This chapter, Introduction to Yoga and Yogic Practices, from Class 12 Yoga explores the holistic science of yoga. These notes provide a simplified overview of key topics like the definition of yoga, its importance in modern life, elements of yogic practices, and their benefits for physical and mental well-being.
Introduction to Yoga and Yogic Practices Class 12 Notes
Shatkarma Meaning, Purpose and their Significance in Yoga Sadhna
Shatkarma (शतकर्मा) is also called ‘shatkriya’, which means ‘six actions’ in Sanskrit. These six yogic techniques are used to cleanse the body and prepare it for deeper yoga practices like asana, pranayama and meditation. These yogic techniques help to remove toxins, balance the digestive, respiratory and excretory systems and improve mental clarity. The six shatkarmas are:
- Kaphalabhati (कपालभाति) – Fast breathing helps to clean lungs and forehead.
- Trataka (त्रटकम्) – Looking at a candle without blinking.
- Neti (नेति) – Nasal cleansing.
- Dhauti (धौति) – Cleaning of the digestive system and stomach.
- Nauli (नौली) – moving your stomach muscles in a round motion.
- Basti (बस्ती) – Cleaning your intestines.
Purpose and Significance:
- To maintain balance between tri-dosh Vata, Pitta and Kapha
- Improve the chemical functioning of the body and mind. Balance prana stream in Ida (left nostril) and Pingala Nadi (right nostril). From that point, reviving the course through Sushumna Nadi (both the nostrils).
- To eliminate toxins from our body.
- To purify our body from the inside and keep our body healthy.
- Contribute strength to our internal systems like the respiratory system, blood circulation, digestive system, and immune system.
1. Kapal Bhati (कपालभाति)
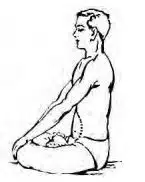
Benefits
- This is a great cleanser for the respiratory passage, including the sinuses.
- It improves respiratory function and promotes circulation.
- It improves balance.
- It removes acidity and gas-related problems.
- It cures sinus, asthma, and hair loss.
Precautions
- Slipped disc patients, and asthma patients should avoid it.
- It should not be performed during menstruation
2. Trataka (त्रटकम्)
Trataka is a yogic eye-cleansing and concentration technique. The word ‘Trataka’ means ‘steady gazing’ in Sanskrit. In this practice, place a light source like a flame at a manageable distance from yourself. Then look at the point of the flame without blinking your eyes until tears start to flow.
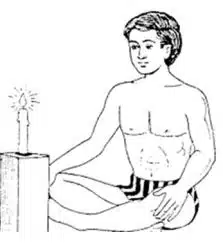
Benefits
- It improves the eyesight and tones up the visual mechanism.
- It also helps in increasing concentration.
- It helps to calm the mind and remove distractions.
Precautions
- People suffering from epilepsy should not practice trataka on a candle. Kids should avoid pract
3. Neti (नेति)
A nasal cleansing procedure which purifies the nasal passages and prevent the onset of sinuses. It can be performed in two ways: either using a neti pot to purify the passages with salt called Jala Neti, or using a thread passed through the nostrils and out from the mouth called Sutra Neti.
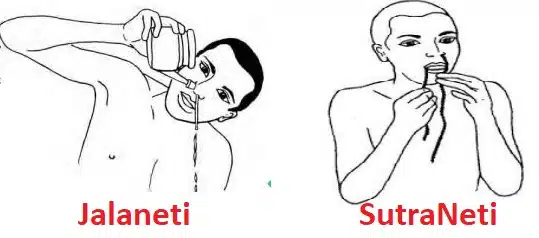
Benefits
- Jal Neti removes excess mucus and impurities inside the nasal cavity.
- It reduces inflammatory conditions and builds up resistance to the atmosphere.
- Helps in preventing cold and cough.
- If practiced daily, it can cure headache and migraine.
4. Dhauti (धौति)
It is a cleansing process for the alimentary canal, including mouth, oesophagus, stomach, intestines and rectum.
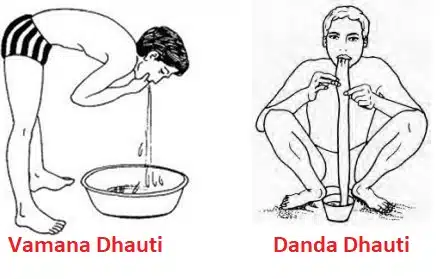
Benefits
- It removes all unwanted contents from the stomach including excess secretions of the stomach and undigested food.
- It cures the problem of gas, acidity and indigestion.
- It helps to cure cough and sore throat.
5. Nauli (नौली)
It is cleansing practice of abdominal muscles to massage and clean stomach and small intestine. This is one of the most difficult techniques to master. Nauli can be performed by Pachima nauli, Madhyama nauli and Vama
nauli.

Benefits
- It tones and massages the entire abdominal area, including muscles, nerves, intestines, reproductive, urinary and excretory organs.
- It is a training of internal organs such as stomach, liver, spleen, urinary bladder, pancreas, gall bladder, and large and small intestine.
- It helps to remove the toxic materials from the digestive tract.
6. Basti (बस्ती)
It is a method for purifying the large intestine either with or without water.

Benefits
- Basti helps in are coming gastric troubles, indigestion and purification of the large intestine absorbs the nutrients and water from undigested waste.
Introduction to Yogasanas: Meaning, Principles and their Health Benefits
Yogasanas have two words, yoga and asana. Yoga originated in Indian philosophy 5000 years ago. The aim of yoga is spiritual, mental, and physical well-being. Nowadays yoga helps to reduce stress, anxiety, and depression. Yoga is not a physical exercise; it is a complete lifestyle. Asana means a stable and comfortable posture that promotes physical stillness and mental calmness.
Physiologically speaking, there are three conditions on which the human body remains healthy. They are –
- Constant supply of adequate nourishment to the endocrine glands and other tissues.
- Effective removal of waste products.
- Proper functioning of all the nerve connections.
Practice of yogic asanas, inattentively, may cause several injuries. Therefore, some important points to be kept in mind while performing yogic asanas are as follows:
- Asanas should not be done by only guidance of an experienced teacher.
- Asanas should be performed slowly and step by step.
- The final posture should be held for some time, but not beyond the capacity.
- In case of injuries or illness, the teacher should be consulted and followed.
- The place should be clean and well ventilated.
- Always breathe through the nose.
- Do not practice beyond your capacity.
- Concentrate on the effects of the asanas on the mind and the body.
- Shavasana may be performed at any point of time during asana practice, especially when feeling physically and mentally tired.
- After completing shatkarma, asanas should be performed, followed by pranayamas.
Practice Guidelines for Asanas
- Time: Early morning is the best time for practicing asanas. It should be kept in mind that after taking lunch up to 4 hours, no asanas, mudras or pranayamas should be done.
- Place: Practicing yoga asanas in a well-ventilated place or open air place is recommended. We should avoid artificial air.
- Duration of asanas: It depends on the availability of the time. Normally, a healthy man should practice asanas for 45 minutes every day, and pranayamas for 15 to 20 minutes. If kriyas are to be performed, 30 minutes can be given for them.
- Restricted conditions: After going through a major surgery, it is advised not to perform asanas within 6 months. One can restart the practice under the guidance of the teacher after 6 months.
- Limitation for women: Normally women during first 3 months of pregnancy should avoid all the asanas.
Types of Asanas
Asanas are an important component of yoga; the asana is designed not only for physical health but also helps to develop mental health. Based on the body posture and purpose, asanas are classified into four main types.
- Supine Lying Asanas: Supine Lying Asanas are helpful for improving flexibility, relaxation, and digestion. To perform lying on the back. Examples: Chakrasana, Sarvangasana, and Pawanmuktasana.
- Prone Lying Asanas: Prone lying asanas are helpful in strengthening the back and also improving spinal alignment. This asana is performed lying on the stomach. Example: Bhujangasana, Salabhasana, and Dhanurasana.
- Sitting Asanas: Sitting asanas are ideal for meditation and breathing exercises; they are helpful for building focus and posture control. Example: padmasana, vajrasana, and paschimottanasana.
- Standing Asanas: Standing asanas focus on improving balance, endurance, and flexibility. It is very beneficial for beginners. Example: Tadasana, Trikonasana, and Utkatasana.
Introduction of Pranayama and Dhyana and their health benefits
Pranayama is a science that helps to improve the flow of energies in the body using breathing. It helps us control our breath and calm the mind and body. The practice of pranayama includes three main steps:
- Purak: breathing in
- Kumbhaka: holding the breath
- Rechaka: breathing out
These are the pranayama mentioned in the Hatha Yoga Texts.
- Anulom- vilom
- Suryabhedana,
- Ujjayi,
- Bharmari,
- Sheetkari,
- Sheetali,
What is Hatha Yoga Texts? Hatha Yoga Texts is written by Yogi Svatmarama in the 15th century; It covers asanas, pranayama, mudras, and meditation.
Before starting pranayama, follow the following practice given below:
- External environment: Select a clean, quiet, and well-ventilated space.
- Right season to begin the practice of pranayama: Ideal seasons for pranayama are March to April (spring) and September to October (autumn).
- Right time: Morning is the best-suited time to practice pranayamas.
- Seat or Asana: The seat should be soft, thick, and comfortable.
- Asana: Asanas such as Padmasana, Siddhasana, Vajrasana, and Sukhasana are considered the most suitable postures for the practice of pranayama.
(Meditation) Dhyana and their health benefits
Meditation means sitting quietly and keeping your mind calm and peaceful. It is a state of deep awareness where the mind becomes calm and still, beyond all thoughts and senses. The main purpose of meditation is to stop too many thoughts and feel peaceful inside, without falling asleep.
Benefits of meditation:
- Reduce stress.
- Increases concentration
- Bring peace and happiness.
- Helps to make focus
- Can improve health
Types of Meditation (Dhyan)
There are many types of meditation, and every meditation has its own way. Some of the common types of meditation are:
- Mindfulness Meditation: In this meditation you just observe your thoughts, sounds, and feelings without reacting.
- Spiritual Meditation: In this meditation you have to sit quietly and connect with God through prayer or reflection.
- Focused Meditation: In this meditation you have to focus on any one thing, like a candle, breath, or sound. It helps to clear your mind of all thoughts and stresses.
- Movement Meditation: In this meditation you have to use gentle body movement, like walking slowly, to stay aware and peaceful.
- Mantra Meditation: In this meditation you have to repeat a calming word or sound like OM again and again.
Benefits of Meditation (Dhyan)
- A feeling of tranquility and freedom in daily life.
- Reduction in psychological disorders like anxiety, tiredness and depression etc.
- Relief from various pains, such as headache, joint pains etc.
- Highly beneficial in insomnia.
- Increase in patience, and affection and sympathy for others.
- Growth in devotion and belief in the Supreme Being.
- A stronger urge and aptitude for service and cooperation in social life.
Identify career opportunities in Yoga
- To accredit the students to become competent and committed professionals willing to perform as yoga instructor, yoga teacher, yoga therapist, resource officer in yoga, yoga instructor and naturopathy doctor.
- To accredit the students to have good health, to practice mental hygiene, to possess emotional stability, to integrate moral values, to attain higher level of consciousness
- To acquaint students with the theory and practical knowledge of yogasana, Bandhas, Mudras and Pranayama.
- To enable students to prepare the yoga programme, yoga demonstrator etc.
Disclaimer: We have taken an effort to provide you with the accurate handout of “Introduction to Yoga and Yogic Practices Class 12 Notes“. If you feel that there is any error or mistake, please contact me at anuraganand2017@gmail.com. The above CBSE study material present on our websites is for education purpose, not our copyrights. All the above content and Screenshot are taken from Yoga Class 12 NCERT Textbook, CBSE Sample Paper, CBSE Old Sample Paper, CBSE Board Paper and CBSE Support Material which is present in CBSEACADEMIC website, NCERT websiteThis Textbook and Support Material are legally copyright by Central Board of Secondary Education. We are only providing a medium and helping the students to improve the performances in the examination.
Images and content shown above are the property of individual organizations and are used here for reference purposes only.
For more information, refer to the official CBSE textbooks available at cbseacademic.nic.in
