Variables Using Block Coding Class 6 Notes, Variables are used in block coding to store information that can change while a program is running. Just like a box that holds a value, a variable can store numbers, text, or other data. In block-based coding platforms, variables are created and used by dragging blocks instead of typing code. Variables help programs remember scores, names, counts, and many other important details.
Variables Using Block Coding Class 6 Notes
What are variables?
A variable is just like a container that can contain a value. Each variable has a name, and this name is used to store the values, which can change during execution. For example, age, marks, and total.
Scope of a Variable
Scope means the part of the program where a variable can be used. If a variable is declared inside a function, it can only be used there, and you cannot access a variable outside its scope.
Naming Variable
Each variable must have a unique name. The name defines what the variable contains. The same variable name should not be written twice in the program.
If variable named as “a” is equal to 2 and variable named as “b” is equal to 2, performing add operation on “a” and “b” is going to result into an output as “4”.
Below are some rules for naming a variable in python:
- A variable name cannot start with a number; it must start with an alphabet or the underscore (_) sign.
- Variable name is case sensitive. Sum and sum are different variables.
- A variable can only contain alpha numeric characters and underscore.
Data types in variables
A data type tells the computer what kind of value a variable holds. The declaration of a variable in a program contains two components—the name of the variable and its type. The common data types that we can use in programming:
- Integer
- Floating-point number
- Character
- String
- Boolean
1. Integer Data Type
Integer data type variables store integer values only. They store whole numbers which have zero, positive and negative values but not decimal values. Variables of the integer data type are only capable of holding single values.
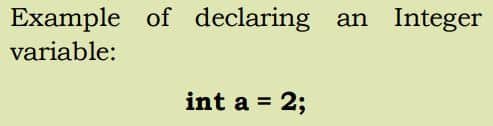
2. Floating Point Number Data Type
Floating-point numbers are used to store decimal values. They hold real numbers with decimal values.
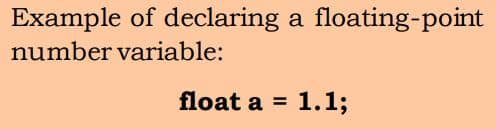
There is another type of floating-point number known as a “double” data type, which is used to store even bigger values.

3. Character Data Type
Character type variables are used to store character values. The character data type is the smallest data type in programming. Any character values can be declared as a char variable.
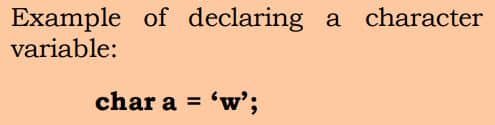
4. String Data Type
To extend the character data type, a user may have a requirement to store and perform an operation on a sequence of characters. In such cases, the String data type is present to fit the gap. The String data type stores value in a sequence of characters i.e. in String format.

5. Boolean Data Type
There is a subtype of Integer Data Type called “Boolean Data Type”, which stores values in Boolean type only i.e. “true” or “false”.

Note: In some programming languages like python, there is no command to declare variables. A variable is created the moment you first assign a value to it. If you want to specify the data type of variable this can be done using casting.
y = str(7)
z = int(7)
a = float(7)
y will be saved as ‘7’
z will be saved as 7
a will be saved as 7.0Performing Operations on Variables
After declaring the data types in programming, now let us move ahead and understand what operations we can perform on the data types and how do we perform these operations:
1. Arithmetic Operations
An arithmetic operation combines two or more numeric expressions using the Arithmetic Operators to form a resulting numeric expression. The basic operators for performing arithmetic are the same in many computer languages:
- Modulus (Remainder)
- Addition
- Subtraction
- Multiplication
- Division
2. Assignment operators
Assignment operators are used to assign values to variables. Different assignment operators are shown below:
| Operators | Example |
|---|---|
| = | Example: a=50 |
| += | Example: x += y |
| -= | Example: x -= y |
| *= | Example: x *= y |
| /= | Example: x /= y |
3. Increment operator
Increment operator adds one to the value.
Example:
A = 8
B = A++
The output of B will be 9 (A+1)A++ has the same meaning as A=A+1
4. Decrement operator
Decrement operator subtracts one from the value.
Example:
A = 8
B = A--
The output of B will be 7 (A-1)A– has the same meaning as A=A-1
Objective Type Questions
1. An integer data type can hold decimal values.
a. True
b. False
2. Variables must be defined with a name and a data type before they can be used.
a. True
b. False
3. Which of the following is not a valid variable name in Python?
a. _test
b. 11 test
c. Test13
d. Test_2
4. Fill in the blanks to declare sum equal to a + b (int _ = a _b).
a. Sum, +
b. Var,
c. Bool, +
d. Add +
5. Which of the following data types is used to store decimal values?
a. Integer
b. Float
c. Boolean
d. String
6. How many times should a data type be mentioned for a variable?
a. Everywhere the variable is used
b. When entering a variable’s value
c. When printing a variable’s value
d. Only once, when declaring the variable
7. Which of the following symbols is used to multiply variables?
a. *
b. +
c. x
d. %
8. What is the alternative to y=y+9?
a. y=x+9
b. y+=9
c. y-=9
d. x=+9
9. Y++ has the same meaning as
a. Y=Y+1
b. X=+2
c. y-=6
d. X=x-5
10. Which of the following symbols is used to find the remainder?
a. *
b. +
c. x
d. %
11. Define variables in programming.
Answer: A variable is just like a container that can contain a value. Each variable has a name, and this name is used to store the values, which can change during execution. For example, age, marks, and total.
12. Can we declare two variables in a program with the same name?
Answer: No, we are not able to declare two variables with the same name in the program. The variable with the same name can exist in different scopes.
13. What are the common data types in programming?
Answer: The common data types in programming languages are
- Integer (int) → whole numbers (e.g., 5, -12)
- Float/Double → decimal numbers (e.g., c.14, -0.001)
- Character (char) → single characters (e.g., ‘A’, ‘z’)
- String → sequence of characters (e.g., “Hello”)
- Boolean (bool) → true/false values
14. Name a data type that can store exponential values.
Answer: Float or double can store exponential values. These are used for scientific notation of very large or small numbers.
15. Write the pseudocode to perform an addition operation on two variables in a program.
Answer: The pseudocode to perform an addition operation on two variables in a program is
BEGIN
DECLARE num1, num2, sum
SET num1 = 10
SET num2 = 20
sum = num1 + num2
PRINT "The sum is: ", sum
ENDDisclaimer: We have provide you with the accurate handout of “Variables Using Block Coding Class 6 Notes“. If you feel that there is any error or mistake, please contact me at anuraganand2017@gmail.com. The above CBSE study material present on our websites is for education purpose, not our copyrights.
All the above content and Screenshot are taken from Coding Code 910A Class 6 CBSE Textbook, CBSE Sample Paper, CBSE Old Sample Paper, CBSE Board Paper and CBSE Support Material which is present in CBSEACADEMIC website, NCERT website This Textbook and Support Material are legally copyright by Central Board of Secondary Education or NCERT. We are only providing a medium and helping the students to improve the performances in the examination.
Images and content shown above are the property of individual organisations and are used here for reference purposes only. To make it easy to understand, some of the content and images are generated by AI and cross-checked by the teachers. For more information, refer to the official CBSE textbooks available at cbseacademic.nic.in.
