Teachers and Examiners (CBSESkillEduction) collaborated to create the Psychology and Sports Class 12 Notes. All the important Information are taken from the NCERT Textbook Physical Education (048) class 12.
Personality: Concept and Definitions
Some athletes struggle in sports due to personality. Personality is a mix of behaviours, emotions and thoughts that make each person unique. Personality helps to select the right sport and manage the stress during competitions.
Personality types
The personality refers to the unique character and behaviours of the individual. There are lots of different theories of personality, like trait theory, psychodynamic theory, humanistic theory, biological theory, etc., but no single theory can define personality completely.
Jung’s Classification of personality types
Carl Gustav Jung is a Swiss psychiatrist; he has developed his own contradictory view about personality which is different from Sigmund Freud’s views. In his book, personality is divided into two types: introversion and extroversion. Introversion helps the person to think deeply; it focuses on internal thought, and extroverts are the people who are socially active and about external interaction. Jung’s theory aimed to explain the complexity of human personality rather than simply labelling people into two fixed categories.
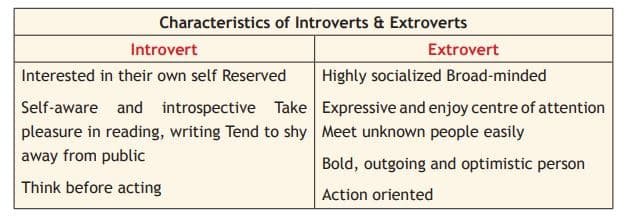
Carl Jung also classified four personality functions, which are based on how people understand and interact with the world.
- Feeling: How the people make decisions based on the emotions and values.
- Thinking: How the people use logic and analysis to make decisions.
- Sensing: Basically focus on facts, details and reality.
- Intuition: Depend on patterns, possibilities and creativity.
These functions are further divided into rational (thinking & sensing) and irrational (feeling and intuition) categories.
Ambiverts
Jung believed that personality is not fixed because people have a mix of characters or traits. Later on, Carl Jung introduced the concept of ambiverts. which basically has both introverted and extroverted characteristics.
Big Five Theory of Personality
The Big Five theory developed by Paul Costa and Robert McCrae, This personality model describes the different characteristics people have. This trait is known as OCEAN.
- Openness: The people have high imagination, creativity and curiosity. They enjoy each and every experience. Openness helps the sportsman to take initiatives, including a variety of ideas.
- Conscientiousness: High conscientious people are organised, responsible and hard-working. They always plan ahead and follow structured routines.
- Extraversion: Extroverted people are social, enthusiastic and talkative. They are the people who participate in social activities.
- Agreeableness: Agreeable people are friendly, cooperative, kind with others, trusting and helpful. The people having low agreeableness will be uncooperative and sometimes rude with others.
- Neuroticism: If the people have low neuroticism, they have more emotional stability; these people can be calm, stable and composed. The people who have high neuroticism have anxiety, stress, mood swings, etc.
Motivation
The word “motivation” comes from the Latin term “movere”, meaning “to move”. Motivation is a process of inspiring, guiding the organism to move in a particular direction. Motivation is influenced by two factors: objective and direction. The first factor, ‘objective’, explains the ‘why’ of an action or behaviour, whereas the second factor, ‘direction’, explains the ‘what’ of an action or behaviour. Without a clear objective and direction, the performance of the sportsman will be affected. Motivated sportsmen can continue playing despite pain, injuries and pressure.
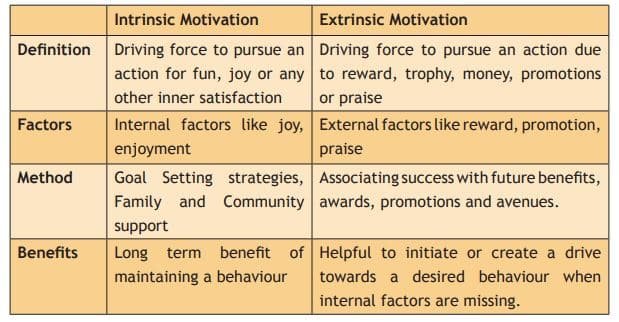
Intrinsic and Extrinsic Motivation
- Intrinsic Motivation: This motivation is also known as internal motivation; this motivation comes from inside yourself, and this motivation helps you to feel good. For example, a football player plays football because they love to play football.
- Extrinsic Motivation: If the person takes participation in a game due to a reward, prize, or medal. It is also known as external motivation. For example, a football player works hard to win a trophy.
Both types of motivation help athletes stay focused, improve performance, and achieve their goals!
Difference between Intrinsic and Extrinsic Motivation
Motivation Techniques
Motivation helps the athletes to improve their sportsmanship performance. This helps them to stay focused on their goals. This motivation can come from within (intrinsic) or from external rewards (extrinsic).
Approaches to Motivate Athletes
- Cognitive Approach: Goal-setting theory is used in the cognitive approach; this goal-setting should be clear.
- Pedagogical Approach: In this approach the coaches motivate the player using fun or giving learning strategies.
- Social Support Strategy: The family members, friends, or team members encourage the sportsman to participate in sports.
- Facilitation Approach: The rewards or recognition help athletes to stay dedicated to sports.
Athletes stay motivated when training is enjoyable, goals are achievable, and support is available.
Exercise Adherence
Exercise adherence means how consistently the person follows the work routine, maintaining regular physical activity even when he/she is facing challenges. High-adherence people do exercise regularly and always stay motivated.
Reasons to exercise
People choose the exercise for different reasons. Some people do it to stay healthy, some people feel energetic, some people want to improve fitness, etc. Exercise helps the mind to reduce stress and feel happy. Some people enjoy playing with friends, or some people prepare for sports competitions.
People engage in exercise and sports for various reasons:
- Overcoming Social Physique Anxiety
- Reduced risk of disease
- Mental Relaxation
Benefits of exercise
- Health benefits like reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease, strengthening bones and muscles, weight management, reducing the risk of some cancers, reducing the risk of falls, etc.
- Provides Stress Relief, Increases Happiness, Promotes Social Cohesion, Enhances Value Orientation
- Cognitive benefits like attention control, improved memory, etc.
- Mental health benefits like exercise as therapy for emotional disorder, fitness as a moderator of life stress, runners’ high, etc.
Strategies for Enhancing Adherence to Exercise
- Goal setting: A moderate bout of acute exercise (20-30 min) is considered to be beneficial for improving positive psychological effects of exercise.
- Adding variety to exercise: Lack of new variety of exercise may lead to boredom and dropping out. Boredom can be tackled with the addition of a variety of exercises and moves that address the same body issues, without loss of therapeutic benefits.
- Social support enhancement: Increasing social support refers to engagement of friends or other members who can contribute towards positive participation in physical activity, exercise and sports because social interaction may help fuel goal achievement and thus produce good results.
- Reinforcement Interventions: Positive as well as negative reinforcement approaches have found to be effective in exercise adherence.
- Feedback: Providing feedback to the participants in physical activity provides much needed direction and energy for prolonging and continuing exercise behaviour.
- Process Orientation: Exercise programmes based on outcome goals or product goals like weight loss, physique and appearance etc.
- Problem Solving: This intervention is based around identifying the obstacles and barriers that stand between the participant and her/his physical activity goals.
- Health Risk Appraisals: Health risk appraisals of participants provide them with relevant information about their current health, risk factors and level of fitness.
- Health Education: It is important that participants seek information from experts on the benefits of exercise, proper exercise techniques and the results that should be expected during exercise.
Aggression
According to the American Psychological Association, aggression is a type of behaviour aimed at causing physical or psychological harm to another. Most psychologist refer to aggression as any behaviour intended to harm or injure any living being who is trying to avoid it.
Type of Aggression
- Hostile aggression: Hostile aggression refers to violence where the person intentionally harms others due to frustration or anger. For example, a boxer punches an opponent.
- Instrumental aggression: This type of aggressive behaviour is used when a player takes advantage due to winning or due to conflict in the game. For example, a basketball player uses strong physical contact to block an opponent.
Psychological Attributes in Sports
Sports scientists study what makes athletes successful, and what the scientist found is that the successful athletes have strong mental skills that help them to stay confident, focused and motivated. These skills include self-esteem, mental imagery, self-talk and goal setting.
- Self-esteem: Self-esteem helps to believe in yourself and feel confident, which helps the athletes to perform better in the sports.
- Mental Imager: This helps the athletes to practise movements in their mind which helps the athletes to reduce nervousness and improve skills.
- Self-talk: The positive thoughts, like “I can do this”, help them stay confident, while negative thoughts can create doubt.
- Goal setting: Goal setting is a powerful technique that helps the athletes stay committed to improving their skills within a specific time frame.
Psychology and Sports Class 12 Notes
Physical Education Class 12 Notes
- Management of Sporting Events Class 12 Notes
- Physical Education Class 12 Chapter 2 Notes
- Physical Education Class 12 Chapter 3 Notes
- Physical Education Class 12 Chapter 4 Notes
- Sports and Nutrition Class 12 Notes
- Test and Measurement in Sports Class 12 Notes
- Physiology and Injuries in Sports Class 12 Notes
- Biomechanics and Sports Class 12 Notes
- Psychology and Sports Class 12 Notes
- Training in Sports Class 12 Notes
Physical Education Class 12 Questions and Answers
- Physical Education Class 12 Chapter 1 MCQ Solutions
- Physical Education Class 12 Chapter 2 Question Answers
- Physical Education Class 12 Chapter 3 Question Answers
- Physical Education and Sports for CWSN Class 12 Questions and Answers
- Sports and Nutrition Class 12 Questions and Answers
- Physical Education Class 12 Chapter 6 Question Answers
- Physiology and Injuries in Sports Class 12 Questions and Answers
- Biomechanics and Sports Class 12 Questions and Answers
- Psychology and Sports Class 12 Questions and Answers
- Training in Sports Class 12 Questions and Answers
