Teachers and Examiners (CBSESkillEduction) collaborated to create the Physical Education Class 11 Chapter 6 Notes. All the important Information are taken from the NCERT Textbook Physical Education (048) class 11.
Define Test, Measurements and Evaluation
In physical education, a test is a tool used to measure a person’s abilities, skills or fitness level. It helps to identify the strength, flexibility, endurance and overall performance of the individual using various physical activities.
Purpose of Test:
- Evaluates physical fitness – The test helps to measure the strength, speed and endurance of any individuals.
- Track progress – During the test individuals can track the performance, which is helpful to identify if any improvement is required or not.
- Guides training programmes – It also helps to make a personalized fitness plans.
Understanding Test, Measurement, Evaluation, and Assessment
- Test – A test is a method for checking someone’s ability or skills. For example, A students run 100 metres.
- Measurement – Measurement gives a number of the test result. For example, the coach recorded the time of 100 metres run.
- Evaluation – Evaluation judges the result of the test. For example, the coach reduces the time of the 100-metre run for improvement.
- Assessment – Assessment is a complete process that includes tests, measurements and evaluations. For example, the coach checks all the test results and makes the training plan.
Importance of Test, Measurements and Evaluation in Sports
Test, measurement and evaluation play an important role in sports. This tool helps the teachers, coaches and students to track progress, set goals and know how to improve performance.
Why testing, measurement and evaluation are important
- Understanding Student Abilities – Before training, it helps to understand the level of the individuals.
- Setting Goals – It allows the teacher to understand how much capability students have; based on capability, a goal can be set.
- Tracking progress – It helps to understand how well students achieve their fitness and skill goals.
- Improving teaching methods – It helps to understand which techniques are better for the individual.
Key benefits of measurement & evaluation:
- Placement: Every student cannot be given the same training programme. Placement refers to the grouping of the students into categories like high fitness and low fitness, swimmers and non-swimmers, and skilled and unskilled.
- Diagnosis: Diagnosis is important to determine the strengths, weaknesses and limitations of individuals in physical education activity so that appropriate training can be provided.
- Prediction: Test scores can be viewed as predictors of one’s future success in school. Physical education teachers may use the physical activity patterns, cardiovascular endurance, blood pressure, body fat, or other factors to predict the student’s fitness level.
- Motivation: Testing, measurement and evaluation give the status of physical fitness, sports skills and other parameters which motivate the student to do better and better.
- Achievement: In a programme of instruction or training, a set of objectives must be established by which participants’ achievement levels can be evaluated.
- Programme evaluation: A physical education teacher may be asked to demonstrate how the students are receiving appropriate physical fitness training.
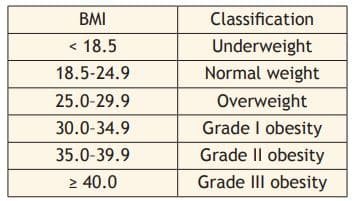
Calculation of BMI, Waist – Hip Ratio, Skin fold measurement
BMI
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a measurement tool to determine if the person’s weight is healthy or not based on the height and weight.
BMI Computation
BMI computes as follows:
BMI = Body mass (kg) / stature (m2)
Example
A Male has a height of 175.3 cm (which is 1.753 m) and a weight of male is 97.1 kg.
BMI = 97.1 / (1.753 x 1753)
BMI = 97.1 / 3.072
BMI = 31.6
Waist – Hip Ratio
Waist-to-Hip Ratio (WHR) helps to check health risks and shows whether a person has an apple-shaped or pear-shaped body.
WHR Calculacation
WHR = Waist measurement / Hip measurement
Why It Matters:
- Apple-shaped body (more fat around the waist) – Higher risk of heart disease and diabetes.
- Pear-shaped body (more fat around hips and thighs) – Lower health risk.
Healthy WHR According to WHO:
- Men: 0.9 or less
- Women: 0.85 or less
For example, A man has a waist of 90 cm and hips of 100 cm.
WHR = 90 / 100
WHR = 0.9 (Healthy range for men)
Somato Types (Endomorphy Mesomorphy & Ectomorphy)
Somatotyping is a method used to classify body types based on shape, muscle structure and fat distribution. Somatotyping helps in the sports selection, exercise planning and understanding physical performance. There are three types of somatotypes.
- Endomorph – rounded body shape.
- Mesomorph – muscular body like an athletic person.
- Ectomorph – slim body shape.
Why somatotyping is used in sports.
- It helps them choose the right training methods.
- It helps to identify which nutrition plans have to be made based on body type.
- Helpful for injury prevention based on the body structure.
Physical Education Class 11 Chapter 6 Notes
Physical Education Class 11 Notes
- Physical Education Class 11 Chapter 1 Notes
- Physical Education Class 11 Chapter 2 Notes
- Physical Education Class 11 Chapter 3 Notes
- Physical Education Class 11 Chapter 4 Notes
- Physical Education Class 11 Chapter 5 Notes
- Physical Education Class 11 Chapter 6 Notes
- Physical Education Class 11 Chapter 7 Notes
- Physical Education Class 11 Chapter 8 Notes
- Physical Education Class 11 Chapter 9 Notes
- Training and Doping in Sports Class 11 Notes
Physical Education Class 11 Questions and Answers
- Physical Education Class 11 Chapter 1 Question Answers
- Physical Education Class 11 Chapter 2 Question Answers
- Physical Education Class 11 Chapter 3 Question Answers
- Physical Education Class 11 Chapter 4 Question Answers
- Physical Education Class 11 Chapter 5 Question Answers
- Physical Education Class 11 Chapter 6 Question Answers
- Physical Education Class 11 Chapter 7 Question Answers
- Physical Education Class 11 Chapter 8 Question Answers
- Physical Education Class 11 Chapter 9 Question Answers
- Training and Doping in Sports Class 11 Questions and Answers
