water and sulpur dioxide.
(c) Barium chloride reacts with aluminium sulphate to give aluminium chloride and a precipitate of barium sulphate.
(d) Potassium metal reacts with water to give potassium hydroxide and hydrogen gas.
Answer:
(a) Hydrogen + Nitrogen → Ammonia, The balanced chemical equation is: 3H2 + N2 → 2NH3
(b) Hydrogen sulphide + Oxygen → Water + Sulphur dioxide, The balanced chemical equation is:2H2S + 3O2 → 2H2O + 2SO2
(c) Barium chloride + Aluminium sulphate → Aluminium chloride + Barium sulphate. The balanced chemical equation is: 3BaCl2 + Al2(SO4)3 → 2AlCl3 + 3BaSO4↓
(d) Potassium + Water → Potassium hydroxide + Hydrogen, The balanced chemical equation is 2K + 2H2O → 2KOH + H2
14. Balance the following chemical equations.
(a) HNO3 +Ca(OH)2 → Ca(NO3)2 + H2O
(b) NaOH + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + H2O
(c) NaCl + AgNO3 → AgCl + NaNO3
(d) BaCl2 + H2SO4 → BaSO4 + HCl
Answer:
(a) HNO3 +Ca(OH)2 → Ca(NO3)2 + 2H2O
(b) 2NaOH + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + 2H2O
(c) NaCl + AgNO3 → AgCl + NaNO₃ (already balanced) (d) BaCl2 + H2SO4 → BaSO4 + 2HCl
15. Write the balanced chemical equations for the following reactions.
(a) Calcium hydroxide + Carbon dioxide → Calcium carbonate + Water
(b) Zinc + Silver nitrate → Zinc nitrate + Silver
(c) Aluminium + Copper chloride → Aluminium chloride + Copper
(d) Barium chloride + Potassium sulphate → Barium sulphate + Potassium chloride
Answer:
(a) Ca(OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3 + H2O
(b) Zn + 2AgNO3 → Zn(NO3)2 + 2Ag
(c) 2Al + 3CuCl2 → 2AlCl3 + 3Cu
(d) BaCl2 + K2SO4 → BaSO4 + 2KCl
16. Write the balanced chemical equation for the following and identify the type of reaction in each case.
(a) Potassium bromide(aq) + Barium iodide(aq) → Potassium iodide(aq) + Barium bromide(s)
(b) Zinc carbonate(s) → Zinc oxide(s) + Carbon dioxide(g)
(c) Hydrogen(g) + Chlorine(g) → Hydrogen chloride(g)
(d) Magnesium(s) + Hydrochloric acid(aq) → Magnesium chloride(aq) + Hydrogen(g)
Answer:
(a) Double Displancement Reaction: 2KBr(aq) + Bal2(aq) → 2Kl(aq) + Babr2(s)
(b) Decomposition Reaction: ZnCO3(s) → ZnO(s) + CO2(g)
(c) Combination Reaction: H2(g) + Cl2(g) → 2HCl(g)
(d) Displacement Reaction: Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) → MgCl2(aq) + H2(g)
16. What does one mean by exothermic and endothermic reactions? Give examples.
Answer: An exothermic reaction is a chemical reaction where heat is released to the surroundings. These reactions make the surrounding warmer. Example CH4 2)2 → CO2 + 2H2O + heat.
An endothermic reaction is a chemical reaction in which heat is absorbed from the surrounding. These reaction make the surroundings cooler. Example CaCO3 → CaO + CO2
17. Why is respiration considered an exothermic reaction? Explain.
Answer: Respiration is considered an exothermic reaction because respiration can release energy in the form of heat. In the process of respiration, then, glucose reacts with oxygen and produces carbon dioxide, water and energy, which helps the body to perform various activities. The chemical equation for respiration is: C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy.
18. Why are decomposition reactions called the opposite of combination reactions? Write equations for these reactions.
Answer: In the combination reaction, two or more substances combine to form a single product, but in the decomposition reaction, a single compound breaks down into two or more simpler substances. That way the decomposition reactions are considered the opposite of combination. An example of a combination reaction are: 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O (Hydrogen and oxygen combine to form water). An example of a decomposition reaction are: 2H2O → 2H2 + O2
19. Write one equation each for decomposition reactions where energy is supplied in the form of heat, light or electricity.
Answer:
(i) Decomposition by heat (Thermal decomposition): Calcium carbonate breaks into calcium oxide and carbon dioxide when heated
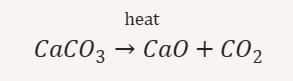
(ii) Decomposition by light (Photolytic decomposition: Silver chloride breaks into silver and chlorine gas in sunlight

(iii) Decomposition by electricity (Electrolytic decomposition): Water breaks into hydrogen and oxygen using electricity
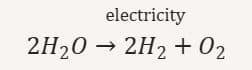
20. What is the difference between displacement and double displacement reactions? Write equations for these reactions.
Answer: A displacement reaction is a chemical reaction in which a more reactive element replaces a less reactive element from its compound. For example, Zn + CuSO4 → ZnSO4 + Cu
In a double displacement reaction, the chemical reaction in which two compounds exchange their ions to form two new compounds. For example, Na2SO4 + BaCl2 → BaSO4↓ + 2NaCl
21. In the refining of silver, the recovery of silver from silver nitrate solution involved displacement by copper metal. Write down the reaction involved.
Answer: Cu(s) + 2AgNO3(aq) → Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2Ag(s)
Note: The copper is more reactive than the silver. So, when the copper is placed in silver nitrate solution, it displaces silver from the solution and forms copper nitrate. Silver is recovered as a solid.
22. What do you mean by a precipitation reaction? Explain by giving examples.
Answer: The precipitation reaction is a type of chemical reaction where the two solutions react to form an insoluble solid, and it is known as precipitate. This solid separates out from the solution and settles at the bottom. This reaction is usually known as a double displacement reaction, where the ions are exchanged between two compounds.
- Example 1: CdSO4(aq) + K2S(aq) → CdS(s) + K2SO4(aq), The cadmium sulphate reacts with potassium sulphide to form cadmium sulphide as a yellow precipitate.
- Example 2: 2NaOH(aq) + MgCl2(aq) → 2NaCl(aq) + Mg(OH)2(s), The sodium hydroxide reacts with magnesium chloride to form magnesium hydroxide as a white precipitate.
23. Explain the following in terms of gain or loss of oxygen with two examples each.
(a) Oxidation
(b) Reduction
Answer:
- Oxidation: Oxidation is a chemical process in which a substance gains oxygen. For example, C + O2 → CO2 where carbon gains oxygen to form carbon dioxide. In the second example, 2Mg + O2 → 2MgO where magnesium gains oxygen to form magnesium oxide.
- Reduction: Reduction is a chemical process where a substance loses oxygen. For example, CuO + H2 → Cu + H2O where copper oxide loses oxygen to form copper. In the second example, Fe2I3 + 3CO → 2Fe + 3CO2 here, Iron (III) oxide loses oxygen to form iron.
24. A shiny brown coloured element ‘X’ on heating in air becomes black in colour. Name the element ‘X’ and the black coloured compound formed.
Answer: The shiny brown-coloured element ‘X’ is copper (Cu). When the copper is heated in air, then it reacts with oxygen to form copper oxide due to heat, forming a black-coloured compound called copper(II) oxide (CuO). The chemical reaction is 2Cu + O2 → 2CuO
25. Why do we apply paint on iron articles?
Answer: We apply paint on iron articles to prevent rusting. Iron reacts with moisture and oxygen and makes iron(III) oxide. But if painted, the surface does not come in contact with moisture and oxygen, then the iron can be prevented from rusting.
26. Oil and fat containing food items are flushed with nitrogen. Why?
Answer: The oil- and fat-containing food items are flushed with nitrogen gas to prevent oxidation, which helps to increase the shelf life of the food. If there is oxygen present in the package, then it will react with oils and fats and become rancid, which can change the taste and smell of the food. Nitrogen is an inert gas that does not react with food components.
27. Explain the following terms with one example each.
(a) Corrosion
(b) Rancidity
Answer:
- (a) Corrosion: Corrosion is a slow damaging process of metal when it reacts with air, moisture or chemicals. For example, iron reacts with oxygen and water to form rust. 4Fe + 3O2 + 6H2O → 4Fe(OH)3.
- (b) Rancidity: Rancidity happens when the oils and fats in food get spoilt due to reaction with oxygen. The food smells bad and tastes bitter. For example, chips and snacks are packed with nitrogen gas to stop oxygen in the package.
Disclaimer: We have provide you with the accurate handout of “Science Class 10 Chapter 1 NCERT Solutions“. If you feel that there is any error or mistake, please contact me at anuraganand2017@gmail.com. The above CBSE study material present on our websites is for education purpose, not our copyrights.
All the above content and Screenshot are taken from Science Class 10 NCERT Textbook, CBSE Sample Paper, CBSE Old Sample Paper, CBSE Board Paper and CBSE Support Material which is present in CBSEACADEMIC website, NCERT website This Textbook and Support Material are legally copyright by Central Board of Secondary Education or NCERT. We are only providing a medium and helping the students to improve the performances in the examination.
Images and content shown above are the property of individual organisations and are used here for reference purposes only. To make it easy to understand, some of the content and images are generated by AI and cross-checked by the teachers. For more information, refer to the official CBSE textbooks available at cbseacademic.nic.in.
