Information Technology (IT) plays a vital role in today’s digital world, and the Basics of Information Technology subject for Class 11 HSC lays a strong foundation for students who want to understand computers, data, software, and communication technologies. These notes are prepared strictly according to the Maharashtra State Board (HSC) syllabus, using simple language and exam-oriented explanations.
Basics of Information Technology Class 11 HSC Notes
Definition of Information Technology
IT (Information Technology) encompasses all of the technologies that we use in order to create, collect, process, protect and store information. It refers to hardware, software (computer programs), and computer networks.
Data and Information
Data and information are interconnected. Data can be any character, text, word, number or raw fact. However, information is data formatted in a manner that allows it to be utilised by human beings in some significant way. Meaning, when you take some meaning from the data, it is known as information.
Need of information
Information is required to take short-term and long-term decisions and also to make strategic decisions in an organisation.
Various concepts used under IT
Computer
The word “computer” comes from the Latin word “computare”, which means “to calculate”. A computer is an electronic device which can take input from the user, process it according to the instruction given to it and give the required result. A computer can process data, images, audio, video and graphics. A computer performs five major computer operations or functions irrespective of their size and make. These are –
- It accepts data or instructions by way of input.
- It stores data.
- It can process data as required by the user.
- It gives results in the form of output.
- It controls all operations inside a computer.
Architecture of Computer

Computer architecture refers to how a computer system is designed and how it works. Every computer system has the following three basic components:
- Input Unit
- Central Processing Unit
- Output Unit
1. Input Unit
The input unit takes direct command and data from the user, and then the computer CPU processes the data and produces output. For example, a keyboard is an input device that enters numbers and characters. Some input devices are barcode readers, Magnetic Ink Character Recognition (MICR), Optical Character Recognition (OCR), etc.
2. Central Processing Unit (CPU)
After receiving data and commands from users, a computer system will process it according to the instructions provided. The CPU further uses these three elements:
- Arithmetic and Logic Unit: This part of the CPU performs arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, division, multiplication, etc. I also perform the logical operation like comparison of the data.
- Control Unit: The control unit controls all the components which are connected to the computer. It makes coordination between all the components of a computer system.
- Memory Unit: Once a user enters data using input devices, the computer system stores this data in its memory unit. This data will now remain here until other components of the CPU process it.

Types of Memory
There are two types of memory.
- Primary Memory: Primary memory is the internal memory of the computer. It is also known as main memory. Primary memory holds the data and instruction on which the computer is currently working. Primary memory is generally of two types.
- RAM (Random Access Memory): RAM is known as read/write memory. It is a temporary memory. The information stored in this memory is lost as the power supply to the computer is switched. off. That’s why RAM is also called “volatile memory”.
- ROM (Read Only Memory): ROM is a permanent type of memory. The content is not lost when the power supply is switched off. ROM cannot be overwritten by the computer. It is also called “Non-Volatile Memory”.
- Secondary Memory: It is an external memory of the computer. It is used to store the huge amount of different programmes and information. The secondary storage devices are:
- Magnetic (Hard) Disc
- Magnetic Tapes
- Pen Drive
- Flash memory
- Optical Disc (CD, DVD)
- SSD, etc.
3. Output Unit
After processing of data, it is converted into a format which humans can understand. After conversion, the output unit displays this data to users. Examples of output devices include monitors, screens, printers and speakers, etc.
Units of Memory
Computer storage and memory are measured by megabytes (MB) and gigabytes (GB). Let’s understand the evolution of memory.
- Bit: It is a binary digit that holds only one of two values: 0 or 1.
- Nibble: A group of 4 bits is called a nibble (for example: 1011, 1001, 1111).
- Byte: A group of 8 bits is called a byte. A byte is the smallest unit. (For example: 11101100, 10000001)

Concept of Hardware and Software
1. Hardware
Computer hardware is a physical component. Hardware are the parts of a computer which we can see, which we can touch and which we can feel. For example, motherboard, graphics card, CPU (Central Processing Unit), ventilation fans, webcam, power supply, keyboard, mouse and so on.
2. Software
A set of instructions given to the computer is known as a program. A program or set of programs is called software. For example, Word, Excel, PowerPoint, Webpage, etc.
Categories of software
1. Open-source software
The software which releases code in the public domain for free. Open-source software is free software. This source code can be copied, modified or distributed by other users and organisations.
2. Closed-source software
It is opposite to open-source software. Only the original authors of the organisation of software can access, copy, and alter that software. In the case of closed-source software, the user has to purchase the software before using it.
Computer software can be classified into two types based on its utility.
- Application Software: Application software is computer software designed to help users perform specific tasks. Applications software (also called end-user programs) includes programs like database programs, word processors, web browsers, presentation software, spreadsheets, etc.
- System Software: System software is the backbone of a computer—it manages hardware and provides a platform for application software to run. For example, operating systems, device drivers, firmware, etc.
What is an operating system?
An operating system (OS) is a software program that allows computer hardware to communicate and work with application software.
Functions of an Operating System
- Boots the Computer: Starts up the system and ensures everything is operational.
- Hardware–Software Bridge: Enables communication between hardware (CPU, memory, devices) and software (apps, programs).
- Resource Management: Controls memory, processes, and input/output devices.
- User Interface: Provides a way for users to interact with the system (e.g., desktop, icons, touch screen).
Operating Systems for Personal Computers
- DOS: DOS stands for Disc Operating System. DOS is a command-based operating system which was used from 1980 to 1990.
- Windows: Windows is the most commonly used operating system. The first Windows operating system was introduced in 1985. For example, Windows 10, Windows 11, etc.
- Mac OS: Apple Corporation’s registered operating system is called Mac OS.
- Chrome OS: Chrome OS is an open-source operating system created by Google to create a better computing experience for people who spend most of their time on the web.
- UNIX: UNIX was trademarked in 1969 by a group of AT&T employees at Bell Labs as a multitasking and multi-user computer operating system.
- Linux: Linux is an open-source, portable, multi-user operating system. It is very similar to the Windows operating system.
Operating Systems for Mobile Phones
There are many different operating systems used in mobile phones. These are Android, Asha, Blackberry, iOS, Windows Phone, etc.
- Android: Android is a free and open-source operating system provided by Google. It is the most popular OS amongst all other OS.
- Asha: Asha is used by Nokia phones. This is a closed-source OS.
- BlackBerry: This is a closed-source operating system for smartphone and tablet devices.
- iOS: iOS is Apple’s closed-source operating system for Apple’s iPhone.
- Windows Phone: Windows Phone is developed by Microsoft as a closed-source operating system for mobile phones.
Introduction to GNU/Linux (GNU Not Unix)
GNU/Linux is a free and open-source operating system that combines GNU Project software (started by Richard Stallman in 1983 to create a free Unix-like OS) and the Linux kernel (developed by Linus Torvalds in 1991). This means that GNU/Linux operating systems are usually free of charge, free to distribute, and they are open source.
Ubuntu is one of the most popular GNU/Linux distributions. There are two main ways to interact with the computer: The GUI (Graphical User Interface) and the CLI (Command Line Interface)
Graphical User Interface (GUI)
A Graphical User Interface (GUI) allows users to interact with a computer using images, icons, menus, and dialogue boxes, instead of typing text commands. In Ubuntu 18.04, the default GUI (desktop environment) is called GNOME.
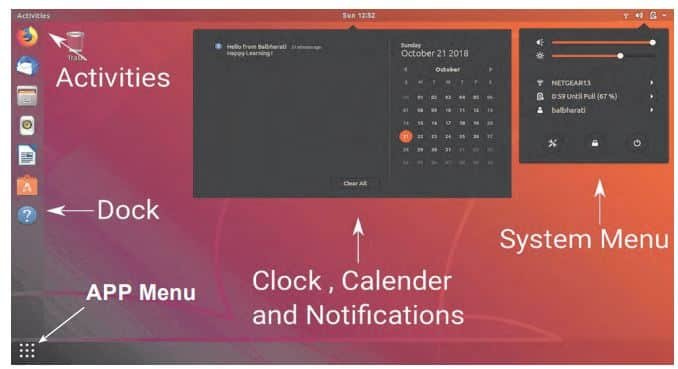
Command Line Interface (CLI)
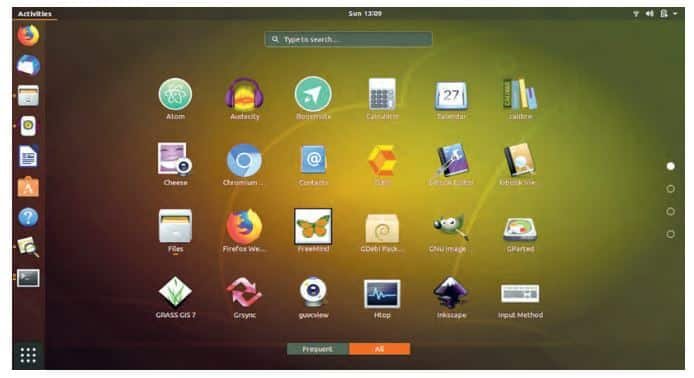
The command line interface is when a user interacts with the computer using text. This is done by typing commands into a terminal. The default CLI on Ubuntu 18.04 is called ‘bash’.
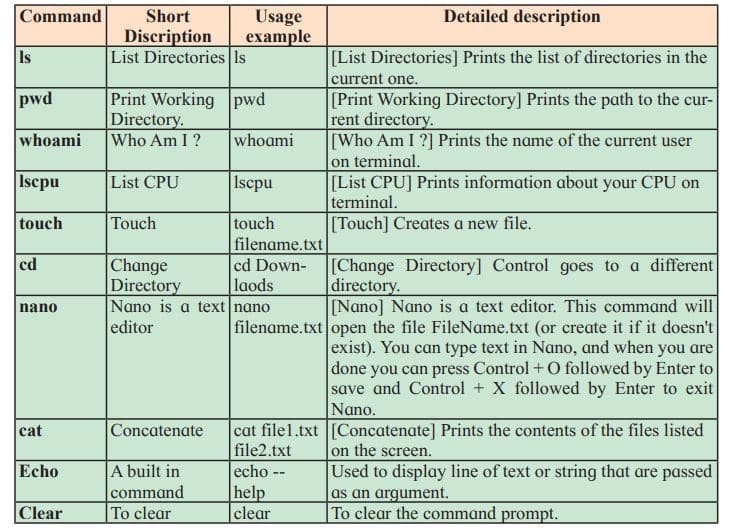
The GNU/Linux File System Hierarchy Standard
In GNU/Linux, the topmost directory is called the root directory, and it is written as /. All directories are stored under the root directory.
This is a brief summary of the file system:
- /: The root directory. All files and directories are stored under this directory, including all hard drives, pen drives, CD drives, etc.
- /bin: Essential system programs are stored here.
- /dev: All connected devices are stored here. Including internal devices, temperature sensors, and batteries.
- /etc: System configuration files are stored here.
- /proc: Files that provide information about processes. This is information like how much RAM is free or how fast the CPUs are running.
- /tmp: Temporary files are stored here.
- /home: Users’ home directories are stored here.
Why Learn and Use GNU/Linux?
There are a huge number of benefits of learning GNU/Linux. Millions of desktops and servers run on GNU/Linux. The Android operating system that the smartphone runs on is a modified version of GNU/Linux.
- Linux is free and open source.
- The Linux operating system is free from viruses.
- Linux is flexible and easily customisable.
- Excellent Support
Computer Network
Interconnection between two or more computers is known as a computer network. A computer network consists of a collection of computers, printers and other equipment that are connected together so that they can communicate with each other.
Types of networks
There are three types of network.
- Local Area Network (LAN): LAN covers a smaller geographical area (size is limited to a few kilometres) and are privately owned.
- Metropolitan Area Network (MAN): A MAN is a larger area than that of a LAN and a smaller area as compared to WAN. It covers a large geographical area and may serve as an ISP (Internet Service Provider).
- Wide Area Network (WAN): Wide Area Network is a computer network that extends over a large geographical area. A communication medium used for WAN is a telephone network or satellite link.
Network Configurations
Network configuration refers to the process of setting up and managing the parameters of a computer network so that devices can communicate with each other. Two of the most widely used types of network architecture are peer-to-peer and client/server.
1. Peer-to-Peer Architecture
In peer-to-peer architecture all computers have the same state. A peer-to-peer network has no dedicated servers. Its implementations are meant for small networks. For example, file transferring between mobile phones using Bluetooth or ShareIt.

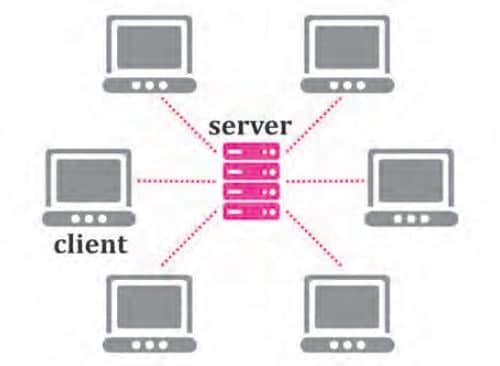
2. Client-Server Architecture
This type of architecture is most suitable for larger networks. So there are two types of machines in a network: client and server.
- Client: A computer that takes any resource from another computer is a client computer.
- Server: If a computer has a resource which is served to another computer.
Internet
Internet means connecting a computer to any other computer anywhere in the world. The internet is the highway of information. The internet is used for searching for information worldwide.
History of the Internet
- 1960s: The Internet began as ARPANET, funded by the U.S. Department of Defence, using packet switching.
- 1970s: Robert Kahn and Vinton Cerf developed TCP/IP, the standard communication protocol.
- 1983: ARPANET adopted TCP/IP, marking the start of the modern internet.
- 1990: Tim Berners-Lee invented the World Wide Web (WWW), making the internet accessible with websites and hyperlinks.
Protocols
A protocol is a set of rules that governs the communications between computers on a network. Examples of protocols are –
- TCP/IP: Transmission Control Protocol & Internet Protocol – It breaks down the message into packets and sends them out into the network.
- DNS (Domain Name System): Translates IP addresses into human-readable domain names (e.g., www.google.com).
- DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol): Automatically assigns IP addresses to computers and users on a network.
- FTP (File Transfer Protocol): Used to transfer and manage files over the internet.
- HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol): Protocol for sending and receiving web pages.
- IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol): Receives emails from a server while keeping a copy stored on the server. Allows sorting/filtering.
- IRC (Internet Relay Chat): Protocol for real-time text communication (chat) over the internet.
- POP3 (Post Office Protocol v3): Receives emails from a server but does not keep a copy on the server.
- SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol): Protocol for sending emails to a server on the internet.
IT-Enabled Services
Meaning of IT-Enabled Services
ITES (Information Technology Enabled Services) refers to services that use Information Technology (IT) to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of an organisation. The outcome of an IT-enabled service is in two forms:
- Direct Improved Service: Benefits realised immediately (e.g., faster customer support, better data handling).
- Indirect Benefits: Benefits realised over time (e.g., stronger customer loyalty, improved brand image, long-term efficiency).
Popular IT-enabled service centres
Popular IT-enabled service centres are
- Call Centres
- Electronic Publishing
- Medical Transcription
- Data Centres
- GIS Mapping (Geographic Information System)
- ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning)
- Knowledge management & archiving.
Careers in IT
Various career opportunities are available for IT professions. These vary from operator to specialised skilled programmers. Some of the career opportunities are as follows:
- Web Designer and Developer
- Software Developer
- Database Manager
- Information Security Analyst
- Professional Accountant
- Financial Advisor
- Cyber Advisor
- Animator
- Games developer
- Audio / Video Editor
Recent trends in IT
- Green Computing: It is the study and practice of environmentally sustainable computing or IT.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Video The Internet of Things (IoT) is the network of physical devices, vehicles, home appliances, and other items embedded with electronics, software, sensors, actuators, and connectivity.
- Cloud Computing: It is the delivery of computing services – servers, storage, databases, networking, software, data analytics and more – over the internet.
- Data Analytics (DA): It is the process of examining data sets in order to draw conclusions about the information they contain, increasingly with the help of specialised systems and software.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the branch of computer science that focuses on creating systems capable of performing tasks that normally require human intelligence.
- Big Data: It refers to data sets that are too large or complex for traditional data-processing application software to adequately deal with. Data with many cases offer greater statistical power, while data with higher complexity may lead to a higher false discovery rate.
- Blockchain: It is a growing list of records, called blocks, which are linked using cryptography. It can be defined as a distributed, decentralised, public ledger.
Disclaimer: We have provide you with the accurate handout of “Basics of Information Technology Class 11 HSC Notes“. If you feel that there is any error or mistake, please contact me at anuraganand2017@gmail.com. The above study material present on our websites is for education purpose, not our copyrights.
All the above content and Screenshot are taken from Information Technology Class 11 Textbook and MSBSHSE (HSC) Support Material which is present in MSBSHSE (HSC) website, This Textbook and Support Material are legally copyright by Maharashtra State Bureau of Textbook Production and Curriculum Research, Pune. We are only providing a medium and helping the students to improve the performances in the examination.
Images and content shown above are the property of individual organisations and are used here for reference purposes only. To make it easy to understand, some of the content and images are generated by AI and cross-checked by the teachers. For more information, refer to the official website.
