Teachers and Examiners (CBSESkillEduction) collaborated to create the Training in Sports Class 12 Notes. All the important Information are taken from the NCERT Textbook Physical Education (048) class 12.
Concept of Talent Identification
Talent is an ability of the person; talent identification helps to find the potential of any person in sport based on their fitness, skills and maturity. Once talent is identified, then the next step is talent development, which helps the person to improve the skills and train for competitions. This process helps to go from beginners to professional level.
Process of Talent Identification and Development is classified into five stages as follows:
- Talent Detection: This is the discovery of potential performers who are not currently involved in the sport in question.
- Talent Identification: Recognizing participants with the potential at an earlier age to become elite performers in the future.
- Talent Development: Provides athletes with a suitable learning environment to accelerate or realize their potential
- Talent Selection: The ongoing process of identifying individuals at various stages of development who demonstrate pre-requisite performance levels.
- Talent Transfer: Focuses on transfer from one sport to another sport where there are more significant opportunities to succeed
Importance of Talent identification
- Discovery of the great talent
- Recognition of the hidden talent
- By recognizing the talent at the early stage, the children can show their skills at their extreme
- Talent identification helps in finding a significant asset for the country
Components of Talent Identification
The main components of Talent Identification (TID) can be divided into the following categories:
- Physiological attributes
- Physical attributes
- Psychological attributes
- Technical/Tactical attributes
- Results
- Intangibles
Introduction to Sports Training Cycle – Micro, Meso, Macro Cycle
Sports training follows structured cycles to help athletes to improve systematically. These cycles ensure proper skill development, fitness progression and recovery.
Types of Training Cycle
Training cycles are divided into three types:
- Micro Cycle (3 – 10 days): Micro Cycle is the shortest cycle which follows daily workouts and recovery.
- Meso Cycle (3 – 6 weeks): Meso Cycle is a medium-term training aimed at building skills, strength and endurance in sportsmen.
- Macro Cycle (3 – 12 months): Long-term training designed for major competitions and overall progress.
Strength
Strength is the ability of muscles to generate force, strength helps to perform tasks like weight lifting, pushing and pulling. Strength plays an important role in sports, helping athletes to perform better in sports. In simple words, strength is the ability of a group of muscles to overcome resistance.
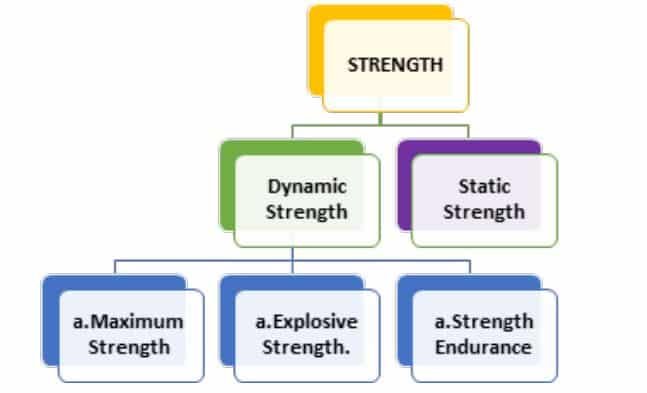
Strength is classified into two forms: static and dynamic stability
Static Strength
Static Strength also known as isometric strength, It is the ability of the muscles to act against resistance. Static strength can be measured with a dynamometer. This type of strength is not seen directly. Some static strength is not usually applied in sports, but it is used in phases in weightlifting. Example: plank or yoga asanas.
Dynamic Strength
Dynamic strength is also known as isotonic strength. In pull-ups and push-ups, we required dynamic strength. In performing such a workout. In dynamic strength, muscles refuse to do work after some time. Example: push-ups and full squats.
Dynamic strength can be divided into three parts.
- Maximum Strength: Ability to apply maximum force in one area. For example, weightlifting, shot put, javelin throw, etc.
- Explosive Strength: It is a mix of strength and speed in the sports. For example, basketball jumps, volleyball spikes, etc.
- Strength Endurance: The ability to maintain strength during the tightness in the sports. For example, swimming, distance running and cycling, etc.
Methods to Develop Strength
Athletes use different types of exercise to build strength during workouts.
- Isometric Exercises: Holding a position without movement. Example: wall pushing and planks.
- Isotonic Exercises: Strength training with movement. For example, weightlifting, running and push-ups, etc.
- Isokinetic Exercise: Special training using machines for controlling movement. Example swimming with equipment.
Endurance
Endurance is the ability of a person to maintain a certain level of energy for a long period during sports or daily activity.
Barrow and McGee defined endurance as “the result of a physiologic capacity of an individual to sustain movement over a period of time”.
Types of Endurance
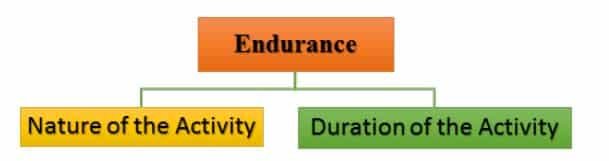
Different games require different types of endurance. The endurance is classified into three categories:
Classification according to the nature of the activity:
This classification is based on the kind of activity required for endurance. It can be classified into the following types:
- Basic Endurance: The ability to perform the activity or sports for a long time. For example: jogging, swimming for more than 30 minutes, etc.
- General Endurance: The ability to perform various movements for an extended period without getting tired. It happens with higher-intensity exercise but for a shorter duration than basic endurance.
- Specific Endurance: Ability to sustain effort in a particular sport. For example, a hacky player needs short bursts of energy, but a marathon runner requires long-lasting endurance.
Classification according to the Duration of the Activity:
This classification considers only cyclic sports activities and is based on physiological factors. classification can be divided into the following sub-categories:
- Speed Endurance: This type of endurance is dependent on the power and capacity of energy for a short period. For example, 400 metres run within 45 seconds.
- Short-Term Endurance: This ability is needed for activities lasting 45 seconds to about 2 minutes. The most appropriate example for short-term endurance is an 800m run.
- Medium-Term Endurance: This type of endurance is used for longer activities from 2 to 11 minutes. For example, the 1500-metre run.
- Long-Term Endurance: This endurance helps the activity for more than 11 minutes. For example, marathons or cross-country races.
Methods to Develop Endurance
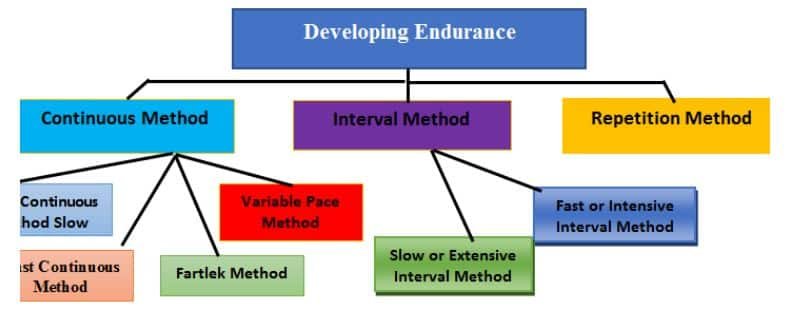
The various methods to develop endurance are discussed below:
Continuous Method
This method is about continuity. In this method, an exercise is done for a longer time without any rest. This method has the following subcategories:
- Slow Continuous Method: In this method, the activity is performed at a certain speed without any break for a long duration depending on the heart rate. The heart rate should be between 140 – 160 beats per minute, and the training should be less than 30 minutes. This method is used for walking, running, cycling, etc.
- Fast Continuous Method: The activity is performed comparatively fast, but the speed remains uniform throughout the training. Heart rate during the training should be between 160-180 beats per minute and the training should be atleast 20 minutes.
- Variable Pace Method: In this method, activity is performed at a changing pace, but this change in speed is pre-planned. The heart rate usually ranges between 140-180 beats per minute during this method. The duration of this method may range from 15 minutes to 1 hour.
- Fartlek Method: Fartlek is a Swedish word that means ‘speed play.’ In other words, it is another variation of the variable pace method. The difference between the two is in the Fartlek method the speed variation is not planned.
Interval Method
The interval training method is a powerful method to improve endurance. It involves exercising at high intensity for a short time, including a brief recovery period.
How it works:
- The athlete pushes hard until their heart rate reaches 180 bpm.
- Take rest until their heart rate drops to 120-130 bpm.
- They start again and push hard until their heart rate reaches 180 bpm.
Repetition Method
The repetition method is characterized by a high intensity that ranges from 90-to 100% of work with an interval of complete recovery. It is the best method to develop speed endurance.
The Essential effects of this method are:
- Improved anaerobic capacity
- Improved lactic acid tolerance
- Improved phosphagen stores
Training in Sports Class 12 Notes
Physical Education Class 12 Notes
- Management of Sporting Events Class 12 Notes
- Physical Education Class 12 Chapter 2 Notes
- Physical Education Class 12 Chapter 3 Notes
- Physical Education Class 12 Chapter 4 Notes
- Sports and Nutrition Class 12 Notes
- Test and Measurement in Sports Class 12 Notes
- Physiology and Injuries in Sports Class 12 Notes
- Biomechanics and Sports Class 12 Notes
- Psychology and Sports Class 12 Notes
- Training in Sports Class 12 Notes
Physical Education Class 12 Questions and Answers
- Physical Education Class 12 Chapter 1 MCQ Solutions
- Physical Education Class 12 Chapter 2 Question Answers
- Physical Education Class 12 Chapter 3 Question Answers
- Physical Education and Sports for CWSN Class 12 Questions and Answers
- Sports and Nutrition Class 12 Questions and Answers
- Physical Education Class 12 Chapter 6 Question Answers
- Physiology and Injuries in Sports Class 12 Questions and Answers
- Biomechanics and Sports Class 12 Questions and Answers
- Psychology and Sports Class 12 Questions and Answers
- Training in Sports Class 12 Questions and Answers

Crazy notes loved it … Scored 92 in physical education because of you guys ❤️❤️
BROOOOOO WHERE IS THE REST OF TOPICS
LIKE SPEED AND FLEXIBILITY
😣😣😥
The remaining available below the notes.
Ohhkkkk
thankyou soooo much 😊🤗🤗