Systematic savings and investment are essential habits that help individuals manage money wisely and achieve financial security. In Class 9, the concept teaches students how regular savings and planned investments contribute to future needs, emergencies, and long-term goals.
Systematic Savings and Investment Class 9 Notes
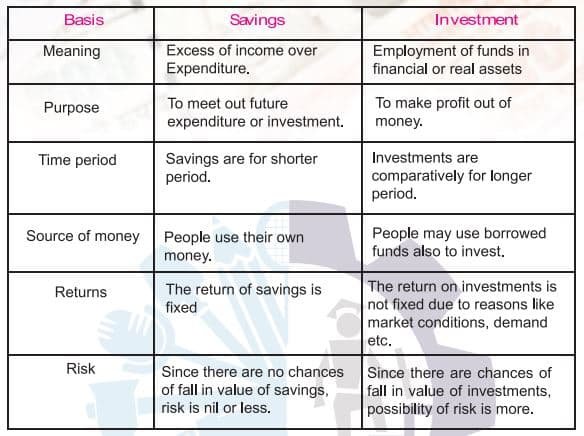
Many of us use the words “saving” and “investing” interchangeably. But they are quite different. Saving is storing money safely, like putting cash in a bank or locker in your house or purse, etc., to meet your upcoming expenses or emergencies. But, with this kind of “saving”, you earn nothing or a low, fixed rate of return, and you can withdraw or have access to your money easily. Saving is the first step to investments. Since, without savings, investments cannot take place. The differences between savings and investments are as follows:
Saving
Savings means setting aside a portion of money or goods for future use. It helps to avoid unnecessary spending. Saving is the portion of disposable income not spent on consumption. Savings can be defined as “the portion of disposable income not spent on consumption”.
Investment
Investment means using money or resources today with the hope of gaining more in the future. Investment means spending funds on financial or real assets, but in investment the risk is involved, and based on that the future benefit will be decided. An investor is expected to be compensated for:
- Sacrificing current consumption
- Effects of inflation and
- Risk taken
Investments can be made in any one of the following assets.
1. Financial assets:
- Equity shares
- Preference shares
- Share warrants
- Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs)
- Global Depository Receipts (GDRs)
- Units of mutual funds
- Debentures
- Debt securities
- Commercial papers
- Deposits with companies and banks
- Post office saving certificates.
- Provident Fund Investment (PF)
- Insurance Policies.
2. Real assets:
- Real estate
- Gold
- Silver
- Diamonds
- Art pieces/artefacts
- Stamps
- Coins
- Antiques
Speculation
Short-term investments are known as speculation. The speculation is a purchase of an asset like real estate, a commodity or goods with the hope that the asset will become more valuable in a specific amount of time. There are two main categories of speculators in the stock market, namely bulls and bears.
Why investment?
Anyone can choose investment with the objective of the following:
- To get a return on investment in the form of dividend, interest, capital gain and capital appreciation.
- To earn above inflation.
- To safeguard the funds from various thefts.
- To get tax advantages like deductions and exemptions from income.
- To create collateral security for future needs.
Calculation of return on investment
To calculate the return on investment, you can use the following formula:
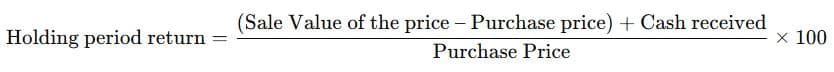
Illustration 1.
Mr Surya purchased a company’s share for ₹900 and sold it for ₹1000 after a period of 1 year. During the period, he also received a dividend of ₹35.
Find out the return.
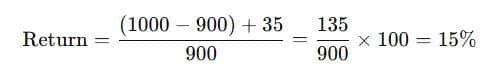
Time Value of Money
The time value of money means that the money available today is worth more than the same amount in the future. This happens because in the future the money can earn interest but lose value because of inflation. For example, let’s see if you take Rs 1000 now and invest it at 6% interest per year; it becomes:
Future Value = 1000 × (1 + 0.06)⁵ = 1000 × 1.338 = 1338
So, 1000 today is worth 1338 in 5 years. If you are waiting 5 years on 1000, it means that you are losing 338 in potential growth.
Interest
Interest is a charge for borrowing money, usually stated as a percentage of the amount borrowed for a specific period of time. Simple interest is computed only on the original amount borrowed. It is the return on that principal for one time period. In contrast, compound interest is calculated each period on the original amount borrowed plus all unpaid accumulated interest. The power of compounding is shown below:
When a fixed sum of 1000 is invested with an interest rate of 10% per year, the returns are as follows:
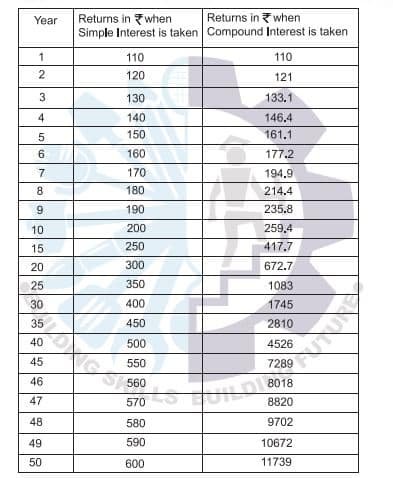
Illustration: 1
Calculation of future value of a one-time investment.
What is the future value of today’s investment of 100 after 5 years if the interest rate is 5% and compounded annually?
If you invest 100 at 5% compound interest for 5 years, the future value is:
FV = 100 × ( 1 + 0.05 ) 5 = 100 × 1.2763 = 127.63
So, 100 today becomes 127.63 after 5 years.
Systematic Investment Plan (SIP)
A Systematic Investment Plan (SIP) is a method of investing a fixed amount regularly in financial assets like mutual funds. It is similar to a recurring deposit, but it is focused on wealth creation and capital gain.
Salient features of SIP
- It allows the investor to buy units on a given date every month or every quarter.
- The investor is free to decide the amount to be invested.
- Small amounts can also be invested.
- Tax benefits are available for specified SIP schemes.
Disclaimer: We have taken an effort to provide you with the accurate handout of “Systematic Savings and Investment Class 9 Notes“. If you feel that there is any error or mistake, please contact me at anuraganand2017@gmail.com. The above CBSE study material present on our websites is for education purpose, not our copyrights.
All the above content and Screenshot are taken from Introduction to Financial Markets Class 9 NCERT Textbook, CBSE Sample Paper, CBSE Old Sample Paper, CBSE Board Paper and CBSE Support Material which is present in CBSEACADEMIC website, NCERT websiteThis Textbook and Support Material are legally copyright by Central Board of Secondary Education. We are only providing a medium and helping the students to improve the performances in the examination.
Images and content shown above are the property of individual organizations and are used here for reference purposes only. For more information, refer to the official CBSE textbooks available at cbseacademic.nic.in
