A bank is a financial institution that accepts deposits from the public and provides loans and credit facilities to individuals, businesses, and organizations. Banks play a crucial role in the economy by ensuring the smooth flow of money, safeguarding savings, and promoting trade and commerce.
What is a Bank Class 9 Notes
What is a bank? What does it do?
A bank is a financial institution that accepts deposits from the public, provides loans to people, and handles millions of customer transactions each day, or you can say that a bank is a place where someone can deposit money for saving and safekeeping and withdraw it when necessary. The bank gives a loan to the borrower (the account holder in this case). Interest has to be paid for the loan. For a salaried person a loan is deducted in Equated Monthly Instalments (EMI).
Origin of banking
The banking process started in Babylonia before 2000 BC in temples, and this is a place where valuable things can be safeguarded. Greeks introduced book-based money transfer. After the Roman Empire fell, Jews and Templars became key bankers. Later on Italians led the banking world in Europe.
In India, the 1809 Bank of Bengal was the first Indian bank. The Government of India started the Imperial Bank of India in 1921; later, in the year 1955, it was renamed the State Bank of India. The government of India nationalised all large banks in the year 1969. In the year 1994, the government of India decided to permit the setting up of private banks in India. Some of the foreign banks have been operating in India for over 100 years. At present the largest bank in India is State Bank of India in terms of deposit values and number of branches.
How to open a bank account?
To become an account holder, first you have to fill out an account opening form and submit necessary documents like a copy of proof of address, proof of identity, photographs, etc. You can make the account for a single person or joint names with a member of family or friends. After completion of the form fill-up, the bank will provide a unique account number, chequebook, passbook, internet banking username, and password for your day-to-day transactions with the bank.
Deposits and withdrawals
Bank pay-in slips are used for depositing cheques and cash into your bank account. The pay-in slips contain the information about the account number and information about how much money you want to deposit. The withdrawal slips are used in the bank to withdraw cash from his/her bank account.
The pay-in slip normally contains the following details.
- Name of the account holder
- Bank account number
- Bank branch name
- Date of deposit
- Amount to be deposited in words and figures
- Signature of the depositor who deposits money
- Denominations of the currency
- Details of the cheque that is to be deposited.
A format of a pay-in slip is given below
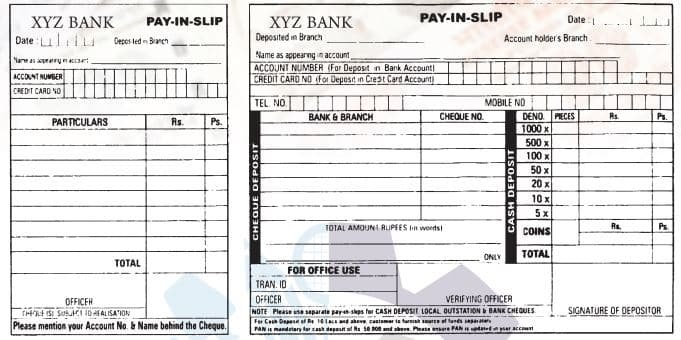
A format of a withdrawal form is given below:

- Name of the account holder
- Bank account number
- Bank branch name
- Date of withdrawal
- Amount to be withdrawn in words and figures
- Signature of the account holder
- Address and phone no. of the account holder
Bank account holders’ documents:
- Passbook: The passbook gives a record of all the transactions that have been made in your account. Some banks can give statements periodically by mentioning all the transactions done by you.
- ATM Card or Debit Card: An ATM card issued by a bank that can be used for withdrawals, deposits, account information, and other types of transactions.
- Chequebook: A cheque is also used in bank transactions. The chequebook containing cheque leaves is used for making payments to others and withdrawing cash from the bank accounts. A chequebook is a very important document and must be kept very safely. The following are the details required to be mentioned in the cheque.
- Date on or after which payment can be made for the cheque.
- Name of the party to whom the payment is to be made.
- The amount to be paid
Types of Bank Accounts
Banks offer different types of accounts, like savings bank accounts or current accounts.
- Saving Bank Account: A savings bank account is used for saving money on a regular basis. This type of account is opened to inculcate the saving habit. A small amount is enough to open a savings bank account. This type of account is basically used for salaried individuals, small savings, and small holdings of housewives and retired persons. Savings accounts give interest twice in a year.
- Current Account: Current accounts are generally opened by businessmen or companies. The balance maintained in this account does not earn any interest like a savings account. The current account holders are given a facility to overdraw from their current account. This overdrawn money needs to be paid back to the bank with interest. Current account holders have a facility like a greater number of deposit and withdrawal forms for the particular account period.
Other services provided by the bank
Banks also offer a number of other services, like accepting payment of telephone bills and taxes like service tax and income tax. They also offer things like credit cards, fixed deposits, recurring deposits, etc.
- Fixed deposits: In a fixed deposit, the depositor invests a lump sum amount with the bank for a predetermined period. The bank offers a fixed interest for the same. The interest rate is higher than savings interest, but the amount is fixed for a particular month; if anyone withdraws the amount before the fixed month, then the rate of interest will decrease.
- Recurring deposits: Recurring deposits are made over a period of time. Investors invest a given sum of money at regular intervals for a period, like every month or every quarter, at the end of the investment period. For example, an investor could invest Rs 100 every month for a period of 12 months.
Automated Teller Machine (ATM)
An automated teller machine is a computerised device that provides the cardholders of banks with access to financial transactions. ATMs permit account holders to carry out banking activities like withdrawing cash or depositing cheques without banking staff. Because of this, the account holder does not depend on the bank’s working hours. The ATM is operated using an ATM card and PIN provided by the bank.
Electronic Banking
Banks also give the facility of internet banking to their users, where the account holder need not visit the bank personally but can operate his account from his home through the internet. Through electronic banking the following benefits are offered to the account holders by most of the banks.
- Checking bank balances
- Checking the banking transactions.
- Bill payment facilities like electricity bill and telephone bill payment
- Money transfer from your bank to another bank
- Requesting for a chequebook to be sent to your house
Disclaimer: We have taken an effort to provide you with the accurate handout of “What is a Bank Class 9 Notes“. If you feel that there is any error or mistake, please contact me at anuraganand2017@gmail.com. The above CBSE study material present on our websites is for education purpose, not our copyrights.
All the above content and Screenshot are taken from Introduction to Financial Markets Class 9 NCERT Textbook, CBSE Sample Paper, CBSE Old Sample Paper, CBSE Board Paper and CBSE Support Material which is present in CBSEACADEMIC website, NCERT websiteThis Textbook and Support Material are legally copyright by Central Board of Secondary Education. We are only providing a medium and helping the students to improve the performances in the examination.
Images and content shown above are the property of individual organizations and are used here for reference purposes only. For more information, refer to the official CBSE textbooks available at cbseacademic.nic.in
