These Physical Education Class 12 Chapter 2 Notes cover all important topics from the CBSE syllabus, including balanced diet, macro and micronutrients, eating for performance, and nutritional considerations for athletes.
Physical Education Class 12 Chapter 2 Notes
Exercise Guidelines of WHO for Different Age Groups
The World Health Organisation (WHO) has given some guidelines for physical activity to maintain good health. The WHO exercise guidelines for different age groups are given below:
Children & Adolescents (5-17 years)
- At least 60 minutes of physical activity daily
- Activity should be based on muscle-strengthening exercises at least 3 times in a week.
Adults (18-64 years)
- At least 150 minutes of aerobic activity per week
- Muscle-strengthening exercises 2 or more days a week
Older Adults (65+ years)
- Same as adults, At least 150 minutes of aerobic activity per week
- Same as adults, muscle-strengthening exercises 2 or more days a week
- If mobility is poor, then focus on balance exercises.
What is Posture?
Posture means how you hold your body when sitting, standing, walking or lying down. Keeping good posture helps the body stay strong. There are two types of posture:
- Dynamic Posture: Dynamic posture refers to how your body maintains itself while moving. for example, in the time of walking, running or lifting objects.
- Static Posture: Static posture refers to how the body holds itself when standing, sleeping or sitting.
Common Postural Deformities
The common postural deformities are the conditions when the body posture is incorrect, movement issue, discomfort or pain. This can develop due to poor habits, injury, weak muscles or lack of exercise.
Types of Postural Deformities

a. Knock Knees
Knock knees, also known as genu valgum, is a knee misalignment problem that occurs when the knees touch each other when standing but the ankles stay apart. The reasons behind knock knees are weak bones, injury, knee problems, etc. This problem can be solved by keeping a pillow between your legs during sleeping, yoga or physical exercise.

b. Flat Foot
Flatfoot means the foot has little or no arch. Flatfoot people will touch the ground when standing. The reasons behind flat feet are genetic, injury or weak bones, etc. This problem can be solved using foot exercises, proper footwear, arch support insoles, etc.

c. Round Shoulder
Round shoulder is a condition when the shoulder bends forward. It can lead to neck pain and difficulty moving the shoulder. The problem occurs when the person has bad posture habits, weak muscles or heredity, etc. To fix round shoulders, strengthen muscles, keep the spine straight or do yoga.
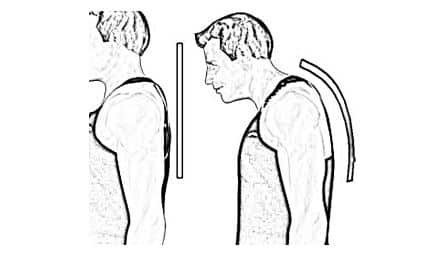
c. Kyphosis
Kyphosis is a condition when the upper back curves too much forward; the posture looks bent. This problem occurs due to heredity, diseases, heavy weightlifting or bad posture. To fix the problem, do take physical therapy, swimming, gym ball exercises, yoga, etc.

d. Lordosis
Lordosis is a condition where the lower back curves too much inward. This posture can sometimes create pain and discomfort. The problem occurs due to poor posture, weak muscles, bone diseases, etc. To fix the problem, do yoga, exercise, maintain a healthy weight, undergo physical therapy or take medical advice.

e. Scoliosis
The Greek word skolios, meaning bent, refers to when the spine is twisted to one or both sides of the body; it is said to have scoliosis. Scoliosis affects girls more often than boys. It can happen at any age. The causes of lordosis are weak muscles, poor posture, bone diseases, etc. To fix the problem, you can do regular exercise, maintain weight, do yoga, or you can take medical advice.

f. Bow Legs
Bow legs mean the knees bend outward, making the legs look like a bow, where the feet and ankles touch each other. It is normally seen in babies and usually fixes itself by age 3 to 4 years. The causes of bow legs include lack of vitamin D, phosphorus & calcium, normal growth phase, etc. To fix this problem, ensure proper nutrition, allow natural growth or take medical help.

Women’s Participation in Sports
Women participation in sports helps them to stay fit and reduces chances of diseases. These are some physical benefits for women participating in sports.
Physical Benefits
- Lifestyle Diseases: Sports helps women to stay active and reduce the chances of diabetes, high blood pressure, obesity, etc.
- Bone Density: Sports helps them to increase their bone density and have stronger bones.
- Toned Muscles: Regular exercise increases the muscle tone of women, which helps them to stay strong.
- Cardiovascular System: Regular exercise helps increase the number of blood vessels (capillaries); this helps bring more oxygen to muscles.
- Obesity: Women have more chance of too much body fat than men; regular participation in sports helps them to stay fit.
Psychological Benefits
- Stress Management: Physical activity releases lots of hormones in our body, which helps us stay happy and reduce stress levels.
- Control Emotions: Physical activity helps to manage their emotions and makes them emotionally strong.
- Confidence: When women participate in sports and win, it increases the confidence level.
- Self-Esteem: Sport helps women to get a boost in their self-image and helps them to realise their own worth.
- Leadership: The women who participate in sports are able to lead people even outside the sports as well.
Social Benefits
- Coordination: Sport helps to increase and improve the coordination between team players.
- Communication: Sport helps to increase communication among each other while playing. It helps women participants to be more vocal and expressive.
- Inter-relationships: Sports is a team effort; women participants learn to maintain their relationship and respect each other.
- Cooperation: Women learn to cooperate with each other when they are playing on the field. This becomes a part of their life also as they learn to work and cooperate with others.
What is Menarche?
Menarche is the term used to describe a female adolescent’s first menstrual cycle. The average age of menarche’s onset is 12.4 years, but it can happen anytime between 10 to 16 years, depending on factors like genetics, nutrition, and overall health.
Menstrual Dysfunction
Menstrual dysfunction is an abnormal condition in a woman’s menstrual cycle. Normal range of the menstruation cycle is 21 to 35 days. If it happens earlier than 21 days or after more than 35 days, then it’s a problem.

There are different types of menstrual disorders which are given below:
- Premenstrual Syndrome: Some women feel sad, irritated, or tired, or get headaches before the period starts. To solve this problem, do exercise, sleep well and eat healthy food, etc.
- Amenorrhoea (Missing Periods): Some women do not get their periods for a long time.
- Dysmenorrhea (Painful Periods): Some women experience strong stomach pain, stomach cramps, and leg pain during their periods.
- Menorrhagia (Heavy Bleeding): Periods with too much bleeding.
- Polymenorrhea (Short Cycle): Period comes less than every 21 days.
- Oligomenorrhea (Long Gaps Between Periods): Periods come after more than 35 days.
- Metrorrhagia (Irregular Bleeding): If women get delayed or random bleeding outside the normal periods.
- Postmenopausal Bleeding: Bleeding after menopause means when periods stop permanently.
Female Athlete Triad
When the female athletes do too much exercise without taking enough food or energy, this condition is known as the Female Athlete Triad. Female Athlete Triad can create health-related problems.
Three Main Problems in Female Athlete Triad
- Eating Problem (Eating Disorders): Not taking enough food or taking an unhealthy diet can lead to poor health or weakness.
- Menstrual Issues (Amenorrhea): Delayed periods, period stops or irregular periods due to low energy and body stress.
- Weak Bones (Osteoporosis): Not taking proper food can make bones weak.
How to Fix Female Athlete Triad
- Take enough food based on the exercise.
- Take vitamins and minerals for strong bones.
- Do exercise in a healthy way.
- Take medical help if you have any disorder or severe symptoms.
Physical Education Class 12 Notes
- Management of Sporting Events Class 12 Notes
- Physical Education Class 12 Chapter 2 Notes
- Physical Education Class 12 Chapter 3 Notes
- Physical Education Class 12 Chapter 4 Notes
- Sports and Nutrition Class 12 Notes
- Test and Measurement in Sports Class 12 Notes
- Physiology and Injuries in Sports Class 12 Notes
- Biomechanics and Sports Class 12 Notes
- Psychology and Sports Class 12 Notes
- Training in Sports Class 12 Notes
Physical Education Class 12 Questions and Answers
- Physical Education Class 12 Chapter 1 MCQ Solutions
- Physical Education Class 12 Chapter 2 Question Answers
- Physical Education Class 12 Chapter 3 Question Answers
- Physical Education and Sports for CWSN Class 12 Questions and Answers
- Sports and Nutrition Class 12 Questions and Answers
- Physical Education Class 12 Chapter 6 Question Answers
- Physiology and Injuries in Sports Class 12 Questions and Answers
- Biomechanics and Sports Class 12 Questions and Answers
- Psychology and Sports Class 12 Questions and Answers
- Training in Sports Class 12 Questions and Answers
Disclaimer: We have taken an effort to provide you with the accurate handout of “Physical Education Class 12 Chapter 2 Notes“. If you feel that there is any error or mistake, please contact me at anuraganand2017@gmail.com. The above CBSE study material present on our websites is for education purpose, not our copyrights. All the above content and Screenshot are taken from Physical Eduction Class 12 NCERT Textbook, CBSE Sample Paper, CBSE Old Sample Paper, CBSE Board Paper and CBSE Support Material which is present in CBSEACADEMIC website, NCERT websiteThis Textbook and Support Material are legally copyright by Central Board of Secondary Education. We are only providing a medium and helping the students to improve the performances in the examination.
Images and content shown above are the property of individual organizations and are used here for reference purposes only.
For more information, refer to the official CBSE textbooks available at cbseacademic.nic.in
