Teachers and Examiners (CBSESkillEduction) collaborated to create the Introduction to Problem Solving Class 11 Questions and Answers. All the important Information are taken from the NCERT Textbook Computer Science (083) class 11.
Introduction to Problem Solving Class 11 Questions and Answers
1. Write pseudocode that reads two numbers and divide one by another and display the quotient.
Answer –
BEGIN
PRINT "Enter the first number:"
READ num1
PRINT "Enter the second number:"
READ num2
IF num2 ≠ 0 THEN
quotient ← num1 / num2
PRINT "The quotient is:", quotient
ELSE
PRINT "Error: Division by zero is not allowed."
ENDIF
END2. Two friends decide who gets the last slice of a cake by flipping a coin five times. The first person to win three flips wins the cake. An input of 1 means player 1 wins a flip, and a 2 means player 2 wins a flip. Design an algorithm to determine who takes the cake?
Answer –
Set p1 = 0
Set p2 = 0
For i in range(5):
Input coin
If coin = 1 then
p1 += 1
Elif coin = 2 then
p2 += 1
If p1 > 2 then
Print "Player 1 wins!"
Exit Loop
Elif p2 > 2 then
Print "Player 2 wins!"
Exit Loop3. Write the pseudocode to print all multiples of 5 between 10 and 25 (including both 10 and 25).
Answer –
BEGIN
FOR num := 10 TO 25 DO
IF num % 5 = 0 THEN
PRINT num
ENDIF
ENDFOR
END4. Give an example of a loop that is to be executed a certain number of times.
Answer –
BEGIN
FOR i := 1 TO 10 DO
PRINT i
ENDFOR
END5. Suppose you are collecting money for something. You need ` 200 in all. You ask your parents, uncles and aunts as well as grandparents. Different people may give either ` 10, ` 20 or even ` 50. You will collect till the total becomes 200. Write the algorithm.
Answer –
Step 1: Start
Step 2: Set money := 0
Step 3: WHILE money < 200 DO
Step 3.1: INPUT input_money
Step 3.2: money = money + input_money
Step 4: END WHILE
Step 5: PRINT "Total ₹200 collected!"
Step 6: Stop6. Write the pseudocode to print the bill depending upon the price and quantity of an item. Also print Bill GST, which is the bill after adding 5% of tax in the total bill.
Answer –
BEGIN
INPUT item_name
INPUT price
INPUT quantity
CALCULATE bill := price * quantity
PRINT "Total Bill:", bill
CALCULATE tax := bill * (5 / 100)
CALCULATE GST_Bill := bill + tax
PRINT "Bill with GST (5%):", GST_Bill
END7. Write pseudocode that will perform the following:
a) Read the marks of three subjects: Computer Science, Mathematics and Physics, out of 100
b) Calculate the aggregate marks
c) Calculate the percentage of marks
Answer –
BEGIN
INPUT computer, maths, phy
COMPUTE aggregate := computer + maths + phy
COMPUTE percentage := (aggregate / 300) * 100
PRINT "Aggregate Marks:", aggregate
PRINT "Percentage:", percentage
END8. Write an algorithm to find the greatest among two different numbers entered by the user.
Answer –
BEGIN
INPUT num1, num2
IF num1 > num2 THEN
PRINT "The greater number is:", num1
ELSE IF num2 > num1 THEN
PRINT "The greater number is:", num2
ELSE
PRINT "Both numbers are equal."
ENDIF
END9. Write an algorithm that performs the following: Ask a user to enter a number. If the number is between 5 and 15, write the word GREEN. If the number is between 15 and 25, write the word BLUE. if the number is between 25 and 35, write the word ORANGE. If it is any other number, write that ALL COLOURS ARE BEAUTIFUL.
Answer –
BEGIN
INPUT num
IF num >= 5 AND num < 15 THEN
PRINT "GREEN"
ELSE IF num >= 15 AND num < 25 THEN
PRINT "BLUE"
ELSE IF num >= 25 AND num < 35 THEN
PRINT "ORANGE"
ELSE
PRINT "ALL COLOURS ARE BEAUTIFUL"
ENDIF
END10. Write an algorithm that accepts four numbers as input and find the largest and smallest of them.
Answer –
BEGIN
INPUT num1, num2, num3, num4
SET max := num1
SET min := num1
FOR each num in {num2, num3, num4} DO
IF num > max THEN
SET max := num
ENDIF
IF num < min THEN
SET min := num
ENDIF
ENDFOR
PRINT "Largest number:", max
PRINT "Smallest number:", min
END11. Write an algorithm to display the total water bill charges of the month depending upon the number of units consumed by the customer as per the following criteria:
- for the first 100 units @ 5 per unit
- for next 150 units @ 10 per unit
- more than 250 units @ 20 per unit
Also add meter charges of 75 per month to calculate the total water bill .
Answer –
BEGIN
INPUT units
SET bill := 0
IF units > 250 THEN
CALCULATE bill := (100 * 5) + (150 * 10) + ((units - 250) * 20)
ELSE IF units > 100 THEN
CALCULATE bill := (100 * 5) + ((units - 100) * 10)
ELSE
CALCULATE bill := units * 5
ENDIF
CALCULATE totalBill := bill + 75
PRINT "Total Water Bill:", totalBill
END12. What are conditionals? When they are required in a program?
Answer – Conditionals are used when programs need to make decisions; they help to check if the input given is valid or not. It also helps to execute specific actions based on user choice, for example, checking even or odd.
14. Following is an algorithm for going to school or college. Can you suggest improvements in this to include other options?
Reach_School_Algorithm
a) Wake up
b) Get ready
c) Take lunch box
d) Take bus
e) Get off the bus
f) Reach school or college
Answer –
Reach_School_Algorithm
a) Wake up
b) Brush your teeth
c) Take bath
d) Dress up
e) Eat breakfast
f) Pack your school bag
g) Take lunch box
h) Choose transport option:
- IF using bus THEN take the bus
- ELSE IF walking THEN start walking
- ELSE IF cycling THEN ride your bicycle
- ELSE IF using carpool THEN get in the car
i) Travel to school or college
j) Reach school or college 15. Write a pseudocode to calculate the factorial of a number (Hint: Factorial of 5, written as 5!=5 4 3 21 ×××× ).
Answer –
BEGIN
INPUT num
SET fact := 1
SET i := 2
WHILE i <= num DO
CALCULATE fact := fact * i
INCREASE i by 1
ENDWHILE
PRINT "Factorial of", num, "is:", fact
END16. Draw a flowchart to check whether a given number is an Armstrong number. An Armstrong number of three digits is an integer such that the sum of the cubes of its digits is equal to the number itself. For example, 371 is an Armstrong number since 3**3 + 7**3 + 1**3 = 371.
Answer –
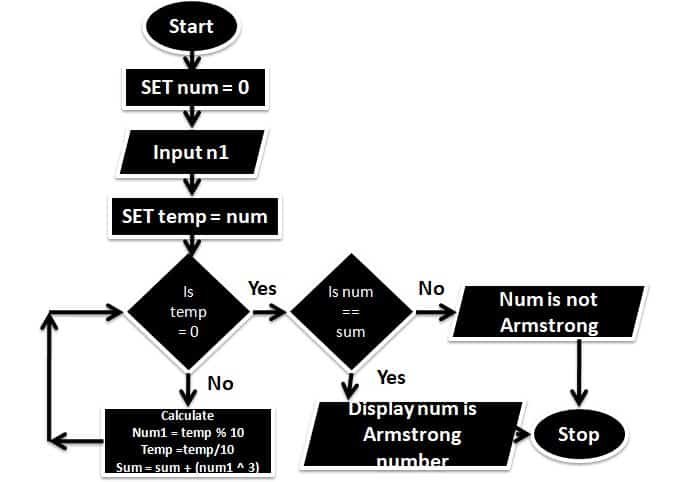
17. Following is an algorithm to classify numbers as “Single Digit”, “Double Digit” or “Big”.
Classify_Numbers_Algo
INPUT Number
IF Number < 9
"Single Digit"
Else If Number < 99
"Double Digit"
Else
"Big"Verify for (5, 9, 47, 99, 100 200) and correct the algorithm if required
Answer –
INPUT Number
IF Number <= 9 THEN
PRINT "Single Digit"
ELSE IF Number <= 99 THEN
PRINT "Double Digit"
ELSE
PRINT "Big"
ENDIF18. For some calculations, we want an algorithm that accepts only positive integers upto 100.
Answer –
BEGIN
INPUT number
IF (number > 0) AND (number <= 100) AND (number is an integer) THEN
ACCEPT
ELSE
REJECT
ENDIF
ENDComputer Science Class 11 Questions and Answers
- Computer Systems and Organisation
- Introduction to problem solving
- Getting Started with Python
- Flow of Control statements in Python
- String in Python
- Lists in Python
- Tuples and Dictionary in Python
- Society, Law and Ethics
Disclaimer: We have taken an effort to provide you with the accurate handout of “Introduction to Problem Solving Class 11 Questions and Answers“. If you feel that there is any error or mistake, please contact me at anuraganand2017@gmail.com. The above CBSE study material present on our websites is for education purpose, not our copyrights. All the above content and Screenshot are taken from Computer Science Class 11 NCERT Textbook and CBSE Support Material which is present in CBSEACADEMIC website, This Textbook and Support Material are legally copyright by Central Board of Secondary Education. We are only providing a medium and helping the students to improve the performances in the examination.
Images and content shown above are the property of individual organizations and are used here for reference purposes only.
For more information, refer to the official CBSE textbooks available at cbseacademic.nic.in
