In the retail business, receiving and storing goods properly is essential to maintain product quality and ensure smooth operations. This chapter 2 retail 401 helps Class 9 students understand the correct procedures and precautions involved in receiving shipments, inspecting goods, updating inventory records, and storing items efficiently.
Receiving and Storage of Goods Class 9 Notes
Session 1: Classification of Goods
Meaning of goods
Goods are bundles of utilities, which are inherently useful and relatively scarce tangible items, such as articles, commodities, merchandise, materials, supplies or wares, produced from agricultural, manufacturing, construction or mining activities. In terms of economics, it is called a commodity. There are two kinds of goods—economical and free goods. Goods that can be obtained with money are called economical goods, and goods which are freely available are called free goods.
Types of goods
There are two types of goods which are dealt with in retail operations—consumer goods and industrial goods.
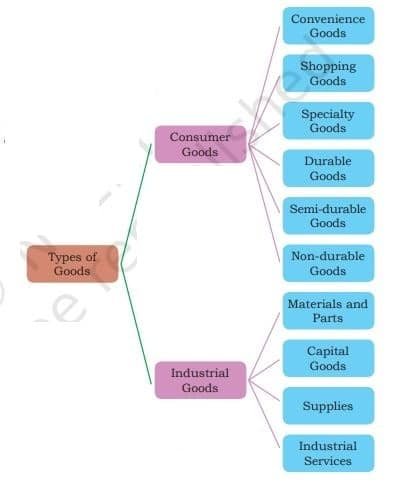
1. Consumer goods
Types of Goods Consumer Goods Consumer goods are those which are ready for consumption by consumers, such as clothing or food. Further, the types of consumer goods have been classified below:
- Convenience goods: Goods which are easily available to the consumer, without any extra effort, are called convenience goods. For example, Fast Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG), such as food, confectionaries, milk, etc. Convenience goods are classified into staple goods and impulse goods.
- Staple Goods: The goods which fulfil the customers basic needs, like bread, milk, butter, sugar, etc., are called staple goods.
- Impulse goods: The goods which are bought without prior planning, like chocolates, soft drinks, wafers, etc., are called impulse goods.
- Shopping goods: Shopping goods are purchased or consumed frequently by the consumers; shopping goods are expensive and semi-durable in nature, like clothes, footwear, radios, televisions, jewellery, etc.
- Speciality goods: Goods which are unique, unusual and special are called speciality goods. For example, high-end and luxury automobiles, antique goods, wedding dresses, etc.
- Unsought goods: There are some goods which are available in the market, but the customers do not know about them or do not buy them unless needed; these are called unsought goods. For example, insurance. Unsought goods are also classified into three types:
- Durable goods: The goods which need to be purchased frequently and last for longer periods are called durable goods.
- Semi-durable goods: The goods that do not last for a long time are called semi-durable goods. For example, clothes, furniture, jewellery, footwear, etc.
- Non-durable goods: The goods which are for immediate consumption and are perishable in nature are called non-durable goods. For example, milk, fruits, bread, etc.
2. Industrial goods
The goods which are used in business or in production are called industrial goods. Industrial goods are not for consumption but are used by industries for producing finished products. Industrial goods are divided into three parts:
- Materials and parts: It is the basic unit of industrial production. It is used for producing finished goods.
- Capital goods: Capital goods make the functioning of an organisation smooth. For example, office accessories.
- Supplies: Supplies meet the day-to-day operation but do not become a part of the finished product.
- Industrial services: Industrial services are used in running a business smoothly. Industrial services can be available internally and externally, such as maintenance services, repair services, machinery repair and business advisory services.
Session 2: Procedure for Receiving and Dispatching Stock to Stores
Every retail store should have a receiving area to receive the goods. When the goods arrive at the back office of a retail store, they may be packed in containers, cartons, crates or others, while some goods may be on hangers and pallets. Receiving goods should be done very carefully and quickly. Some of the functions of the receiving section of a retail store.
- Receive incoming materials.
- Physically check received material.
- Arrange for speedy and proper inspection.
- Raise goods inward note.
- Notify the user departments about the availability or non-availability of materials required by them.
- Inform the purchase section regarding excess supply, shortage or defective supply.
- Deliver material to appropriate places for storage.
- Prepare record keeping.
Procedure required for receiving goods
The procedure required for receiving goods includes:
- identifying goods for the retail store.
- checking goods ordered for the retail store.
- confirming the dispatch of goods.
- receiving goods with order and invoice.
- checking the quantity of goods, description about the goods and quality of container.
- thorough checking of goods before the invoice is signed.
- following the standard provision for the process of receiving goods.
- ticking the goods received correctly against the invoice and their immediate placement on the selling floor.
- allocating pre-sold goods for earliest possible delivery.
- confirming the number of cartons to match the quantity mentioned in the bill of lading/invoice.
- examining containers for signs of damage, including broken seals, leaks or tears.
- verifying the weight of goods received.
- marking the delivery slip according to the goods.
- rejecting and informing the supplier about damaged or incorrect goods.
- making arrangements for repairing or replacing damaged goods.
Procedure required for dispatching goods
The store’s operations assistant has to follow a procedure for dispatching goods to the store floor. The Store
- The assistant should:
- Be careful with paperwork.
- Ensure that the correct goods are dispatched.
- Dispatch goods correctly in terms of quantity, description and quality to the store floor.
- Avoid dispatching damaged products to the store floor.
- Ensure correct packaging while dispatching the products.
- Build confidence among the dispatching staff and ensure that they correctly handle the equipment to reach the products.
- daily record the goods dispatched and inform higher authority.
- Maintain all the paperwork correctly with evidence.
Refusal procedure in relation to type of goods delivered
When the goods arrive for delivery, they should be perfect in all aspects, like the seal should not be broken, and the container should not be torn or leaking. If the delivery executive is in a hurry and cannot wait, then he/she should write ‘unchecked’ and sign. If the package looks damaged, the executive can deal in two ways.
- Refuse to take the product.
- Accept the product, make the delivery executive aware of the damaged goods and sign the delivery note, writing damaged on the delivery paperwork.
Some of the simple steps to minimise the problem of store returns are as follows:
- Always check the retailer’s return policy: it is important to check the retailer’s policy while shopping online.
- Keep tags on receipts: Attach the receipt of purchase and do not remove any tags until you’re sure that you’re going to keep it.
- Ready for return: The retailer should be prepared for receiving return requests for goods and make the necessary arrangements for it.
- Hold the emotion: Do interact with the salespeople.
- Delay in returning goods: Many retailers have a fixed time period, after a purchase takes place, to accept the returns.
Reporting to the supervisor about product shortages or oversupply
It is the duty of the store operation assistant to report to the supervisor about different types of products that are in short supply and those which have an oversupply.
Session 3: Storage of Goods in Retail Operations
It is important that the goods should be stored in a location where they are safe and can be found easily. It is also important to store products in the right condition and to safeguard the products and to minimise wastage.
Meaning of storage
There is a gap between production and ultimate consumption of goods. Storage means proper arrangement of goods for retaining all its actual properties and qualities till the final consumption required by the consumer.
Need for storage
Storage plays an important role in a retail organisation. Some reasons for storage are:
- Every customer wants a variety of goods. Therefore, every retailer must focus on sufficient arrangement of goods.
- Many products are consumed on a regular basis, but many products are consumed on a seasonal basis. Therefore, retailers should carefully store the goods.
- Some products are consumed seasonally. In such a condition the retailer can get the product easily.
- Many products or commodities need extra care for storage, like medicines and drugs.
- Storage of raw material should be done in such a place from where the products can be got easily.
- Storage of goods during the recession phase increases the carrying cost and minimises the returns.
- The storage of commodities varies with the demand of goods.
Techniques of storing goods
The various techniques to be adopted by the shopkeeper or the store operations:
a. Shelving and racking: Shelving and racking should be done as per the requirement of the retail store. Ensure that:
- Shelves and racks are on a level.
- The retailer follows the instructions given by manufacturers while installing shelves and racks.
- Shelves and racking are fixed to the wall.
- The retailer provides safety ladders when storing goods in the storage department to avoid accidents.
- There is sufficient space for the movement of retail employees while keeping and taking off goods from the shelves and racks.
- Personal protective equipment is used.
- Goods are kept logically; for example, put the heaviest product at the bottom.
- Common goods or commodities are easily accessible.
b. Pallets: If pallets are used with racking units, one should avoid:
- Use of pallets which can’t bear the load of goods.
- Use of damaged or badly constructed pallets.
- Use inappropriate pallets for the material.
- Poor handling of material on pallets.
c. Storage of dangerous or hazardous goods: Storage of hazardous goods needs special care and attention. A retailer should:
- Follow the instructions on the safety data sheet as given by the manufacturer while storing dangerous or hazardous goods.
- Only keep a limited quantity of hazardous substances.
- Keep incompatible substances separate.
- Prevent the leakage of dangerous substances from the container.
- Train the staff for using the spill kit, and also keep the spill kit near the storage area.
- Do regular checking for any leaks or spills from the container.
- Ensure that the staff wears personal protective equipment while handling hazardous substances.
d. Storing food safely in a retail store: Food and catering retail ensure that food is safely stored in the retail store. The following steps must be initiated by the store operations assistant for safe storage of food items:
- Control temperature in all storage areas.
- Store dried food at a different place.
- Check the expiry dates.
- Make sure the storage area is clean.
- Do not overload the refrigerator.
- Follow the storage instructions on food packaging.
e. Storing goods and materials safely: Goods and materials should be stored safely. A store operations assistant should ensure that:
- All exit routes are marked.
- Exit routes are kept clear to reduce fire risks. There should be a fire extinguisher near the exit route.
- No flammable items are stored near a source of ignition, like a heater.
- Dangerous substances, such as chemicals, are stored appropriately.
- All spills are cleared to avoid slips.
- The retail store has the adequate equipment to clean up the spills.
- Personal protective equipment is provided to their staff members for storing or moving materials.
- Training is provided to their staff for using PPE.
- Minimum materials are used during processing and/or kept in production areas.
- Proper security is arranged for high-value goods.
- Appropriate signage is used.
Session 4: Process of Goods Handling
When the goods are received in bulky packages, then they should be handled carefully during packing, moving or storing of goods. Following are the advantages of effective handling of goods:
- Lowers the unit material handling costs.
- Reduces the manufacturing time.
- Contributes towards a better control of goods flow.
- Improves safety in working and movement of materials.
- Provides for fewer rejects.
- Achieves decreased storage requirement.
Material handling activities
Basically there are three handling activities—receiving, in-storage handling and shipping.
- Receiving: When material reaches the store, it is received by the retail store operations assistant. The basic duty of an operations assistant is unloading the goods from the vehicle.
- In-store handling: The materials handling must be done with the proper equipment by experienced and trained staff. There is a range of equipment to handle material, such as cranes, moving trucks, slings, pallet jacks, forklifts, etc.
- Shipping: Shipping consists of checking and loading orders onto transportation vehicles. As in receiving, shipping is manually performed in most systems.
Moving, handling and storing of materials
When material is received, then it needs to be moved to its respective place; this moving material is called material moving in retail. There are basically two conditions when material moves:
- When the material comes from manufacturers or suppliers
- When the material needs to be kept on shelves for sales.
There are two ways to move the material.
- Manually
- Equipment
Potential hazards for workers
There are various hazards associated with workplace and common retail activities that can cause injuries, such as falling of goods and improper use of equipment and material. Also, there are some potential injuries that can occur while handling material manually, which are as follows:
- Fractures
- Cuts
Disclaimer: We have taken an effort to provide you with the accurate handout of “Receiving and Storage of Goods Class 9 Notes“. If you feel that there is any error or mistake, please contact me at anuraganand2017@gmail.com. The above CBSE study material present on our websites is for education purpose, not our copyrights. All the above content and Screenshot are taken from Retail Class 9 NCERT Textbook, CBSE Sample Paper, CBSE Old Sample Paper, CBSE Board Paper and CBSE Support Material which is present in CBSEACADEMIC website, NCERT websiteThis Textbook and Support Material are legally copyright by Central Board of Secondary Education. We are only providing a medium and helping the students to improve the performances in the examination.
Images and content shown above are the property of individual organizations and are used here for reference purposes only. For more information, refer to the official CBSE textbooks available at cbseacademic.nic.in
