Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is an integrated management system that helps organizations plan, manage, and automate their core business processes using a single centralized software platform. ERP combines various functional areas such as finance, human resources, production, inventory, sales, and customer management into one unified system.
Enterprise Resource Planning Class 12 Notes
Introduction
Most of the organizations are moving to Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) packages as a solution to their information management problem.
What is an enterprise?
“An enterprise is a group of people and other resources working together for a common goal.” An enterprise acts as a single entity, and an organization is divided into different units based on the operations performed in it.
What is a resource?
A resource is anything that can be used to meet human needs, achieve goals, or support activities—whether it’s natural, financial, human, or informational. There are different types of resources in an enterprise, like men, material, money, and machines.
What is planning?
Planning helps managers to improve future performance by establishing objectives and selecting a course of action for the benefit of the organization.
The concept of Enterprise Resource Planning
Many enterprises, such as finance, sales, inventory, HR, and production, work independently. Every department maintains its own data and system. This information is usually restricted to the other department; because of this, some basic problems can occur:
- Duplication of the data
- Other departments cannot access important information.
- In the manual it takes a lot of time for giving information from one department to another.
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) is a centralized software system that integrates all core business processes.
It combines:
- Accounts Payable (finance)
- Stock Control Systems (inventory)
- Order Monitoring Systems (sales/production)
- Customer Databases (CRM)
For better benefit and efficiency, each department must know what the other departments are doing. An enterprise can be considered as a system and all its departments as its subsystems. ERP replaces the old standalone computer systems in each area of an enterprise, such as finance, human resources, manufacturing, sales, etc. For example, the finance department can use ERP to see if any sales order has been shipped from the warehouse so as to make further payments.
Functional Units of ERP
The ERP system helps the management in making the planning process more productive and efficient. The entire ERP package contains many modules or subunits.
- Financial module: It can collect financial data from various functional departments and generate valuable financial reports. Financial reports include balance sheets, general ledgers, trial balances, financial statements, etc.
- Manufacturing module: This module of ERP enables an enterprise to combine technology and business processes to get integrated solutions.
- Production planning module: This module identifies the materials required and allocates optimal resources using data and sales forecasting with the sales data.
- HR module: HR stands for Human Resource. The HR module maintains an updated and complete employee database, including personal information, salary details, attendance, performance, promotion, etc., of all employees in an enterprise.
- Inventory control module: This module covers processes of maintaining the appropriate level of stock in the warehouse.
- Purchasing module: The purchase module helps for generating purchase orders, evaluating the supplier, and billing.
- Marketing module: The marketing module is used for monitoring and tracking customer orders, increasing customer satisfaction, and eliminating credit risks.
- Sales and distribution module: This module helps for tracking inquiries, order placement, order scheduling, dispatching, and invoicing.
- Quality management module: This module is used for managing the quality of the product.
An ERP system integrates separate business functions—material management, product planning, sales, distribution, financial and others—into single applications.
1. Product Life Cycle Management (PLM)
PLM is the process of managing the entire life cycle of a product from its conception, design, and manufacturing to service and disposal. It ensures that every stage of the product’s journey is monitored and optimized.
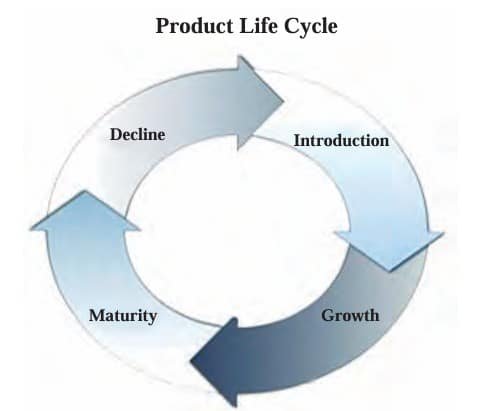
General schematic diagram of a four-stage product life cycle. The information gathered from the product life cycle will help an enterprise to understand the status of a product in the existing market.
2. Management Information System (MIS)
In MIS there are three components: management, information, and system. MIS is a computer-based system that provides managers and other employees with the information they need to make decisions.
3. Supply Chain Management (SCM)
The supply chain includes all activities involved in moving goods from the supplier to the customer. It begins with collecting raw materials and ends when the consumer receives the product.
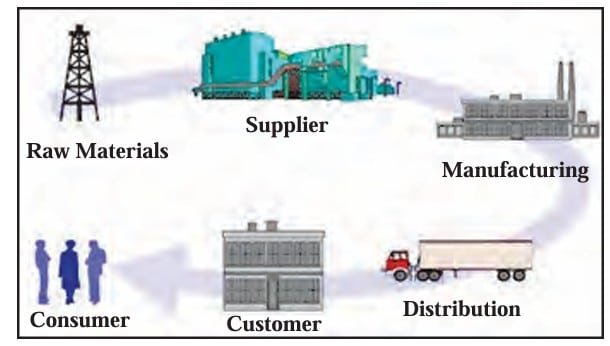
4. Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
CRM is a term applied to processes implemented by a company to handle its contact with its customers. CRM covers methods and technologies used by companies to manage their relationships with clients. It is not only the responsibility of the customer service group or IT team. It touches all major parts of an enterprise.

5. Decision Support System (DSS)
Decision Support Systems are interactive, computer-based systems that aid users in judgment and choice activities. It is a computer program application that analyzes business data and presents it so that users can make business decisions more easily.
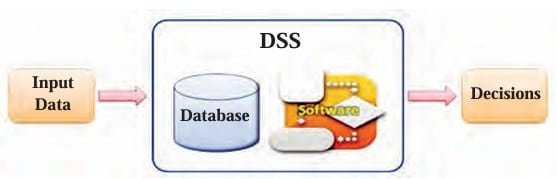
ERP solution providers/ERP packages
Selection of an ERP package is very crucial in the implementation of an ERP system. If an ERP package is chosen correctly, implemented judiciously, and used efficiently, the productivity of the enterprise will be increased. Some of the popular ERP packages are Oracle, SAP, Odoo, Bitrix24, etc., Microsoft Dynamics, and Tally.
- Oracle: Oracle was originally known for its database system rather than its ERP system. The ERP310 package from Oracle provides a strong finance and accounting module.
- SAP: SAP stands for Systems, Applications, and Products for data processing. SAP developed Customer Relationship Management (CRM), Supply Chain Management (SCM), and Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) software.
- Odoo: Odoo is an open-source ERP tool that offers capabilities such as CRM, HR, accounting, sales, document management, inventory management, invoicing, project management, The software is available in both cloud-based and on-premise options.
- Bitrix24: Bitrix24 is a free online ERP solution that works for businesses of all sizes. It includes apps for customer relationship management (CRM), project management, task management, employee management, document management, and human resource (HR) management.
- Microsoft Dynamics: Microsoft Dynamics is part of Microsoft business solutions. It provides a group of enterprise resource planning products primarily aimed at midsized enterprises.
- Tally ERP: Tally solutions Pvt Ltd is an Indian software company.Solutions Tally ERP is business accounting software for accounting, inventory, and payroll systems.
ERP and Internet
Traditionally, ERP systems were installed on-premise (within a company’s own servers and data centers). The new trend is that vendors now make ERP software available via the internet. Web-based ERP provides a cost-effective solution for enterprises. End users can access ERP tools from anywhere, without needing complex local installations. Many ERP systems today run in the cloud as software as a service (SaaS).
Benefits of ERP
There are so many advantages to implementing an ERP system in an enterprise. Some of the major benefits are briefly explained:
- Improved resource utilization: An enterprise can plan and manage its resources effectively by installing ERP software. So the wastage or loss of all types of resources can be reduced, and improved resource utilization can be ensured.
- Better customer satisfaction: Using an ERP system, a customer will get more attention and service from an enterprise without spending more money and time.
- Provides accurate information: the enterprise has to plan and manage the future cleverly. To achieve this, an enterprise needs high-quality, relevant, updated, and accurate information.
- Decision-making capability: Accurate and relevant information given to decision-makers will help them to take better decisions for running a system more smoothly.
- Increased flexibility: An ERP system allows organizations to be more flexible so that they can more easily adapt and capitalize on new business opportunities.
- Information integrity: The entire information about an enterprise is stored in a centralized database so that complete visibility into all the important processes across various departments of an organization can be achieved. Limitations in ERP implementation
- High cost: The cost of ERP software configuration and implementation is very high.
- Requirement of additional trained staff: To run an ERP system, trained and experienced employees are to be appointed in the enterprise.
- Operational and maintenance issues: Implementation of an ERP needs major changes in the current process of an enterprise.
- Security Control: Implementation of an ERP needs to follow security measures at each and every stage.
Future of ERP
- Artificial intelligence services are impacting every facet of business operations.
- The concept of machine learning is going to revolutionize ERP. It will help businesses to achieve high levels of automation.
- Embedded business intelligence, analytics, and data management features built into ERP will be the future of ERP.
- There will be more ERP transactions triggered by sensors and external systems or devices.
Disclaimer: We have provide you with the accurate handout of “Enterprise Resource Planning Class 12 Notes“. If you feel that there is any error or mistake, please contact me at anuraganand2017@gmail.com. The above study material present on our websites is for education purpose, not our copyrights.
All the above content and Screenshot are taken from Information Technology Class 12 Textbook and MSBSHSE (HSC) Support Material which is present in MSBSHSE (HSC) website, This Textbook and Support Material are legally copyright by Maharashtra State Bureau of Textbook Production and Curriculum Research, Pune. We are only providing a medium and helping the students to improve the performances in the examination.
Images and content shown above are the property of individual organisations and are used here for reference purposes only. To make it easy to understand, some of the content and images are generated by AI and cross-checked by the teachers. For more information, refer to the official website.
