An Operating System (OS) is a vital software that acts as an interface between the computer hardware and the user. It manages hardware resources, provides a platform for applications to run smoothly, and ensures efficient operation of processes, memory, and storage.
Overview of an Operating System
Overview of OS: Windows 98, Windows NT, LINUX
The first operating system of microsoft develop was known as DOS (Disk operating system). The DOS was a single user interface. After DOS new operating system was introduce which was knon as windows 3.1, this operating system was Graphical User Interface. Later on Windows 95 was introduced, and after that Windows 98, a new version of the operating system, was introduced.
1. Windows 98
Windows 98 was released in 1998 by Microsoft. Windows 98 was basically designed for home users. Windows 98’s easy-to-use interface with features like Plug and Play and limited security and stability compared to later systems.
2. Windows NT
Windows NT was released in 1993 by Microsoft and built for business and professional use. Windows NT is a powerful operating system made for multitasking and multi-user environments. It uses preemptive multitasking, which means each task gets a fixed time to run before the next one starts.
Feature of Windows NT
- Virtual memory management: Provides extra memory by using part of the disc when RAM is full.
- Symmetric multiprocessing: Allows tasks to run on multiple CPUs at the same time for faster performance.
- Multithreading: Breaks a task into smaller parts (threads) so they can run in parallel, improving efficiency.
Architecture of Windows NT
Windows NT has a layered architecture with two main parts: User Mode and Kernel Mode. Users Mode helps to run an application, and Kernel Mode controls hardware and system resources. This helps to make windows NT stable, secure and portable.
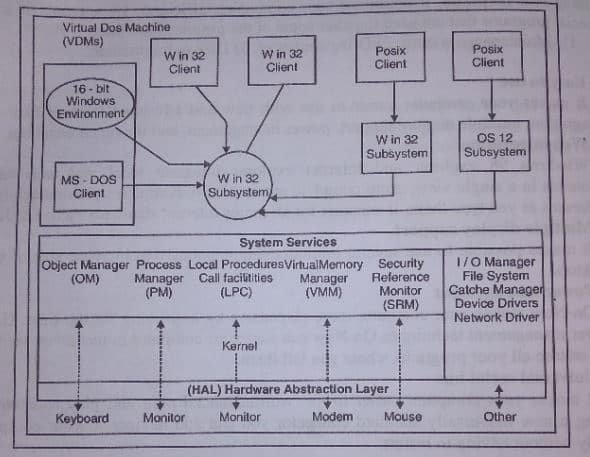
- User Mode: It helps to run an application on the computer. It also provides different environments to support multiple types of applications. For example,
- Win16-based client (Windows 3.x)
- MS-DOS client
- Win32 client (Windows 32-bit apps)
- POSIX client
- OS/2 client
- System Service Layer: This layer works as a bridge between User Mode and Kernel Mode. It provides important services like I/O Manager, Object Manager, Process Manager and Security Reference Monitor.
- Kernel Mode: This is the core of Windows NT and is responsible for direct hardware control and system-level operation.
- Kernel – manages low-level tasks like thread scheduling and interrupt handling.
- Executive Services – include memory management, I/O, and process control.
- Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL) – allows Windows NT to run on different hardware platforms by hiding hardware details.
Features of Windows NT
- NTFS (New Technology File System): It can store large files and keeps the data safe with permissions.
- Modular Architecture: Windows NT is divided into different subsystems and layers. The lowest layer is a hardware abstraction layer.
- Process Management: It helps to create and end processes and manages process execution. It can delete objects when the process is finished.
- Virtual Memory Management: It helps to use memory efficiently and allows programs to use more memory than physically available.
- Security: Ensures the file and data protection using permissions.
3. Linux
The first version of Linux was released in 1991 by Linus Torvalds. It is open-source operating system any one can use this operating sytem. The linux operating sytem known for stability, security and flexibility. This operating system is popular in servers and supercomputers and also available for desktops.
A feature of Linux
- Linux is network friendly: Linux gives high priority to the network support. Linux supports most of the major protocols. Linux supports Internet, Novell, Windows and AppleTalk networks.
- Linux is a multi-user: Linux is a multi-user operating system, which means more than one person can work on the computer at the same time.
- Linux is open: Linux being open means anyone can see how it works inside; the kernel (core of Linux), GNU tools, and basic utilities are all available.
- Linux is “free”: the Linux operating system is free for modification and for use.
Disclaimer: We have provide you with the accurate handout of “Overview of an Operating System“. If you feel that there is any error or mistake, please contact me at anuraganand2017@gmail.com. The above study material present on our websites is for education purpose, not our copyrights.
Images and content shown above are the property of individual organisations and are used here for reference purposes only. To make it easy to understand, some of the content and images are generated by AI and cross-checked by the teachers.
