Welcome to our CBSE Class 12 Physical Education notes for the chapter “Sports and Nutrition”. This chapter focuses on the importance of a balanced diet, essential nutrients, and proper eating habits for athletes and sportspersons.
Sports and Nutrition Class 12 Notes
Balanced Diet
A balanced diet is important. A balanced diet consists of different food groups, each providing essential nutrients:
- Cereals and millets (wheat, rice, jowar, bajra, ragi, etc.): Majorly provide carbohydrates, vitamins B, iron (bajra), protein (cereals) and calcium (ragi).
- Pulses (lobia, chana, moong, lentils): Pulses provide protein, carbohydrates, vitamins B, iron, fibre and vitamin C.
- Milk and Milk Products (milk, curd, paneer, cheese and khoa): Milk and milk products provide good quality protein and also provide other nutrients like carbohydrates, fat, calcium and riboflavin.
- Meat and Meat Products (meat, fish, chicken, eggs): Good sources of protein and other nutrients are vitamins B, retinol (liver), and calcium (fish).
- Nuts and Oil Seeds (groundnuts, almonds, cashew nuts, pistachios, til seeds): Provide a good source of fat; they also provide protein, vitamin B, calcium and other minerals.
- Green Leafy Vegetables (spinach (palak), fenugreek leaves (methi), mustard leaves (sarson), bathua): Green leafy vegetables are a good source of carotene (vitamin A), B vitamins (especially riboflavin and folic acid), iron (especially sarson and bathua) and fibre. They are also a source of calcium.
- Root Vegetables (potato, yam, sweet potato, colocasia): The major nutrient supplied by root vegetables is carbohydrates. Carotene is provided only by yellow yam.
- Other Vegetables (brinjal, okra (ladyfinger), beans, cauliflower, etc.): Good source of fibre, vitamins, and minerals.
- Fruits (mango, papaya, oranges, guava, apricots): Rich source of carotene, citrus fruits like oranges, mausambi, amla and guavas are good sources of vitamin C, and dried fruits like dates and raisins are rich in iron. Fibre is provided by most fruits.
- Sugar and jaggery: These are simply carbohydrates. Jaggery also has iron.
- Fats and Oils (ghee, butter, oils): Rich source of fat. Vitamin D also is provided by butter/fortified oils.
Nutrition
Nutrition is the process of taking food and how the body processes it into energy and other vital nutrients required, which is very important for life. Nutrients are essential substances found in food which the body needs to function properly.
When we eat, our body breaks down food into nutrients, which include:
- Carbohydrates: Carbohydrates give energy to the body for daily activities.
- Proteins: Support growth, muscle repair, and overall body maintenance.
- Fats: Serve as an energy source and help in cell function and hormone production.
- Vitamins & Minerals: Essential for bodily functions like immunity, bone health, and organ function.
- Water & Fibre: Aid digestion, detoxification, and proper nutrient absorption.
Macro and Micro Nutrients: Food sources and functions
Nutrients are divided into macronutrients and micronutrients based on how much the body needs.
Macronutrients: Macronutrients are essential for the body and needed in large amounts. These macronutrients include carbohydrates, proteins, fats, and water. They provide energy and support growth in the body.
- Carbohydrates: 55-60%
- Protein: 10-15%
- Fats: 20-30%
- Water, though it doesn’t provide energy, is essential for body functions.
Micronutrients: Micronutrients require small amounts of nutrients in our body. Micronutrients include vitamins and minerals, which are essential for overall health.
Nutritive and Non-Nutritive Components of Diet
Food gives energy and helps our body to grow. Food contains nutrients that are important for our bodies. Food has nutritive components like carbohydrates, proteins and fats, which give energy and help our body to grow. But some foods do not provide nutrition, but they affect taste, smell and shelf life. These are called non-nutritive components.
Non-nutritive Factors that Interfere with Nutrient Absorption
- Phytates: It is found in cereals and millets. These phytates bind iron, zinc, calcium and magnesium and make these nutrients unavailable for digestion.
- Tannins: These are present in millets like bajra and ragi, spices, tamarind, tea, turmeric and certain vegetables and fruits. Tannins interfere with absorption of iron and protein.
- Trypsin Inhibitors: It is present in soybeans and duck eggs and makes protein harder to digest.
- Oxalates: They are found in green vegetables and block calcium absorption.
- Goitrogens: They are found in cabbage, cauliflower, turnips, soybeans, bajra, peanuts and lentils and are also known as anti-thyroid substances that affect iodine levels.
Beneficial Non-Nutritive Factors of Foods
- Phytochemicals: They are found in colourful fruits and vegetables and are helpful for protecting against diseases like cancer.
- Anthocyanins: It is found in berries and may be helpful to reduce inflammation.
- Flavonoids: They are found in soybeans and chickpeas and support heart and bone health.
- Artificial sweeteners: This non-nutritive can be helpful to reduce sugar intake.
- Preservatives: This is helpful to keep food fresh longer.
- Spices: These add flavour to the food and have health benefits.
- Coffee: Coffee contains caffeine, which is helpful for keeping us alert.
Healthy Weight
Everyone has to maintain a healthy weight, and it is very important for overall health. If you are losing 5-10% of body weight, it can increase the risk of diseases like diabetes, heart disease, stroke and obesity-related cancers. The healthy weight helps you live a longer and healthier life.
How to Measure Healthy Weight
There are several ways to check if your weight is healthy or not.
- Body Mass Index (BMI): BMI simple tool to calculate using height and weight to estimate body fat.
- Waist Circumference: The distance around the waist/stomach is measured by this method.
- Body Fat Percentage: It is a special tool to measure how much fat the body has.
BMI Categories
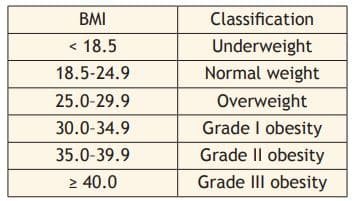
A high waist circumference of more than 102 cm in men and 88 cm in women increases health risks, even if BMI is under 35. Body fat percentage also matters and can be measured by special equipment.
Eating for Weight Control
Balancing a weight depends on what you eat and how much energy you use. Burn more calories than what you eat; it will be helpful for losing weight. As per the study, weight loss of 1 to 2 kg per week is safest and healthiest for your body.
Healthy Eating for Weight Control
- Eat a balanced diet.
- Take high-fibre foods.
- Avoid high-cholesterol food.
- Choose low-fat food.
- Use the bake or grill food.
- Take limited sugar.
- Dont take junk food
- Avoid sugary drinks like soda and processed juices.
- Eat small meals more often.
The Pitfalls of Dieting
When you eat less food than your body will create a calorie deficit and help you to lose weight, but only dieting is not a solution because everyone will not be able to do dieting. Suppose you have done dieting, and you stop dieting after some time; the lost weight comes back quickly. The best way to reduce weight is to take balanced food and physical exercise, which will be helpful for losing your weight without any deficiencies.
Food Intolerance
Food intolerance means when the body struggles to digest certain foods. Symptoms usually appear like stomach pain, bloating, headaches and diarrhoea.
Common Causes of Food Intolerance
- Absence of an enzyme: Enzymes are needed to digest foods. If some of these enzymes are missing, then proper digestion may be affected. For example, lactose intolerance is caused by a deficiency of the lactase enzyme in the body. Some people are unable to digest lactose-related products like milk, butter, ghee, etc.
- Chemical causes of food intolerance: Certain chemicals in foods and drinks can cause intolerance, including amines in some cheeses and caffeine in coffee, tea, and chocolates.
- Toxins due to food poisoning: Some foods have naturally occurring chemicals that can have a toxic effect on humans, causing diarrhoea, nausea, and vomiting. Peanuts or undercooked beans can create a digestive problem.
- Salicylates: Salicylates are derivatives of salicylic acid, which occurs naturally in plants as a defence mechanism against harmful bacteria, fungi, insects, and diseases.
- Gluten intolerance: Gluten is a protein found primarily in wheat, barley and rye. If a person has a gluten intolerance, this protein can cause digestive problems such as gas, abdominal pain or diarrhoea.
- Food additives and intolerance: Additives are used to enhance flavours, make foods look more appealing, and increase their shelf life. Food additive intolerance has been a steadily growing problem over the last many years because more and more foods contain additives.
Food Myths
- Fewer carbohydrates mean better health
- Oils/Margarine have fewer calories than Ghee/Butter
- Apples and brinjals are rich in iron because they turn brown
- Milk should be avoided after eating fish
- Drinking water during meals harms digestion
Importance Of Diet In Sports And Pre, During And Post Requirement
Importance of Diet in Sports
Nutrition plays an important role in the performance and body recovery of athletes. Athletes must take balanced and nutritious foods that boost their energy, endurance and long-term health. A proper diet can maintain fitness during training and competition.
Why Diet Matters for Sportspeople
- The body needs proper nutrition to repair muscles during the time of training.
- Different sports require different body types; diet helps to maintain the ideal muscle-fat balance.
- Eating the right foods will help to recover faster from injury.
- Enhances performance with special nutrients.
- A balanced diet enhances body strength.
Post Training/Competition
After training or competition, athletes need proper recovery to perform the next day and prevent injuries. The main emphasis during the recovery phase must be on the following:
- To replace fluids lost during exercise.
- To refill carbohydrate stores (muscle and liver glycogen)
- To replace electrolytes (sodium, potassium, chloride)
Physical Education Class 12 Notes
- Management of Sporting Events Class 12 Notes
- Physical Education Class 12 Chapter 2 Notes
- Physical Education Class 12 Chapter 3 Notes
- Physical Education Class 12 Chapter 4 Notes
- Sports and Nutrition Class 12 Notes
- Test and Measurement in Sports Class 12 Notes
- Physiology and Injuries in Sports Class 12 Notes
- Biomechanics and Sports Class 12 Notes
- Psychology and Sports Class 12 Notes
- Training in Sports Class 12 Notes
Physical Education Class 12 Questions and Answers
- Physical Education Class 12 Chapter 1 MCQ Solutions
- Physical Education Class 12 Chapter 2 Question Answers
- Physical Education Class 12 Chapter 3 Question Answers
- Physical Education and Sports for CWSN Class 12 Questions and Answers
- Sports and Nutrition Class 12 Questions and Answers
- Physical Education Class 12 Chapter 6 Question Answers
- Physiology and Injuries in Sports Class 12 Questions and Answers
- Biomechanics and Sports Class 12 Questions and Answers
- Psychology and Sports Class 12 Questions and Answers
- Training in Sports Class 12 Questions and Answers
Disclaimer: We have taken an effort to provide you with the accurate handout of “Sports and Nutrition Class 12 Notes Chapter 5“. If you feel that there is any error or mistake, please contact me at anuraganand2017@gmail.com. The above CBSE study material present on our websites is for education purpose, not our copyrights.
All the above content and Screenshot are taken from Physical Eduction Class 12 NCERT Textbook, CBSE Sample Paper, CBSE Old Sample Paper, CBSE Board Paper and CBSE Support Material which is present in CBSEACADEMIC website, NCERT websiteThis Textbook and Support Material are legally copyright by Central Board of Secondary Education. We are only providing a medium and helping the students to improve the performances in the examination.
Images and content shown above are the property of individual organizations and are used here for reference purposes only.
For more information, refer to the official CBSE textbooks available at cbseacademic.nic.in

iam very happy to text you
this chapters content is very nice and wonderful subject for all students who is reading and fallow the chaoters.