Identifying patterns is an important concept in Data Science Class 10 (Subject Code 419). It helps students analyze data, recognize trends, and make predictions. By learning how to observe and interpret different types of patterns—such as numerical, visual, or logical—students improve their problem-solving and analytical skills.
Identifying Patterns Class 10 Notes
What are partiality, preference, and prejudice?
Partiality means when you treat someone or something better than others, even if they do not deserve it. “Preference” means you like one thing more than another. Prejudice means you decide something is bad or wrong without knowing the full truth. This can create unfair results, and when we use data, unfair choices are called bias. Bias can make wrong decisions, so we must avoid this.
How to identify the partiality, preference, and prejudice?
We can categorize common statistical and cognitive biases in the following ways:
- Selection Bias
- Linearity Bias
- Confirmation Bias
- Recall Bias
- Survivor Bias
1. Selection Bias
In Selection Bias occurs when the data used to train a model is not a good match for the real-world data. This means that the model learns from data, but the data does not match; in this condition, the model can generate bias. For example, if a website shows only certain videos and collected user feedback, then the model learns only from the visible data and misses out on the hidden part.
2. Linearity Bias
Linearity bias assumes that change in one quantity produces an equal and proportional change in another. Unlike selection bias, linearity bias is a cognitive bias. This is produced not through some statistical process but rather through how mistakenly we perceive the world around us.
3. Confirmation Bias
Confirmation bias, or observer bias, is an outcome of seeing what you want to see in the data. This can occur when researchers go into a project with some subjective thoughts about their study, which are either conscious or unconscious.
4. Recall Bias
Recall bias is a type of measurement bias. It is common at the data labeling stage of any project. This type of bias occurs when you label similar types of data inconsistently. Thus, resulting in lower accuracy.
5. Survivor Bias
The survivorship bias is based on the concept that we usually tend to twist the data sets by focusing on successful examples and ignoring the failures. This type of bias also occurs when we are looking at the competitors.
Probability for Statistics
Probability means guessing how likely something is to happen. It helps us to deal with random events and make predictions. It is the basics of how we make predictions in statistics. We can use probability to predict how likely or unlikely particular events may be.
Probability is a very essential tool in statistics. There are two problems and the nature of their solution that will illustrate the difference.
- Problem 1: Assume a coin is “fair.”
- Question: If a coin is tossed 10 times, how many times will we get “tail” on the top face?
- Problem 2: You pick up a coin.
- Question: Is this a fair coin? That is, does each face have an equal chance of appearing?
Problem 1 uses math and logic to find answers, but problem 2 uses real-life testing and data to find answers. Both use probability, but the difference between the two is the first question is about prediction, while the other one is checking the reality.
The Central Limit Theorem
The Central Limit Theorem says that if you collect a sample from any group of people or things and calculate the average, then the result will look like a normal (bell-shaped) curve, even if the original group did not look like that.
Key Point
- When the sample size is 30 or more, then the CLT works well.
- The average of the sample will be close to the real average of the whole group.
- The spread of the sample will also match the real group spread.
- This helps us to predict things about a big group by studying just a small part of it.
For example, imagine you have 50 houses, and every house has 5 people. You want to know the average weight of the people. if you are going to check each and every person’s weight, then it will be difficult. Instead, we pick 30 people randomly (this is your sample) and find the average weight of this group. Repeat this many times with different groups and find the average of all these sample averages. Now finally you will get the average, which is very close to the real average, and when you convert it into a graph, it will look like a normal curve.
Formula
To find the sample standard deviation:
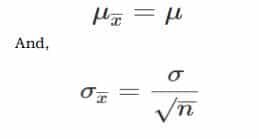
Where,
- μ = Population mean
- σ = Population standard deviation
- μx¯ = Sample mean
- σx¯ = Sample standard deviation
- n = Sample size
Why is the Central Limit Theorem important?
The Central Limit Theorem helps us to make good guesses of the big group of people or things by studying a small random sample. The theorem says that if you take enough samples, then the average will form a normal (bell-shaped) curve, even if the original data is messy or uneven.
This is useful because:
- We don’t need to check everyone in a population.
- We can trust the sample averages to be close to the real average.
- As we take more samples, our errors become smaller.
Real-Life Uses of CLT
- Voting Polls: News channels use CLT to guess how many people support a candidate. They take a small sample and make a prediction.
- Income Surveys: CLT helps to find the average family income in a region without asking every family.
Disclaimer: We have taken an effort to provide you with the accurate handout of “Identifying Patterns Class 10 Notes“. If you feel that there is any error or mistake, please contact me at anuraganand2017@gmail.com. The above CBSE study material present on our websites is for education purpose, not our copyrights.
All the above content and Screenshot are taken from Data Science Class 10 Microsoft Textbook published on CBSE Website, CBSE Sample Paper, CBSE Old Sample Paper, CBSE Board Paper and CBSE Support Material which is present in CBSEACADEMIC website This Textbook and Support Material are legally copyright by Central Board of Secondary Education. We are only providing a medium and helping the students to improve the performances in the examination.
Images and content shown above are the property of individual organisations and are used here for reference purposes only. To make it easy to understand, some of the content and images are generated by AI and cross-checked by the teachers. For more information, refer to the official CBSE textbooks available at cbseacademic.nic.in.
